
The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta, are a clade of algae.
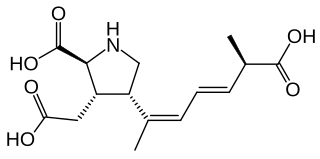
Domoic acid (DA) is a kainic acid-type neurotoxin that causes amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). It is produced by algae and accumulates in shellfish, sardines, and anchovies. When sea lions, otters, cetaceans, humans, and other predators eat contaminated animals, poisoning may result. Exposure to this compound affects the brain, causing seizures, and possibly death.
Amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) is an illness caused by consumption of shellfish that contain the marine biotoxin called domoic acid. In mammals, including humans, domoic acid acts as a neurotoxin, causing permanent short-term memory loss, brain damage, and death in severe cases.

The Scotch bonnet is a medium-sized to large species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the subfamily Cassinae, the helmet shells and bonnet shells. The common name "Scotch bonnet" alludes to the general outline and color pattern of the shell, which vaguely resemble a tam o' shanter, a traditional Scottish bonnet or cap. The shell is egg-shaped and fairly large, 2 to 4 inches in maximum dimension, with a regular pattern of yellow, orange or brown squarish spots. The surface sculpture of the shell is highly variable: the surface can be smooth and polished, have grooves, be granulated, or even be nodulose on the shoulder of the whorls.

AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, both marine and freshwater, as well as sea-grass.

Saxifraga granulata, commonly called meadow saxifrage, is a species of flowering plant in the family Saxifragaceae. It is native to Europe and Morocco.

Nitzschia is a common pennate marine diatom. In the scientific literature, this genus, named after Christian Ludwig Nitzsch, is sometimes referred to incorrectly as Nitzchia, and it has many species described, which all have a similar morphology. In its current circumscription, Nitzschia is paraphyletic.
Grethe Berit Rytter Hasle was a Norwegian planktologist. Among the first female professors of natural science at the University of Oslo, she specialized in the study of phytoplankton.

Bacillariaceae is a family of diatoms in the phylum Heterokontophyta, the only family in the order Bacillariales. Some species of genera such as Nitzchia are found in halophilic environments; for example, in the seasonally flooded Makgadikgadi Pans in Botswana.

Acanthopleura granulata, common name the West Indian fuzzy chiton, is a medium-sized tropical species of chiton. This type of chiton's activity does not depend on spring-neap oscillations leading to lower locomotion loss. Its morphology is different from usual chitons as it has a fifth valve, which is split into halves.
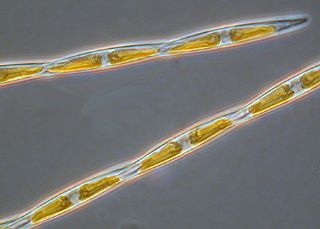
Pseudo-nitzschia is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of Pseudo-nitzschia occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health.

Neohelice granulata is a species of crab in the family Varunidae, and the only species in the genus Neohelice. In 2009, it was estimated that N. granulata was the sixth most studied species of crab.

The Capsalidae is a family of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, which includes about 200 species.

Climate change in Maine encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of Maine.











