
The music of the Cameroon includes diverse traditional and modern musical genres. The best-known contemporary genre is makossa, a popular style that has gained fans across Africa, and its related dance craze bikutsi.
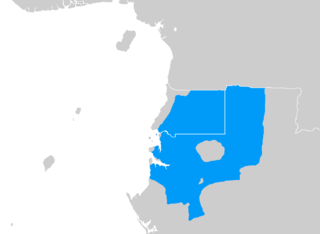
Fang is a Central African language spoken by around 1 million people, most of them in Equatorial Guinea, and northern Gabon, where it is the dominant Bantu language; Fang is also spoken in southern Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, and small fractions of the islands of São Tomé and Príncipe. It is related to the Bulu and Ewondo languages of southern Cameroon.
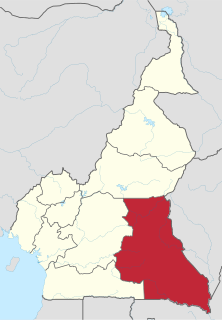
The East Region occupies the southeastern portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the east by the Central African Republic, to the south by Congo, to the north by the Adamawa Region, and to the west by the Centre and South Regions. With 109,002 km² of territory, it is the largest region in the nation as well as the most sparsely populated. Historically, the peoples of the East have been settled in Cameroonian territory for longer than any other of the country's many ethnic groups, the first inhabitants being the Baka pygmies.

The South Region is located in the southwestern and south-central portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the east by the East Region, to the north by the Centre Region, to the northwest by the Littoral Region, to the west by the Gulf of Guinea, and to the south by the countries of Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and Congo. The South occupies 47,720 km2 of territory, making it the fourth largest region in the nation. The major ethnic groups are the various Beti-Pahuin peoples, such as the Ewondo, Fang, and Bulu.

The Centre Region occupies 69,000 km² of the central plains of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the north by the Adamawa Region, to the south by the South Region, to the east by the East Region, and to the West by the Littoral and West Regions. It is the second largest of Cameroon's regions in land area. Major ethnic groups include the Bassa, Ewondo, and Vute.

Bikutsi is a musical genre from Cameroon. It developed from the traditional styles of the Beti, or Ewondo, people, who live around the city of Yaoundé. It was popular in the middle of the 20th century in West Africa. It is primarily dance music.
The Ekang are a group of closely related Bantu ethnic groups located in rain forest regions of Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and São Tomé and Príncipe. Though they separate themselves into several individual clans, they all share a common origin, history and culture.

Moszna is a small village in south-west Poland, approximately 30 km (19 mi) from Opole, known for its notable fairy-tale castle.

The Fang people, also known as Fãn or Pahouin, are a Bantu ethnic group found in Equatorial Guinea, northern Gabon, and southern Cameroon. Representing about 85% of the total population of Equatorial Guinea, concentrated in the Río Muni region, the Fang people are its largest ethnic group. The Fang are also the largest ethnic group in Gabon, making up about a quarter of the population. In other countries, in the regions they live, they are one of the most significant and influential ethnic groups.
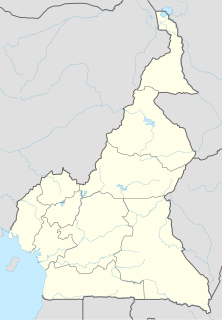
Sangmélima is a town on the Lobo River, and also the chief town of Lobo division, in the South Province, Republic of Cameroon, Africa. The language spoken there is Bulu. French, is also spoken as it is one of the official languages in Cameroon.

Charles Atangana, also known by his birth name, Ntsama, and his German name, Karl, was the paramount chief of the Ewondo and Bane ethnic groups during much of the colonial period in Cameroon. Although from an unremarkable background, Atangana's loyalty and friendship with colonial priests and administrators secured him successively more prominent posts in the colonial government. He proved himself an intelligent and diplomatic administrator and an eager collaborator, and he was eventually named paramount chief of two Beti-Pahuin subgroups, the Ewondo and Bane peoples. His loyalty and acquiescence to the German Empire was unquestioning, and he even accompanied the Germans on their escape from Africa in World War I.

Arbeitsdorf ("work-village") was a concentration camp established by the Nazis in Stadt des KdF-Wagens bei Fallersleben 1942.

The Nilgiri Mountains form part of the Western Ghats in western Tamil Nadu, India. At least 24 of the Nilgiri Mountains' peaks are above 2,000 metres (6,600 ft), the highest peak being Doddabetta, at 2,637 metres (8,652 ft).

Nowa Dęba is a town in Tarnobrzeg County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Poland, with a population of 11,310, as of 2 June 2009. Nowa Dęba belongs to historic Lesser Poland, and is located in the Sandomierz Forest, along European route E371. Near the town is the Tarnobrzeg Special Economic Zone (TSSE), as well as a large military training area of the Polish Army. Nowa Dęba has a sports club Stal, established in 1953.
Beti is a group of Bantu languages, spoken by the Beti-Pahuin peoples who inhabit the rain forest regions of Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and São Tomé and Príncipe. The varieties, which are largely mutually intelligible and variously considered dialects or closely related languages, are:

Dja-et-Lobo is a department of South Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 19,911 km2 and as of 2005 had a total population of 196,951. The capital of the department lies at Sangmélima.
Birni Lalle is a village and rural commune in Niger.
The Nyongo Society is the name of a supposed group of witches believed to exist in Cameroon and Nigeria. The legends were first written about in the 1950s by British social anthropologist, Edwin Ardener, while describing what he called the Nyongo Terror in the present-day Southwest Province in Cameroon. Today the belief in this society can be found from the coast of Cameroon to the Bakossi and Beti peoples in the interior of the country. It is even found amongst the northern parts of the country with the Bamileke and Bamenda peoples.

The Beti people are a Central African ethnic group primarily found in central Cameroon. They are also found in Equatorial Guinea and northern Gabon. They are closely related to the Bulu people, the Fang people and the Yaunde people, who are all sometimes grouped as Ekang.
Doğangir is a village in the İskilip District of Çorum Province in Turkey.





















