
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology.
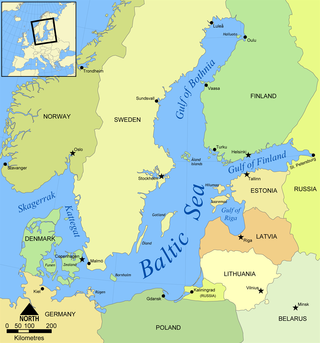
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries, and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. The term "Baltic states" refers specifically to one such grouping.
Estonian Education and Research Network (EENet) is a structural unit of the Information Technology Foundation for Education (HITSA) whose main goal is to ensure the development and stable functioning of the information technology infrastructure necessary for research, education and culture.

Western Norway is the region along the Atlantic coast of southern Norway. It consists of the counties Rogaland, Vestland, and Møre og Romsdal. The region has no official or political-administrative function. The region has a population of approximately 1.4 million people. The largest city is Bergen and the second-largest is Stavanger. Historically the regions of Agder, Vest-Telemark, Hallingdal, Valdres, and northern parts of Gudbrandsdal have been included in Western Norway.
Comparative education is a discipline in the social sciences which entails the scrutiny and evaluation of different educational systems, such as those in various countries. Professionals in this area of endeavor are absorbed in advancing evocative terminologies and guidelines for education worldwide, enhancing educational structures and producing a context to which the success and effectivity of education programs and initiatives can be assessed.
The Grieg Academy is a disputed historical term used to refer to the higher education music programs in Bergen, Norway, as well as various collaborations across music institutions in Bergen. However, since 2016, due to mergers between several Norwegian institutions, the structure of Grieg Academy has changed and its remaining components are expected to be a doctoral research school and various research groups. Specifically, this is due to a merger between the University of Bergen’s Faculty of Humanities with the Bergen Academy of Art and Design, as well as a nearly simultaneous merger between Bergen University College and two other university colleges in western Norway: Stord/Haugesund University College and Sogn og Fjordane University College to become, in January 2017, Western Norway University of Applied Sciences (HVL) The music programs across HVL briefly became the largest music department in western Norway in terms of the number of full time teachers, but this has rapidly changed due to an unofficial policy of not replacing retiring teachers.
Tallinn University is a public research university in Estonia. Located in the centre of Tallinn, the capital city of Estonia, Tallinn University is one of the three largest institutions of higher education in the country. Both QS World University and Times Higher Education rankings place it among the top 1000 universities in the world.

Scandinavian studies is an interdisciplinary academic field of area studies, mainly in the United States and Germany, that primarily focuses on the Scandinavian languages and cultural studies pertaining to Scandinavia and Scandinavian language and culture in the other Nordic countries. While Scandinavia is defined as Denmark, Norway and Sweden, the term Scandinavian in an ethnic, cultural and linguistic sense is often used synonymously with North Germanic and also refers to the peoples and languages of the Faroe Islands and Iceland; furthermore a minority in Finland are ethnically Scandinavian and speak Swedish natively.
The Royal Ministry of Education and Research is a Norwegian government ministry responsible for education, research, kindergartens and integration. The ministry was established in 1814 as the Royal Ministry of Church and Education Affairs.

The culture of Estonia combines an indigenous heritage, represented by the country's Finnic national language Estonian, with Nordic and German cultural aspects. The culture of Estonia is considered to be significantly influenced by that of the Germanic-speaking world. Due to its history and geography, Estonia's culture has also been influenced by the traditions of other Finnic peoples in the adjacent areas, also the Baltic Germans, Balts, and Slavs, as well as by cultural developments in the former dominant powers, Sweden, Denmark and Russia. Traditionally, Estonia has been seen as an area of rivalry between western and eastern Europe on many levels. An example of this geopolitical legacy is an exceptional combination of multiple nationally recognized Christian traditions: Western Christianity and Eastern Christianity. The symbolism of the border or meeting of east and west in Estonia was well illustrated on the reverse side of the 5 krooni note. Like the mainstream cultures in the other Nordic countries, Estonian culture can be seen to build upon ascetic environmental realities and traditional livelihoods, a heritage of comparatively widespread egalitarianism arising out of practical reasons, and the ideals of closeness to nature and self-sufficiency.
Baltic 21 is a plan to cooperate on implementing regional sustainable development. It is managed by the Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS).
The Baltic Development Forum is an independent think-tank and non-profit high-level and agenda-setting networking organisation with strategic partners and sponsors from large companies, major cities, institutional investors, business associations and academia in the Baltic Sea Region. The network involves more than 8,000 decision-makers from all over the region and beyond.

Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Lake Peipus and Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,200 other islands and islets on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, covering a total area of 45,339 square kilometres (17,505 sq mi). The capital city Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest urban areas of the country. The Estonian language is the indigenous and the official language of Estonia; it is the first language of the majority of its population, as well as the world's second most spoken Finnic language.

University of Tartu Viljandi Culture Academy is an Estonian institution of higher education, situated in the provincial town of Viljandi, central Estonia. The UT Viljandi Culture Academy merged with the University of Tartu in 2005. The UT VCA has been teaching professional higher education and performing applied research within information science, culture education and creative arts since 1952. The academy has about 1000 students, half of whom are open university students. The teaching and instruction are based on the continuity and sustainability of Estonian native culture enriched by new impulses which widen the notion of traditional culture. As of 2021, the Director of the institution is Juko-Mart Kõlar.

Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8) is a regional co-operation format that includes Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, and Sweden. Under NB8, regular meetings are held of the Baltic and Nordic countries' Prime Ministers, Speakers of Parliaments, Foreign Ministers, branch ministers, Secretaries of State and political directors of Foreign Ministries, as well as expert consultations where regional issues and current international topics are reviewed.

Northern Future Forum is an annual, informal meeting of prime ministers, policy innovators, entrepreneurs and business leaders from the 9 nations of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Initially referred to as the UK Nordic Baltic Summit, the name Northern Future Forum was introduced at the second meeting in Stockholm, 2012. The group had a period of abeyance since the Stavanger meeting in 2016 was postponed following the outcome of the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, and David Cameron subsequently stepping down as UK prime minister, to be succeeded by Theresa May. The summit was reconvened in October 2018 in Oslo.

The National Library of Kosovo is the highest library institution in Kosovo established by the Assembly and is located in Pristina.
David G. Hebert is a musicologist and comparative educationist, employed as Professor of Music at Western Norway University of Applied Sciences, where he leads the Grieg Academy Music Education (GAME) research group. He has contributed to the fields of music education, ethnomusicology, sociomusicology, comparative education, and East Asian Studies. Since 2018, he has been manager of the Nordic Network for Music Education, a multinational state-funded organization that sponsors intensive Master courses and exchange of university music lecturers and students across Northern Europe. He is also a visiting professor in Sweden with the Malmo Academy of Music at Lund University, and an honorary professor with the Education University of Hong Kong. He has previously been sponsored by East Asian governments as a visiting research scholar with Nichibunken in Kyoto, Japan, and the Central Conservatory of Music, in Beijing, China.

The Baltic Sea Parliamentary Conference (BSPC) was established in 1991 as a forum for political dialogue between parliamentarians from the Baltic Sea Region. BSPC aims at raising awareness and opinion on issues of current political interest and relevance for the Baltic Sea Region. It promotes and drives various initiatives and efforts to support a sustainable environmental, social and economic development of the Baltic Sea Region. It strives at enhancing the visibility of the Baltic Sea Region and its issues in a wider European context.
Helga Rut Guðmundsdóttir is a professor of music education at the University of Iceland School of Education.











