
Castine is a town in Hancock County in eastern Maine, United States. The population was 1,320 at the 2020 census. Castine is the home of Maine Maritime Academy, a four-year institution that graduates officers and engineers for the United States Merchant Marine and marine related industries. Approximately 1000 students are enrolled. During the French colonial period, Castine was the southern tip of Acadia and served as the regional capital between 1670 and 1674.

Penobscot Indian Island Reservation is an Indian reservation for the Penobscot Tribe of Maine, a federally recognized tribe of the Penobscot in Penobscot County, Maine, United States, near Old Town. The population was 758 at the 2020 census. The reservation extends for many miles alongside 15 towns and two unorganized territories in a thin string along the Penobscot River, from its base at Indian Island, near Old Town and Milford, northward to the vicinity of East Millinocket, almost entirely in Penobscot County. A small, uninhabited part of the reservation used as a game preserve and hunting and gathering ground is in South Aroostook, Aroostook County, by which it passes along its way northward.

King William's War was the North American theater of the Nine Years' War (1688–1697), also known as the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg. It was the first of six colonial wars fought between New France and New England along with their respective Native allies before France ceded its remaining mainland territories in North America east of the Mississippi River in 1763.

King Philip's War was an armed conflict in 1675–1676 between a group of indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands and the English New England Colonies and their indigenous allies. The war is named for Metacomet, the Pokanoket chief and sachem of the Wampanoag who adopted the English name Philip because of the friendly relations between his father Massasoit and the Plymouth Colony. The war continued in the most northern reaches of New England until the signing of the Treaty of Casco Bay on April 12, 1678.

Jean-Vincent d'Abbadie, Baron de Saint-Castin (1652–1707) was a French military officer serving in Acadia and an Abenaki chief. He is the father of two prominent sons who were also military leaders in Acadia: Bernard-Anselme and Joseph. He is the namesake of Castine, Maine. He died at Pau, France, in 1707.
Bernard-Anselme d'Abbadie de Saint-Castin (1689–1720) was a French military officer serving in Acadia. He was a member of a successful privateering force at the time of Queen Anne's War, and led native and French forces in the defense of Acadia.
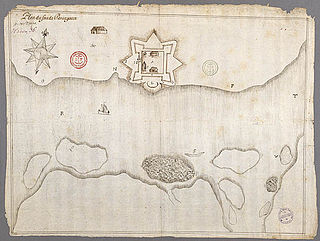
Fort Pentagouët was a French fort established in present-day Castine, Maine, which was the capital of Acadia (1670–1674). It is the oldest permanent settlement in New England.
Madockawando was a sachem of the Penobscot, an adopted son of Assaminasqua, whom he succeeded. He led the Penobscot on the side of the French against the English during King William's War.

Fort William Henry is located in the village of New Harbor in the town of Bristol, Maine. The fort was, in its time, the largest in New England. The fort was originally built in 1692 but destroyed four years later by New France in the Siege of Pemaquid (1696). A reconstruction was built in 1908. The fort was added to the National Register of Historic Places on December 1, 1969. Fort William Henry is now operated as a museum about the fort's history.

The siege of Pemaquid occurred during King William's War when French and Native forces from New France attacked the English settlement at Pemaquid, a community on the border with Acadia. The siege was led by Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville and Baron de St Castin between August 14–15, 1696. Commander of Fort William Henry, Captain Pasco Chubb, surrendered the fort. Iberville killed three of the soldiers and sent the other 92 back to Boston.

The siege of Pemaquid was a successful attack by a large band of Abenaki Indians on the English fort at Pemaquid, Fort Charles, then the easternmost outpost of colonial Massachusetts. The French-Abenaki attack was led by Jean-Vincent d'Abbadie de Saint-Castin and Father Louis-Pierre Thury and Chief Moxus. The fall of Pemaquid was a significant setback to the English. It pushed the frontier back to Casco (Falmouth), Maine.
The Northeast Coast campaign was the first major campaign by the French of Queen Anne's War in New England. Alexandre Leneuf de La Vallière de Beaubassin led 500 troops made up of French colonial forces and the Wabanaki Confederacy of Acadia. They attacked English settlements on the coast of present-day Maine between Wells and Casco Bay, burning more than 15 leagues of New England country and killing or capturing more than 150 people. The English colonists protected some of their settlements, but a number of others were destroyed and abandoned. Historian Samuel Drake reported that, "Maine had nearly received her death-blow" as a result of the campaign.

The Battle of Port La Tour occurred on July 18, 1677, at Port La Tour, Acadia, as part of the Northeast Coast Campaign during the First Abenaki War in which the Mi'kmaq attacked New England fishermen. The New Englanders eventually overwhelmed them and many Mi'kmaq were enslaved.

The Maliseet militia was made up of warriors from the Maliseet of northeastern North America. Along with the Wabanaki Confederacy, the French and Acadian militia, the Maliseet fought the British through six wars over a period of 75 years. They also mobilized against the British in the American Revolution. After confederation, Maliseet warriors eventually joined Canada's war efforts in World War I and World War II.
The Battle of Falmouth was fought at Falmouth, Maine when the Canadiens and Wabanaki Confederacy attacked the English New Casco Fort. The battle was part of the Northeast Coast Campaign (1703) during Queen Anne's War.

The Northeast Coast campaign of 1746 was conducted by the Wabanaki Confederacy of Acadia against the New England settlements along the coast of present-day Maine below the Kennebec River, the former border of Acadia. During King George's War from July until September 1746, they attacked English settlements on the coast of present-day Maine between Berwick and St. Georges. Within two months there were 9 raids - every town on the frontier had been attacked. Casco was the principal settlement.

The Northeast Coast campaign of 1747 was conducted by the Wabanaki Confederacy of Acadia against the New England settlements along the coast of present-day Maine below the Kennebec River, the former border of Acadia. It took place from July until September 1747, and formed part of King George's War. The Wabanaki carried out 11 raids on English settlements on the coast between Berwick and St. Georges, with every town on the frontier being attacked. Casco was the principal settlement.
The Northeast Coast campaign of 1675 was conducted during the First Abenaki War and involved the Wabanaki Confederacy raiding colonial American settlements along the New England Colonies/Acadia border in present-day Maine. Allied with French colonists in New France, they killed eighty colonists and burned many farms, blunting the tide of colonial British expansion in the north. Settlers deserted community after community, leaving only the settlements south of the Saco River to maintain an English presence in the region. Historian Georges Cerbelaud Salagnac writes, that Castine and the Abenaki “displayed consummate skill at it, holding in check at every point, from the Penobscot River to Salmon Falls, N.H., and even beyond, 700 regular troops, and even inflicting humiliating defeats upon them.” These raids were part of continuing warfare as the French and British fought for control in North America into the 18th century, as part of their rivalry in Europe.
The Northeast Coast campaign of 1676 took place during King Philip's War. It involved the Wabanaki Confederacy raiding colonial American settlements along the New England Colonies/Acadia border in present-day Maine. In the first month, they laid waste to 15 leagues of the coast east of Casco. They killed and captured colonists and burned many farms, blunting the tide of colonial American expansion. The campaign led colonists to abandon the region and retreat to Salem, Massachusetts. The campaign is most notable for Richard Waldron entering the war, the death of Chief Mog, and the attack on the Mi’kmaq that initiated their involvement in the war.
The First Abenaki War was fought along the New England/Acadia border primarily in present-day Maine. Richard Waldron and Charles Frost led the forces in the northern region, while Jean-Vincent d'Abbadie de Saint-Castin worked with the tribes that would make up the Wabanaki Confederacy. The natives engaged in annual campaigns against the English settlements in 1675, 1676, and 1677. Waldron sent forces so far north that he attacked the Mi'kmaq in Acadia.










