
Interstate 89 (I-89) is an Interstate Highway in the New England region of the United States traveling from Bow, New Hampshire, to the Canada–United States border between Highgate Springs, Vermont, and Saint-Armand, Quebec. As with all odd-numbered primary Interstates, I-89 is signed as a north–south highway. However, it follows a primarily northwest-to-southeast path. The route forms a major part of the main connection between the cities of Montreal and Boston. In Quebec, the route continues as Route 133. The eventual completion of Autoroute 35 will lead to a nonstop limited-access highway route between Boston and Montreal, following I-93 south from I-89's terminus. The largest cities directly served by I-89 are Concord, the state capital of New Hampshire; Montpelier, the state capital of Vermont; and Burlington, Vermont. I-89 is one of three main Interstate highways whose route is located entirely within New England, along with I-91 and I-93.

Methuen is a 23-square-mile city in Essex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 53,059 at the 2020 census. Methuen lies along the northwestern edge of Essex County, just east of Middlesex County and just south of Rockingham County, New Hampshire. The city is bordered by Haverhill to the northeast, North Andover to the southeast, Lawrence and Andover to the south, Dracut to the west, Pelham, New Hampshire to the northwest, and Salem, New Hampshire to the north. Methuen is located 17 miles (27 km) southwest from Newburyport, 30 miles (48 km) north-northwest of Boston and 25 miles (40 km) south-southeast of Manchester, New Hampshire.

Dracut is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. At the 2020 census, the town's population was 32,617, making it the second most populous town in Massachusetts with an open town meeting system of governance. The town covers a total area of 21.36 square miles, 0.5 square miles of which are water.

Nelson is a town in Cheshire County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 629 at the 2020 census, down from 729 at the 2010 census. Nelson includes the village of Munsonville.

Pelham is a town in Hillsborough County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 14,222 at the 2020 census, up from 12,897 at the 2010 census. Pelham is a part of the Merrimack Valley.

The Merrimack River is a 117-mile-long (188 km) river in the northeastern United States. It rises at the confluence of the Pemigewasset and Winnipesaukee rivers in Franklin, New Hampshire, flows southward into Massachusetts, and then flows northeast until it empties into the Gulf of Maine at Newburyport. From Pawtucket Falls in Lowell, Massachusetts, onward, the Massachusetts–New Hampshire border is roughly calculated as the line three miles north of the river.

The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1628–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, one of the several colonies later reorganized as the Province of Massachusetts Bay. The lands of the settlement were in southern New England, with initial settlements on two natural harbors and surrounding land about 15.4 miles (24.8 km) apart—the areas around Salem and Boston, north of the previously established Plymouth Colony. The territory nominally administered by the Massachusetts Bay Colony covered much of central New England, including portions of Massachusetts, Maine, New Hampshire, and Connecticut.

The Connecticut River is the longest river in the New England region of the United States, flowing roughly southward for 406 miles (653 km) through four states. It rises 300 yards south of the U.S. border with Quebec, Canada, and discharges at Long Island Sound. Its watershed encompasses 11,260 square miles (29,200 km2), covering parts of five U.S. states and one Canadian province, via 148 tributaries, 38 of which are major rivers. It produces 70% of Long Island Sound's fresh water, discharging at 18,400 cubic feet (520 m3) per second.

The Province of New Hampshire was an English colony and later a British province in New England. It corresponds to the territory between the Merrimack and Piscataqua rivers on the eastern coast of North America. It was named after the English county of Hampshire in southern England by Captain John Mason in 1629, its first named proprietor. In 1776, the province established an independent state and government, the State of New Hampshire, and joined with twelve other colonies to form the United States.
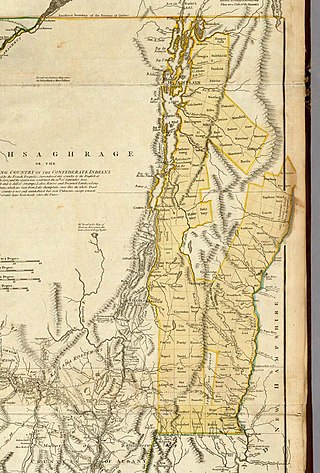
The New Hampshire Grants or Benning Wentworth Grants were land grants made between 1749 and 1764 by the colonial governor of the Province of New Hampshire, Benning Wentworth. The land grants, totaling about 135, were made on land claimed by New Hampshire west of the Connecticut River, territory that was also claimed by the Province of New York. The resulting dispute led to the eventual establishment of the Vermont Republic, which later became the U.S. state of Vermont.

The Province of Maine refers to any of the various English colonies established in the 17th century along the northeast coast of North America, within portions of the present-day U.S. states of Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec and New Brunswick. It existed through a series of land patents made by the kings of England during this era, and included New Somersetshire, Lygonia, and Falmouth. The province was incorporated into the Massachusetts Bay Colony during the 1650s, beginning with the formation of York County, Massachusetts, which extended from the Piscataqua River to just east of the mouth of the Presumpscot River in Casco Bay. Eventually, its territory grew to encompass nearly all of present-day Maine.
Title I: The State and Its Government, is the collection of New Hampshire Revised Statutes Annotated which relate to the state's government as a whole. Like other portions of the RSAs, the Title is divided into Chapters and Sections organized in numbers and subsections organized in lowercase letters.

The area that is now Massachusetts was colonized by English settlers in the early 17th century and became the Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the 18th century. Before that, it was inhabited by a variety of Native American tribes. Massachusetts is named after the Massachusett tribe that inhabited the area of present-day Greater Boston. The Pilgrim Fathers who sailed on the Mayflower established the first permanent settlement in 1620 at Plymouth Colony which set precedents but never grew large. A large-scale Puritan migration began in 1630 with the establishment of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, and that spawned the settlement of other New England colonies.

Halls Stream or Rivière Hall is a 25.2-mile-long (40.6 km) tributary of the Connecticut River in eastern North America. For most of its length, it forms the Canada–United States border, with the province of Quebec (Canada) to its west and the state of New Hampshire to its east.

Beaver Brook is a 30.7-mile-long (49.4 km) river located in New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the United States. It is a tributary of the Merrimack River, part of the Gulf of Maine watershed.

The Merrimack Valley is a bi-state region along the Merrimack River in the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Massachusetts. The Merrimack is one of the larger waterways in New England and has helped to define the livelihood and culture of those living along it for millennia.

Pawtucket Falls is a waterfall on the Merrimack River at Lowell, Massachusetts. The waterfall and rapids below it drop a total of 32 feet in a little under a mile, and was an important fishing ground for the Pennacook Indians in pre-colonial times.

The geology of New Hampshire is similar to that of the rest of New England in comprising a series of metamorphosed sedimentary and volcanic rocks of Late Proterozoic to Devonian age, intruded by many plutons and dikes ranging in age from Late Proterozoic to early Cretaceous. New Hampshire is known as "the Granite State", but less than half is underlain by granite; much of it is schist or gneiss, both of which are metamorphic rocks.

















