
The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is a group of islands north of the Canadian mainland.
Seal Bay is a bay which indents the northeastern end of Riiser-Larsen Ice Shelf just southward of Cape Norvegia, on the coast of Queen Maud Land. It was discovered in the year 1930 by Capt. Hjalmar Riiser-Larsen and so named by him because of the abundance of seals in the bay.
Ketchum Glacier is an eastward flowing glacier at the base of Palmer Land, Antarctica, about 50 nautical miles (90 km) long, descending between the Latady Mountains and the Scaife Mountains into Gardner Inlet. It was discovered by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, under Finn Ronne, who named it for Commander Gerald Ketchum, U.S. Navy, commander of the icebreaker USS Burton Island (AG-88) which broke the ice to free the RARE from Marguerite Bay for the return home.
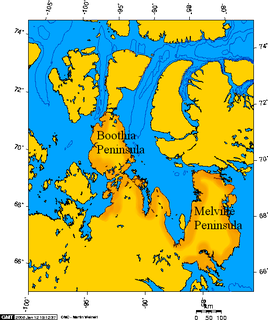
The Simpson Peninsula is a peninsula in the Gulf of Boothia in Canada's Nunavut territory. It is surrounded by waterways on three sides: Pelly Bay to the west, the Gulf of Boothia to the north, and Committee Bay to the east. Kugaaruk, a Netsilik Inuit hamlet, is located on its western coast.
Daspit Glacier is a glacier 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, flowing east-northeast along the south side of Mount Shelby to the head of Trail Inlet, on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by members of the East Base of the United States Antarctic Service, 1939–41, and was originally named Fleming Glacier after Rev. W.L.S. Fleming. It was photographed from the air in 1947 by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne, and charted in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. It was renamed by Ronne for Captain Lawrence R. Daspit, U.S. Navy, who assisted in obtaining Navy support for the Ronne expedition, the original name being transferred to Fleming Glacier on the Rymill Coast.
Window Buttress is a cliff rising to about 800 m near the southeast end of Fuchs Ice Piedmont, Adelaide Island, 3 nautical miles (6 km) west-northwest of the summit of Mount Ditte. So named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC), 1982, from the window-like structure near the top of the cliff, which is visible only from the southwest.

Olstad Glacier is a heavily crevassed glacier descending to the west coast of Peter I Island about 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) south of Tofte Glacier. Peter I Island was circumnavigated by the Norwegian whale catcher Odd I in January 1927 and was explored from the Norvegia in February 1929.
Nils Larsen Glacier is a glacier descending to the west coast of Peter I Island close northward of Norvegia Bay. In February 1929 the crew of the Norvegia carried out a series of investigations of this island, landing on February 2. Named for Nils Larsen, captain of the Norvegia.
Dalgliesh Bay is a bay, 1 nautical mile (2 km) wide and indenting 3 nautical miles (6 km), lying between Lainez Point and Bongrain Point on the west side of Pourquoi Pas Island, off the west coast of Graham Land. It was first roughly surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition under John Rymill. It was resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and named for David G. Dalgliesh, FIDS medical officer at Stonington Island in 1948–49, who accompanied the 1948 sledge survey party to this area.
Eureka Glacier is a broad, gently sloping glacier, 18 nautical miles (33 km) long and 17 nautical miles (31 km) wide at its mouth, which flows westward from the west side of Palmer Land into George VI Sound. It is bounded on its north side by the nunataks south of Mount Edgell, on its south side by the Traverse Mountains and Terminus Nunatak, and at its head Prospect Glacier provides a route to the Wordie Ice Shelf. It was first surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under John Rymill and resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. The name, from the ancient Greek word eureka, expresses the triumph of discovery and arose because the BGLE sledge party found their way to George VI Sound via this glacier in 1936.
Framnes Head is a small rock point in Sandefjord Cove on the west side of Peter I Island. It was charted and named by a Norwegian expedition in the Norvegia under Nils Larsen, who made the first landing on Peter I Island at this point in February 1929.
Point Moreno is a point at the east side of the entrance to the small cove at the head of Scotia Bay, on the south coast of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands. Charted in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under Bruce, who named it for Francisco P. Moreno, noted Argentine scientist and director of the Museo de la Plata.
Meridian Glacier is a broad glacier, 9 nautical miles (17 km) long, which flows south along the west side of Godfrey Upland and joins Clarke Glacier between Behaim Peak and Elton Hill, in southern Graham Land, Antarctica. Finn Ronne and Carl R. Eklund of the United States Antarctic Service travelled along this glacier in January 1941. It was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in November 1947, and was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in December 1958. The glacier was so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee because the glacier flows from north to south along the meridian.
Tvistein Pillars are two flat-topped pillar rocks standing 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) southwest of Cape Eva, the north extremity of Peter I Island, off the coast of Antarctica. The rocks were sighted from the Odd I by a Norwegian expedition under Eyvind Tofte in 1927. The name Tvistein was applied by a Norwegian expedition under Nils Larsen which charted the island from the Norvegia in 1929.
Sandefjord Cove is a cove between Cape Ingrid and the terminus of Tofte Glacier on the west side of Peter I Island. A Norwegian expedition under Eyvind Tofte circumnavigated Peter I Island in the Odd I in 1927. In February 1929 the Norvegia under Nils Larsen carried out a series of investigations all around the island, landing on February 2 to hoist the Norwegian flag. Named for Sandefjord, Norway, center of the Norwegian whaling industry.
Horn Bluff is a prominent rocky headland on the northern side of the coastal island at the western side of Deakin Bay, Antarctica. The feature rises to 325 metres (1,070 ft) and is marked by the columnar structure of the dolerite forming the upper part of it. It was discovered and mapped as part of the mainland by the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (1911–14) under Douglas Mawson, who applied the name for W.A. Horn of Adelaide, a patron of the expedition. The headland was shown to be on an island by Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions air photos taken in 1962.
Tofte Glacier is a glacier immediately south of Sandefjord Cove on the west side of Peter I Island. Discovered in 1927 by a Norwegian expedition in the Odd I and named for Eyvind Tofte, leader of the expedition.







