| o | |
|---|---|
Hangul  | |
| Korean name | |
| Revised Romanization | o |
| McCune–Reischauer | o |
ㅗ (o) is one of the Korean hangul.
| o | |
|---|---|
Hangul  | |
| Korean name | |
| Revised Romanization | o |
| McCune–Reischauer | o |
ㅗ (o) is one of the Korean hangul.

| Preview | ㅗ | ᅩ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | HANGUL LETTER O | HANGUL JUNGSEONG O | ||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 12631 | U+3157 | 4457 | U+1169 |
| UTF-8 | 227 133 151 | E3 85 97 | 225 133 169 | E1 85 A9 |
| Numeric character reference | ㅗ | ㅗ | ᅩ | ᅩ |

In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion.

In Newtonian mechanics, momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If m is an object's mass and v is its velocity, then the object's momentum p is: In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement of momentum is the kilogram metre per second (kg⋅m/s), which is dimensionally equivalent to the newton-second.
Power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt, equal to one joule per second. Power is a scalar quantity.

In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 paper, On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies, the theory is presented as being based on just two postulates:

In mathematics, a tensor is an algebraic object that describes a multilinear relationship between sets of algebraic objects related to a vector space. Tensors may map between different objects such as vectors, scalars, and even other tensors. There are many types of tensors, including scalars and vectors, dual vectors, multilinear maps between vector spaces, and even some operations such as the dot product. Tensors are defined independent of any basis, although they are often referred to by their components in a basis related to a particular coordinate system; those components form an array, which can be thought of as a high-dimensional matrix.
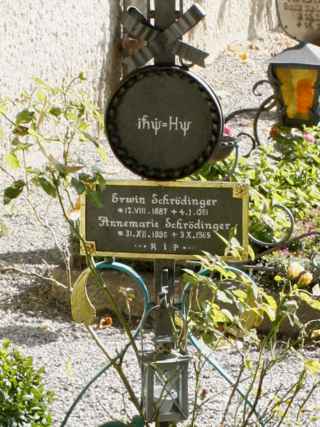
The Schrödinger equation is a partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a non-relativistic quantum-mechanical system. Its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of quantum mechanics. It is named after Erwin Schrödinger, who postulated the equation in 1925 and published it in 1926, forming the basis for the work that resulted in his Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933.

In science, work is the energy transferred to or from an object via the application of force along a displacement. In its simplest form, for a constant force aligned with the direction of motion, the work equals the product of the force strength and the distance traveled. A force is said to do positive work if it has a component in the direction of the displacement of the point of application. A force does negative work if it has a component opposite to the direction of the displacement at the point of application of the force.

In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of work, other than pressure-volume work, that may be performed by a thermodynamically closed system at constant temperature and pressure. It also provides a necessary condition for processes such as chemical reactions that may occur under these conditions. The Gibbs free energy is expressed asWhere:

In biochemistry, Michaelis–Menten kinetics, named after Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten, is the simplest case of enzyme kinetics, applied to enzyme-catalysed reactions of one substrate and one product. It takes the form of a differential equation describing the reaction rate to , the concentration of the substrate A. Its formula is given by the Michaelis–Menten equation:

McCune–Reischauer romanization is one of the two most widely used Korean-language romanization systems. It was created in 1937 and the ALA-LC variant based on it is currently used for standard romanization library catalogs in North America.
Time dilation is the difference in elapsed time as measured by two clocks, either because of a relative velocity between them, or a difference in gravitational potential between their locations. When unspecified, "time dilation" usually refers to the effect due to velocity.

The writing system of the Korean language is a syllabic alphabet of character parts organized into character blocks representing syllables. The character parts cannot be written from left to right on the computer, as in many Western languages. Every possible syllable in Korean would have to be rendered as syllable blocks by a font, or each character part would have to be encoded separately. Unicode has both options; the character parts ㅎ (h) and ㅏ (a), and the combined syllable 하 (ha), are encoded.
The Gyeonggi dialect or Seoul dialect of the Korean language is the prestige dialect in South Korea, as well as the basis of the standardized form of the language in the country. It is mainly concentrated in the Seoul National Capital Area, which includes Seoul, Incheon, and Gyeonggi Province. It is also spoken in parts of North Korea, including in Kaesong, as well as among the Korean diaspora.
The Gyeongsang dialects, also known as Southeastern Korean, are dialects of the Korean language from the historical region of Gyeongsang Province. Today, that region is divided into Daegu, Busan, Ulsan, North Gyeongsang Province, and South Gyeongsang Province.
In linear algebra, an eigenvector or characteristic vector is a vector that has its direction unchanged by a given linear transformation. More precisely, an eigenvector, , of a linear transformation, , is scaled by a constant factor, , when the linear transformation is applied to it: . The corresponding eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root is the multiplying factor .

In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the condenser microphone. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
Koryo-mar is a dialect of Korean spoken by Koryo-saram, ethnic Koreans who live in the countries of the former Soviet Union. It is descended from the Hamgyŏng dialect and multiple other varieties of Northeastern Korean. Koryo-mar is often reported as difficult to understand by speakers of standard Korean; this may be compounded by the fact that the majority of Koryo-saram today use Russian and not Korean as their first language.
Hangul (Korean: 한글) is the native script of Korea. It was created in the mid fifteenth century by King Sejong, as both a complement and an alternative to the logographic Sino-Korean Hanja. Initially denounced by the educated class as eonmun, it only became the primary Korean script following independence from Japan in the mid-20th century.

The Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Hangeul in South Korea and Chosŏn'gŭl in North Korea, is the modern writing system for the Korean language. The letters for the five basic consonants reflect the shape of the speech organs used to pronounce them. They are systematically modified to indicate phonetic features. The vowel letters are systematically modified for related sounds, making Hangul a featural writing system. It has been described as a syllabic alphabet as it combines the features of alphabetic and syllabic writing systems.
ㅙ is one of the Korean hangul. This compound vowel is ㅗ + ㅐ. To pronounce this vowel, shape your mouth to make the ㅗ sound. Then start to say the ㅗ sound and while quickly saying the ㅐ sound. The resulting sound is ㅙ (wae) as in ‘wedding’.