The Bible is a collection of sacred texts or scriptures. Varying parts of the Bible are considered to be a product of divine inspiration and a record of the relationship between God and humans by Christians, Jews, Samaritans, and Rastafarians.

Beowulf is an Old English epic poem consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is one of the most important works of Old English literature. The date of composition is a matter of contention among scholars; the only certain dating pertains to the manuscript, which was produced between 975 and 1025. The author was an anonymous Anglo-Saxon poet, referred to by scholars as the "Beowulf poet".
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. Its adherents, known as Christians, believe that Jesus is the Christ, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible, called the Old Testament in Christianity, and chronicled in the New Testament. It is the world's largest religion with about 2.4 billion followers.

A church building or church house, often simply called a church, is a building used for Christian religious activities, particularly for Christian worship services. The term is often used by Christians to refer to the physical buildings where they worship, but it is sometimes used to refer to buildings of other religions. In traditional Christian architecture, a church interior is often structured in the shape of a Christian cross. When viewed from plan view the vertical beam of the cross is represented by the center aisle and seating while the horizontal beam and junction of the cross is formed by the bema and altar.

The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 260 million baptised members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops in local synods. Roughly half of Eastern Orthodox Christians live in Russia. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the Bishop of Rome, but the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognised by all as primus inter pares of the bishops. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played a prominent role in the history and culture of Eastern and Southeastern Europe, the Caucasus, and the Near East.
In Abrahamic religions, the Holy Spirit is an aspect or agent of God, by means of which people become His messenger or servant. The term is also used to describe aspects of other religions and belief structures.

The Old Testament is the first part of Christian Bibles, based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites believed by most Christians and religious Jews to be the sacred Word of God. The second part of the Christian Bible is the New Testament.

Paganism is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism. This was either because they were increasingly rural and provincial relative to the Christian population, or because they were not milites Christi. Alternate terms in Christian texts for the same group were hellene, gentile, and heathen. Ritual sacrifice was an integral part of ancient Graeco-Roman religion and was regarded as an indication of whether a person was pagan or Christian.

Catacombs are human-made subterranean passageways for religious practice. Any chamber used as a burial place is a catacomb, although the word is most commonly associated with the Roman Empire.

A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small, and is distinguished from a church. The term has several senses. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type of these. Secondly, a chapel is a place of worship, sometimes non-denominational, that is part of a building or complex with some other main purpose, such as a school, college, hospital, palace or large aristocratic house, castle, barracks, prison, funeral home, cemetery, airport, or a military or commercial ship. Thirdly, chapels are small places of worship, built as satellite sites by a church or monastery, for example in remote areas; these are often called a chapel of ease. A feature of all these types is that often no clergy were permanently resident or specifically attached to the chapel. Finally, for historical reasons, chapel is also often the term used for independent or nonconformist places of worship in Great Britain—outside the established church, even where in practice they operate as a parish church.

The Old City is a 0.9 square kilometers (0.35 sq mi) walled area within the modern city of Jerusalem.

Old Norse religion, also known as Norse paganism, is the most common name for a branch of Germanic religion which developed during the Proto-Norse period, when the North Germanic peoples separated into a distinct branch of the Germanic peoples. It was replaced by Christianity during the Christianization of Scandinavia. Scholars reconstruct aspects of North Germanic religion by historical linguistics, archaeology, toponymy, and records left by North Germanic peoples, such as runic inscriptions in the Younger Futhark, a distinctly North Germanic extension of the runic alphabet. Numerous Old Norse works dated to the 13th century record Norse mythology, a component of North Germanic religion.

Blót is the term for "sacrifice" in Norse paganism. A blót could be dedicated to any of the Norse gods, the spirits of the land, and to ancestors. The sacrifice involved aspects of a sacramental meal or feast.

Kanjirappally is a taluk and a town in Kottayam district situated about 38 km (24 mi) away from the district capital, in the state of Kerala, India. National Highway connects Kanjirapally to major nearest cities. Kanjirappally, also known as the Gateway of Highrange since it is the geographic entrance to the 'Malanad' or the Hill country of Kerala, which extends to Idukki district and then to Tamil Nadu. Kanjirapally is one of the most busiest towns in kottayam district. It is a part of the Palai city metro. A new airport has been proposed which is near to kanjirapally in Erumeli.
In Christianity, the gospel, or the Good News, is the news of the coming of the Kingdom of God. The message of good news is described as a narrative in the four canonical gospels.

Anglo-Saxon paganism, sometimes termed Anglo-Saxon heathenism, Anglo-Saxon pre-Christian religion, or Anglo-Saxon traditional religion, refers to the religious beliefs and practices followed by the Anglo-Saxons between the 5th and 8th centuries AD, during the initial period of Early Medieval England. A variant of the Germanic paganism found across much of north-western Europe, it encompassed a heterogeneous variety of disparate beliefs and cultic practices, with much regional variation.

In religion and folklore, Hell is an afterlife location in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, often torture as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hells as eternal destinations, the biggest examples of which are Christianity and Islam, whereas religions with reincarnation usually depict a hell as an intermediary period between incarnations, as is the case in the dharmic religions. Religions typically locate hell in another dimension or under Earth's surface. Other afterlife destinations include Heaven, Paradise, Purgatory, Limbo, and the underworld.

The Christian Quarter is one of the four quarters of the walled Old City of Jerusalem, the other three being the Jewish Quarter, the Muslim Quarter and the Armenian Quarter. The Christian Quarter is situated in the northwestern corner of the Old City, extending from the New Gate in the north, along the western wall of the Old City as far as the Jaffa Gate, along the Jaffa Gate - Western Wall route in the south, bordering on the Jewish and Armenian Quarters, as far as the Damascus Gate in the east, where it borders on the Muslim Quarter. The Christian quarter contains about 40 Christian holy places. Among them is the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, one of Christianity's holiest places. Most of its residents are Palestinian Christians, despite their dwindling numbers.
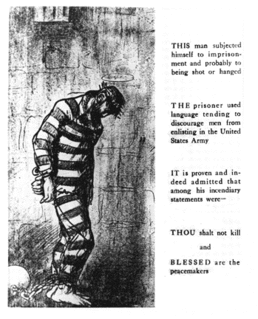
Christian pacifism is the theological and ethical position that any form of violence is incompatible with the Christian faith. Christian pacifists state that Jesus himself was a pacifist who taught and practiced pacifism and that his followers must do likewise. Notable Christian pacifists include Martin Luther King, Jr., Leo Tolstoy, and Ammon Hennacy. Hennacy believed that adherence to Christianity required not just pacifism but, because governments inevitably threatened or used force to resolve conflicts, anarchism. However, most Christian pacifists, including the peace churches, Christian Peacemaker Teams and individuals such as John Howard Yoder, make no claim to be anarchists.

The Christian biblical canons are the books Christians regard as divinely inspired and which constitute a Christian Bible. Which books constituted the Christian biblical canons of both the Old and New Testament was generally established by the 5th century, despite some scholarly disagreements, for the ancient undivided Church.