Related Research Articles

A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development, or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene or from a parent with the disorder. When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA.

Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a group of 13 genetic connective-tissue disorders in the current classification, with the latest type discovered in 2018. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Complications may include aortic dissection, joint dislocations, scoliosis, chronic pain, or early osteoarthritis.
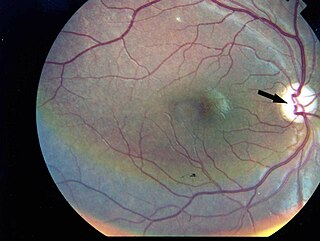
Wolfram syndrome, also called DIDMOAD, is a rare autosomal-recessive genetic disorder that causes childhood-onset diabetes mellitus, optic atrophy, and deafness as well as various other possible disorders including neurodegeneration.

Alport syndrome is a genetic disorder affecting around 1 in 5,000-10,000 children, characterized by glomerulonephritis, end-stage kidney disease, and hearing loss. Alport syndrome can also affect the eyes, though the changes do not usually affect vision, except when changes to the lens occur in later life. Blood in urine is universal. Proteinuria is a feature as kidney disease progresses.

Arthrogryposis (AMC) describes congenital joint contracture in two or more areas of the body. It derives its name from Greek, literally meaning 'curving of joints'.

Olivopontocerebellar atrophy (OPCA) is the degeneration of neurons in specific areas of the brain – the cerebellum, pons, and inferior olivary nucleus. OPCA is present in several neurodegenerative syndromes, including inherited and non-inherited forms of ataxia and multiple system atrophy (MSA), with which it is primarily associated.

Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition in its own right. An estimated 150,000 people in the United States have a diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia at any given time. SCA is hereditary, progressive, degenerative, and often fatal. There is no known effective treatment or cure. SCA can affect anyone of any age. The disease is caused by either a recessive or dominant gene. In many cases people are not aware that they carry a relevant gene until they have children who begin to show signs of having the disorder.
Albinism-black lock-cell migration disorder is the initialism for the following terms and concepts that describe a condition affecting a person's physical appearance and physiology: (1) A – albinism, (2) B – black lock of hair, (3) C – cell migration disorder of the neurocytes of the gut, and (4) D – sensorineural deafness. The syndrome is caused by mutation in the endothelin B receptor gene (EDNRB).

Flynn–Aird syndrome is a rare, hereditary, neurological disease that is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. The syndrome involves defects in the nervous, auditory, skeletal, visual, and endocrine systems and encompasses numerous symptoms, bearing striking similarity to other known syndromes of neuroectodermal nature such as: Werner syndrome, Cockayne syndrome and Refsum syndrome.

Cohen syndrome is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder with varied expression, characterised by obesity, intellectual disability, distinct craniofacial abnormalities and potential ocular dysfunction.

MERRF syndrome is a mitochondrial disease. It is extremely rare, and has varying degrees of expressivity owing to heteroplasmy. MERRF syndrome affects different parts of the body, particularly the muscles and nervous system. The signs and symptoms of this disorder appear at an early age, generally childhood or adolescence. The causes of MERRF syndrome are difficult to determine, but because it is a mitochondrial disorder, it can be caused by the mutation of nuclear DNA or mitochondrial DNA. The classification of this disease varies from patient to patient, since many individuals do not fall into one specific disease category. The primary features displayed on a person with MERRF include myoclonus, seizures, cerebellar ataxia, myopathy, and ragged red fibers (RRF) on muscle biopsy, leading to the disease's name. Secondary features include dementia, optic atrophy, bilateral deafness, peripheral neuropathy, spasticity, or multiple lipomata. Mitochondrial disorders, including MERRFS, may present at any age.
Brown-Vialetto-Van-Laere syndrome (BVVL), sometimes known as Brown's Syndrome, is a rare degenerative disorder often initially characterized by progressive sensorineural deafness.
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa is a skin condition characterized by blister formation within the lamina lucida of the basement membrane zone.

Gillespie syndrome, also called aniridia, cerebellar ataxia and mental deficiency, is a rare genetic disorder. The disorder is characterized by partial aniridia, ataxia, and, in most cases, intellectual disability. It is heterogeneous, inherited in either an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive manner. Gillespie syndrome was first described by American ophthalmologist Fredrick Gillespie in 1965.

Mohr–Tranebjærg syndrome (MTS) is a rare X-linked recessive syndrome also known as deafness–dystonia syndrome and caused by mutation in the TIMM8A gene. It is characterized by clinical manifestations commencing with early childhood onset hearing loss, followed by adolescent onset progressive dystonia or ataxia, visual impairment from early adulthood onwards and dementia from the 4th decade onwards. The severity of the symptoms may vary, but they progress usually to severe deafness and dystonia and sometimes are accompanied by cortical deterioration of vision and mental deterioration.

Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome, or Alper's disease, is any of a group of autosomal recessive disorders that cause a significant drop in mitochondrial DNA in affected tissues. Symptoms can be any combination of myopathic, hepatopathic, or encephalomyopathic. These syndromes affect tissue in the muscle, liver, or both the muscle and brain, respectively. The condition is typically fatal in infancy and early childhood, though some have survived to their teenage years with the myopathic variant and some have survived into adulthood with the SUCLA2 encephalomyopathic variant. There is currently no curative treatment for any form of MDDS, though some preliminary treatments have shown a reduction in symptoms.

Arts syndrome is a rare metabolic disorder that causes serious neurological problems in males due to a malfunction of the PRPP synthetase 1 enzyme. Arts Syndrome is part of a spectrum of PRPS-1 related disorders with reduced activity of the enzyme that includes Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease and X-linked non-syndromic sensorineural deafness.

Gustavson syndrome, also known as Severe X-linked intellectual disability, Gustavson type, is a rare genetic disorder characterized by severe intellectual disabilities, microcephaly, developmental delay, optic atrophy-induced severe vision impairment/loss, severe hearing loss, spasticity, epilepsy, hypomobility of major joints, facial dysmorphisms, and premature death. Some other frequent symptoms include severe postnatal growth retardation, infantile apnea, brain atrophy, dilation of the fourth cerebral ventricle, recurrent upper respiratory tract infections, and a small fontanelle. This disorder was first discovered in 1993, by Gustavson et al., when they described 7 male children from a 2-generation family, these children had the symptoms mentioned above, and they came to the conclusion that this case was part of a novel X-linked recessive syndrome. No new cases have been reported since then (1993).
CAPOS syndrome is a rare genetic neurological disorder which is characterized by abnormalities of the feet, eyes and brain which affect their normal function. These symptoms occur episodically when a fever-related infection is present within the body. The name is an acronym for "cerebellar ataxia, areflexia, pes cavus, optic atrophy, and sensorineural hearing loss".

Wolfram-like syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder that shares some of the features shown by those affected with the autosomal recessive Wolfram syndrome. It is a type of WFS1-related disorder.
References
- ↑ "Olivopontocerebellar atrophy deafness — About the Disease — Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Search a disease". www.orpha.net. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- ↑ "Olivopontocerebellar Atrophy: Background, Pathophysiology, Epidemiology". 2022-03-11.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Sensory 5. "Olivopontocerebellar atrophy deafness | Rare Diseases". RareGuru. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- ↑ Pratap-Chand, R.; Gururaj, A. K.; Dilip-Kumar, S. (1995-02-01). "A syndrome of olivopontocerebellar atrophy and deafness with onset in infancy". Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. 91 (2): 133–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1995.tb00419.x . ISSN 0001-6314. PMID 7785423.