
The defence of Greenland is the responsibility of the Kingdom of Denmark; the government of Greenland does not have control of Greenland's military or foreign affairs. In the history of Greenland there have been many changes of presence regarding who is in charge of the security of Greenlandic people and its land.

Ellesmere Island is Canada's northernmost and third largest island, and the tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of 196,236 km2 (75,767 sq mi), slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total length of the island is 830 km (520 mi).

Hans Island is an island in the centre of the Kennedy Channel of Nares Strait in the high Arctic region, split between the Canadian territory of Nunavut and the Danish autonomous territory of Greenland. The island itself is barren and uninhabited with an area of 130 hectares, measuring 1,290 by 1,199 metres, and a maximum elevation of 168.17 m (551.7 ft). Its location in the strait that separates Ellesmere Island of Canada from northern Greenland was for years a border dispute, the so-called Whisky War between the two countries of Canada and Denmark. Hans Island is the smallest of three islands in Kennedy Channel off the Washington Land coast; the others are Franklin Island and Crozier Island. The strait at this point is 35 km (22 mi) wide, placing the island within the territorial waters of both Canada and Denmark (Greenland). A 1,280-metre-long (4,200 ft) border traverses the island.
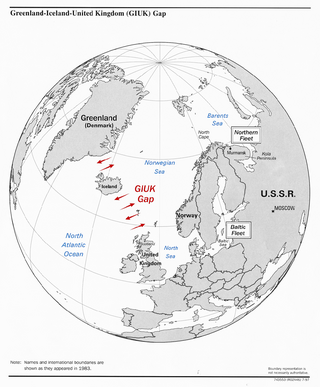
The GIUK gap is an area in the northern Atlantic Ocean that forms a naval choke point. Its name is an acronym for Greenland, Iceland, and the United Kingdom, the gap being the two stretches of open ocean among these three landmasses. It separates the Norwegian Sea and the North Sea from the open Atlantic Ocean. The term is typically used in relation to military topics. The area has for some nations been considered strategically important since the beginning of the 20th century.

Alert, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada, is the northernmost continuously inhabited place in the world, on Ellesmere Island at latitude 82°30'05" north, 817 km (508 mi) from the North Pole. It takes its name from HMS Alert, which wintered 10 km (6.2 mi) east of the present station, off what is now Cape Sheridan, in 1875–1876.

Eureka is a small research base on Fosheim Peninsula, Ellesmere Island, Qikiqtaaluk Region, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut. It is located on the north side of Slidre Fiord, which enters Eureka Sound farther west. It is the third-northernmost permanent research community in the world. The only two farther north are Alert, which is also on Ellesmere Island, and Nord, in Greenland. Eureka has the lowest average annual temperature and the lowest amount of precipitation of any weather station in Canada.

Pituffik Space Base, formerly Thule Air Base, is the United States Space Force's northernmost base, and the northernmost installation of the U.S. Armed Forces, located 750 mi (1,210 km) north of the Arctic Circle and 947 mi (1,524 km) from the North Pole on the northwest coast of the island of Greenland. Pituffik's Arctic environment includes icebergs in North Star Bay, two islands, a polar ice sheet, and Wolstenholme Fjord – the only place on Earth where four active glaciers join. The base is home to a substantial portion of the global network of missile warning sensors of Space Delta 4, and space surveillance and space control sensors of Space Delta 2, providing space awareness and advanced missile detection capabilities to North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD), the United States Space Force, and joint partners.

Canadian Forces Station Alert, often shortened to CFS Alert, is a signals intelligence intercept facility of the Canadian Armed Forces at Alert, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada.

Island Command Greenland, or simply "GLK", was a Level.II authority responsible directly to the Defence Command. It was, among other things, responsible for the military defense of Greenland, maritime and sovereignty maintenance and enforcement, as well as search and rescue. Personnel assigned to the Danish liaison office at Thule Air Base (FOTAB) as well as the Sirius Patrol were also a part of the Greenland Command. Island Command Greenland was amalgamated with Island Command Faroes to a Joint Arctic Command on 31 October 2012.

Nares Strait is a waterway between Ellesmere Island and Greenland that connects the northern part of Baffin Bay in the Atlantic Ocean with the Lincoln Sea in the Arctic Ocean. From south to north, the strait includes Smith Sound, Kane Basin, Kennedy Channel, Hall Basin and Robeson Channel. Nares Strait has a nearly permanent current from the north, powered by the Beaufort Gyre, making it harder to traverse for ships coming from the south.

Kennedy Channel is an Arctic sea passage between Greenland and Canada's most northerly island, Ellesmere Island.

Lincoln Sea is a body of water in the Arctic Ocean, stretching from Cape Columbia, Canada, in the west to Cape Morris Jesup, Greenland, in the east. The northern limit is defined as the great circle line between those two headlands. It is covered with sea ice throughout the year, the thickest sea ice in the Arctic Ocean, which can be up to 15 m (49 ft) thick. Water depths range from 100 m (330 ft) to 300 m (980 ft). Water and ice from Lincoln Sea empty into Robeson Channel, the northernmost part of Nares Strait, most of the time.

The Sirius Dog Sled Patrol, known informally as Siriuspatruljen and formerly known as North-East Greenland Sledge Patrol and Resolute Dog Sled Patrol, is an elite Danish naval unit. It conducts long-range reconnaissance patrolling, and enforces Danish sovereignty in the Arctic wilderness of northern and eastern Greenland, an area that includes the Northeast Greenland National Park, which is the largest national park in the world. Patrolling is usually done in pairs and using dog sleds with about a dozen dogs, sometimes for four months and often without additional human contact.

Canada–Denmark relations are the current and historical relations between Canada and Denmark. Canada has an embassy in Copenhagen. Denmark has an embassy in Ottawa and a consulate-general in Toronto. Both countries are full members of NATO and the Arctic Council. Relations between the two countries have attracted attention in light of the dispute over Hans Island, which was resolved in 2022.

Operation Nanook is an annual sovereignty operation and manoeuvre warfare exercise conducted by the Canadian Armed Forces in the Arctic. Sovereignty patrols in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago and northern Canada are conducted by the Canadian Rangers, Canadian Coast Guard in tandem with the Royal Canadian Mounted Police. The exercise portion is intended to train the different elements of the Canadian Armed Forces to operate in the Arctic environment.

The Greenland wolf is a subspecies of gray wolf that is native to Greenland. Historically, it was heavily persecuted, but today it is fully protected and about 90% of the wolf's range falls within the boundaries of the Northeast Greenland National Park.

The Arctic Policy of the Kingdom of Denmark defines the Kingdom's foreign relations and policies with other Arctic countries, and the Kingdom's strategy for the Arctic on issues occurring within the geographic boundaries of "the Arctic" or related to the Arctic or its peoples. In order to clearly understand the Danish geopolitical importance of the Arctic, it is necessary to mention Denmark's territorial claims in areas beyond its exclusive EEZ in areas around the Faroe Islands and north of Greenland covering parts of the North Pole, which is also claimed by Russia.

The Joint Arctic Command is a direct Level II authority in the Danish Defence. Joint Arctic Command's primary mission in peacetime is to ensure Danish sovereignty by monitoring the area around the Faroe Islands and Greenland. The command also handles tasks such as fisheries inspection, search and rescue (SAR), patient transport and other tasks that support the civil society. In short, the Joint Arctic Command handles military tasks, coast guard duties and disaster response - all in one organisation.
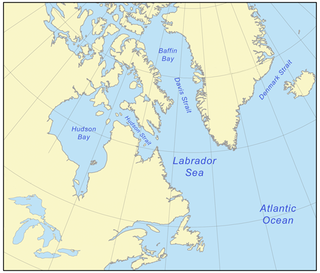
The Canadian Arctic Rift System is a major North American geological structure extending from the Labrador Sea in the southeast through Davis Strait, Baffin Bay and the Arctic Archipelago in the northwest. It consists of a series of interconnected rifts that formed during the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Extensional stresses along the entire length of the rift system have resulted in a variety of tectonic features, including grabens, half-grabens, basins and faults.

The Whisky War, also known as the Liquor Wars, was a bloodless war and border dispute between the Kingdom of Denmark and Canada over Hans Island. Between 1973 and 2022, the island was under dispute between the two nations, although never amounting to direct conflict or violence.


















