Related Research Articles
This article concerns the period 479 BC – 470 BC.
Year 474 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Medullinus and Vulso. The denomination 474 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

In Greek mythology, Taras was the eponymous founder of the Greek colony of Taras, in Magna Graecia.

Pyrrhus was a Greek king and statesman of the Hellenistic period. He was king of the Greek tribe of Molossians, of the royal Aeacid house, and later he became king of Epirus. He was one of the strongest opponents of early Rome, and had been regarded as one of the greatest generals of antiquity. Several of his victorious battles caused him unacceptably heavy losses, from which the term "Pyrrhic victory" was coined.
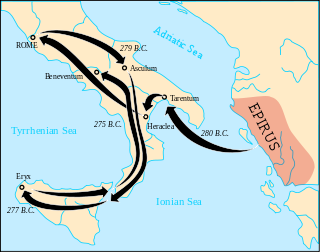
The Battle of Heraclea took place in 280 BC between the Romans under the command of consul Publius Valerius Laevinus, and the combined forces of Greeks from Epirus, Tarentum, Thurii, Metapontum, and Heraclea under the command of Pyrrhus, king of Epirus. Although the battle was a victory for the Greeks and their casualties were lower than the Romans, they had lost many veteran soldiers that would be hard to replace on foreign soil.

The Battle of Asculum took place near Asculum in 279 BC between the Roman Republic under the command of the consuls Publius Decius Mus and Publius Sulpicius Saverrio, and the forces of King Pyrrhus of Epirus. The battle took place during the Pyrrhic War, after the Battle of Heraclea of 280 BC, which was the first battle of the war. There exist accounts of this battle by three ancient historians: Dionysius of Halicarnassus, Plutarch, and Cassius Dio. Asculum was in Lucanian territory, in southern Italy.

The Pyrrhic War was largely fought between the Roman Republic and Pyrrhus, the violent king of Epirus, who had been asked by the people of the Greek city of Tarentum in southern Italy to help them in their war against the Romans.

The Messapians were an Iapygian tribe who inhabited Salento in classical antiquity. Two other Iapygian tribes, the Peucetians and the Daunians, inhabited central and northern Apulia respectively. All three tribes spoke the Messapian language, but had developed separate archaeological cultures by the seventh century BC. The Messapians lived in the eponymous region Messapia, which extended from Leuca in the southeast to Kailia and Egnatia in the northwest, covering most of the Salento peninsula. This region includes the Province of Lecce and parts of the provinces of Brindisi and Taranto today.
The Iapygians or Apulians were an Indo-European-speaking people, dwelling in an eponymous region of the southeastern Italian Peninsula named Iapygia between the beginning of the first millennium BC and the first century BC. They were divided into three tribal groups: the Daunians, Peucetians and Messapians. After their lands were gradually colonized by the Romans from the late 4th century onward and eventually annexed to the Roman Republic by the early 1st century BC, Iapygians were fully Latinized and assimilated into Roman culture.

Oria is a town and comune in the Apulia region, in the province of Brindisi, in southern Italy. It is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Oria.
The history of Taranto dates back to the 8th century BC when it was founded as a Greek colony, known as Taras.

The Battle of Tarentum in March 212 BC was a military engagement in the Second Punic War.

The Peucetians were an Iapygian tribe which inhabited western and central Apulia in classical antiquity. Two other Iapygian tribes, the Daunians and the Messapians, inhabited northern and southern Apulia respectively. All three tribes spoke the Messapian language, but had developed separate archaeological cultures by the seventh century BC; however, in Peucetian territory ancient Greek and Oscan language were spoken as well, as the legends of the currencies from Rubi and Azetium were trilingual. Peucetians lived in the eponymous region Peucetia, which was bordered by the Ofanto river and the Murge in the north, the Bradano river in the west and the territories of the Greek colony of Taras and the Messapians in the south. This region is mostly coincident with the Metropolitan City of Bari and parts of the provinces of Taranto and Barletta-Andria-Trani today.
The Hellenistic armies is the term applied to the armies of the successor kingdoms of the Hellenistic period. The Hellenistic armies emerged after the death of Alexander the Great, when his vast empire was split between his successors, also known as the Diadochi. During the Wars of the Diadochi, the Macedonian army under Philip II and Alexander gradually adopted new units and tactics, further developing Macedonian warfare and improving on the tactics used in the Classical era. The armies of the Diadochi bear few differences from those of Alexander, but during the era of the Epigonoi, the differences were obvious, favoring numbers over quality and weight over maneuverability. The limited availability of Greek conscripts in the east led to an increasing dependence on mercenary forces, whereas in the west, Hellenistic armies were continuously involved in wars, which soon exhausted local manpower, paving the way for Roman supremacy. The major Hellenistic states were the Seleucid Empire, Ptolemaic Egypt and Macedonia during the Antigonid kingdom. Smaller states included Attalid Pergamum, Pontus, Epirus, the Achaean League, the Aetolian League, Syracuse, and other nations such as Athens, Sparta, etc.

The Battle of Tarentum of 209 BC was a battle in the Second Punic War. The Romans, led by Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, recaptured the city of Tarentum that had betrayed them in the first Battle of Tarentum in 212 BC. This time the commander of the city, Carthalo, turned against the Carthaginians, and supported the Romans.
The history of Illyrian warfare of the Illyrians spans from the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC up to the 1st century AD in the region of Illyria and in southern Italy where the Iapygian civilization flourished.

The Daunians were an Iapygian tribe that inhabited northern Apulia in classical antiquity. Two other Iapygian tribes, the Peucetians and the Messapians, inhabited central and southern Apulia respectively. All three tribes spoke the Messapic language, but had developed separate archaeological cultures by the seventh century BC.
Artas was a king of the Messapians. Artas was a strong ally of Athens during the Pelopponesian War and led an anti-Spartan campaign against Taras. Artas is also called Artos and in Greek is known as 'Bread-man'.
The Illyrians were a group of Indo-European speaking peoples, who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan populations, along with the Thracians and Greeks.

The Iapygian–Tarentine wars were a set of conflicts and wars between the Greek colony of Taras and the three Iapygian peoples, the Messapians, Peucetians and Daunians.
References
- ↑ Hyria - 460 BC Archived 2013-12-19 at the Wayback Machine , Tarantine vs Iapygian
- ↑ Pausanias (10.10.6.)