Tax noncompliance is a range of activities that are unfavorable to a government's tax system. This may include tax avoidance, which is tax reduction by legal means, and tax evasion which is the illegal non-payment of tax liabilities. The use of the term "noncompliance" is used differently by different authors. Its most general use describes non-compliant behaviors with respect to different institutional rules resulting in what Edgar L. Feige calls unobserved economies. Non-compliance with fiscal rules of taxation gives rise to unreported income and a tax gap that Feige estimates to be in the neighborhood of $500 billion annually for the United States.

The Tax Court of Canada, established in 1983 by the Tax Court of Canada Act, is a federal superior court which deals with matters involving companies or individuals and tax issues with the Government of Canada.
The court system of Canada is made up of many courts differing in levels of legal superiority and separated by jurisdiction. In the courts, the judiciary interpret and apply the law of Canada. Some of the courts are federal in nature, while others are provincial or territorial.

The United States Tax Court is a federal trial court of record established by Congress under Article I of the U.S. Constitution, section 8 of which provides that the Congress has the power to "constitute Tribunals inferior to the supreme Court". The Tax Court specializes in adjudicating disputes over federal income tax, generally prior to the time at which formal tax assessments are made by the Internal Revenue Service.

In law, a trial is a coming together of parties to a dispute, to present information in a tribunal, a formal setting with the authority to adjudicate claims or disputes. One form of tribunal is a court. The tribunal, which may occur before a judge, jury, or other designated trier of fact, aims to achieve a resolution to their dispute.

The High Court of Singapore is the lower division of the Supreme Court of Singapore, the upper division being the Court of Appeal. The High Court consists of the chief justice and the judges of the High Court. Judicial Commissioners are often appointed to assist with the Court's caseload. There are two specialist commercial courts, the Admiralty Court and the Intellectual Property Court, and a number of judges are designated to hear arbitration-related matters. In 2015, the Singapore International Commercial Court was established as part of the Supreme Court of Singapore, and is a division of the High Court. The other divisions of the high court are the General Division, the Appellate Division, and the Family Division. The seat of the High Court is the Supreme Court Building.
DaimlerChrysler Corp. v. Cuno, 547 U.S. 332 (2006), is a United States Supreme Court case involving the standing of taxpayers to challenge state tax laws in federal court. The Court unanimously ruled that state taxpayers did not have standing under Article III of the United States Constitution to challenge state tax or spending decisions simply by virtue of their status as taxpayers. Chief Justice John Roberts delivered the majority opinion, which was joined by all of the justices except for Ruth Bader Ginsburg, who concurred separately.
Tax protesters in the United States have advanced a number of arguments asserting that the assessment and collection of the federal income tax violates statutes enacted by the United States Congress and signed into law by the President. Such arguments generally claim that certain statutes fail to create a duty to pay taxes, that such statutes do not impose the income tax on wages or other types of income claimed by the tax protesters, or that provisions within a given statute exempt the tax protesters from a duty to pay.

The government of the U.S. state of Oregon, as prescribed by the Oregon Constitution, is composed of three government branches: the executive, the legislative, and the judicial. These branches operate in a manner similar to that of the federal government of the United States.
In some jurisdictions, an assessor is a judge's or magistrate's assistant. This is the historical meaning of this word.
Tax assessment, or assessment, is the job of determining the value, and sometimes determining the use, of property, usually to calculate a property tax. This is usually done by an office called the assessor or tax assessor.

The Oregon Judicial Department (OJD) is the judicial branch of government of the state of Oregon in the United States. The chief executive of the branch is the Chief Justice of the Oregon Supreme Court. Oregon’s judiciary consists primarily of four different courts: the Oregon Supreme Court, the Oregon Tax Court, the Oregon Court of Appeals, and the Oregon circuit courts. Additionally, the OJD includes the Council on Court Procedures, the Oregon State Bar, Commission on Judicial Fitness and Disability, and the Public Defense Services Commission. Employees of the court are the largest non-union group among state workers.
This article concerns the legal mechanisms by way of which a decision of an England and Wales magistrates' court may be challenged. There are four mechanisms under which a decision of a magistrates' court may be challenged:

The courts of South Africa are the civil and criminal courts responsible for the administration of justice in South Africa. They apply the law of South Africa and are established under the Constitution of South Africa or under Acts of the Parliament of South Africa.

In United States federal courts, magistrate judges are judges appointed to assist U.S. district court judges in the performance of their duties. Magistrate judges generally oversee first appearances of criminal defendants, set bail, and conduct other administrative duties. The position of magistrate judge or magistrate also exists in some unrelated state courts .
Tax protesters in the United States advance a number of constitutional arguments asserting that the imposition, assessment and collection of the federal income tax violates the United States Constitution. These kinds of arguments, though related to, are distinguished from statutory and administrative arguments, which presuppose the constitutionality of the income tax, as well as from general conspiracy arguments, which are based upon the proposition that the three branches of the federal government are involved together in a deliberate, on-going campaign of deception for the purpose of defrauding individuals or entities of their wealth or profits. Although constitutional challenges to U.S. tax laws are frequently directed towards the validity and effect of the Sixteenth Amendment, assertions that the income tax violates various other provisions of the Constitution have been made as well.
In 1964 Tanganyika and Zanzibar formed the United Republic of Tanzania. After the Treaty of the Union, the two countries continued to remain with their own legal systems including court structures. In the 1977 Constitution of the United Republic of Tanzania, the High Court of Tanganyika whose jurisdiction was and still is territoriality limited to Tanzania Mainland was called the High Court of Tanzania and the High Court of Zanzibar retained its original name. It is essential to note that the High Court of Tanzania only has territorial jurisdiction over legal issues arising in Tanzania Mainland and the High Court of Zanzibar has territorial jurisdiction over legal issues arising in Zanzibar.

The judiciary of Italy is composed of courts and public prosecutor offices responsible for the administration of justice in the Italian Republic. Both bench judges and public prosecutor belong to the magistracy, that is to say a public office only accessible to Italian citizens who hold an Italian Juris Doctor and have successfully partaken in one of the relevant competitive public examinations organised by the Ministry of justice. The magistracy embodies the judicial power, one of the three independent powers of the State in which no hierarchy exists.

Most local governments in the United States impose a property tax, also known as a millage rate, as a principal source of revenue. This tax may be imposed on real estate or personal property. The tax is nearly always computed as the fair market value of the property, multiplied by an assessment ratio, multiplied by a tax rate, and is generally an obligation of the owner of the property. Values are determined by local officials, and may be disputed by property owners. For the taxing authority, one advantage of the property tax over the sales tax or income tax is that the revenue always equals the tax levy, unlike the other types of taxes. The property tax typically produces the required revenue for municipalities' tax levies. One disadvantage to the taxpayer is that the tax liability is fixed, while the taxpayer's income is not.
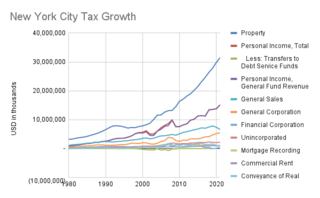
S.7000-A is the name given to the current dominant property tax law in effect in New York State affecting New York City. Surrounding areas such as Nassau County have similar laws. The bill was enacted in 1981 in response to the Hellerstein decision. The law is embodied in Article 18 of the New York State Real Property Law.











