
Vinton County is a county located in the U.S. state of Ohio. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,800, making it the least populous county in the state. Its county seat is McArthur. The county is named for Samuel Finley Vinton, US Representative from Ohio.

Jackson County is a county located in the U.S. state of Ohio. As of the 2020 census, the population was 32,653. Its county seat is Jackson. The county is named for Andrew Jackson, a hero of the War of 1812 who was subsequently elected President of the United States. It is known as "The Little Wales of Ohio." Jackson County comprises the Jackson, OH Micropolitan Statistical Area.

Leetonia is a village in northern Columbiana County, Ohio, United States. The population was 1,833 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Salem micropolitan area, about 16 miles (26 km) south of Youngstown.

Zaleski is a village in Vinton County, Ohio, United States. The population was 230 at the 2020 census.

Rockwood is a city in Roane County, Tennessee, United States. Its population was 5,562 at the time of the 2010 census. It is included in the Harriman, Tennessee Micropolitan Statistical Area.

Anthracite iron or anthracite pig iron is the substance created by the smelting together of anthracite coal and iron ore, that is using anthracite coal instead of charcoal to smelt iron ores—and was an important historic advance in the late-1830s, enabling a great acceleration of the industrial revolution in Europe and North America.

Georges Creek Valley is located in Allegany County, Maryland along the Georges Creek. The valley is rich in wide veins of coal, known historically as "The Big Vein." Coal was once extracted by deep mines but is only mined today through surface mining. The Georges Creek Valley was once a major center for the US coal industry.

Moonville is a ghost town in southeastern Brown Township, Vinton County, Ohio, United States. Little remains of this former mining community except a few foundations, a cemetery, and an abandoned railroad tunnel which is the subject of numerous ghost stories.

Mount Savage is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Allegany County, Maryland, United States. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 873.

The Phoenix Iron Works, located in Phoenixville, Pennsylvania, was a manufacturer of iron and related products during the 19th century and early 20th century. Phoenix Iron Company was a major producer of cannon for the Union Army during the American Civil War. The company also produced the Phoenix column, an advance in construction material. Company facilities are a core component of the Phoenixville Historic District, a National Register of Historic Places site that was in 2006 recognized as a historic landmark by ASM International.

Zaleski State Forest is a state forest in the U.S. state of Ohio, located primarily in Vinton County, with areas in Athens County as well. The 28,000 acre (110 km²) forest surrounds Lake Hope State Park in Vinton County, and borders the Waterloo Wildlife Research Station in Athens County.

The Tennessee Coal, Iron and Railroad Company (1852–1952), also known as TCI and the Tennessee Company, was a major American steel manufacturer with interests in coal and iron ore mining and railroad operations. Originally based entirely within Tennessee, it relocated most of its business to Alabama in the late nineteenth century, following protests over its use of free convict labor. With a sizable real estate portfolio, the company owned several Birmingham satellite towns, including Ensley, Fairfield, Docena, Edgewater and Bayview. It also established a coal mining camp it sold to U.S. Steel which developed it into the Westfield, Alabama planned community.
The Ghost Town Trail is a rail trail in Western Pennsylvania that runs 36 miles (58 km) between Black Lick, Indiana County, and Ebensburg, Cambria County. Established in 1991 on the right-of-way of the former Ebensburg and Black Lick Railroad, the trail follows the Blacklick Creek and passes through many ghost towns that were abandoned in the early 1900s with the decline of the local coal mining industry. Open year-round to cycling, hiking, and cross-country skiing, the trail is designated a National Recreation Trail by the United States Department of the Interior.

Kay Moor, also known as Kaymoor, is the site of an abandoned coal mine, coal-processing plant, and coal town near Fayetteville, West Virginia. The town site is located in the New River Gorge at Kaymoor Bottom (38°03′00″N81°03′17″W). It is linked to the mine portal 560 feet (170 m) above on Sewell Bench (38°02′52″N81°03′58″W) in the wall of the Gorge by conveyors.
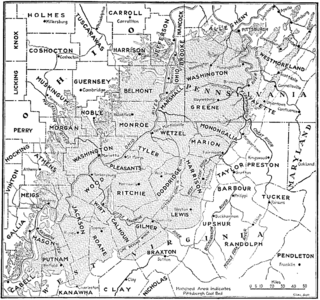
The Pittsburgh Coal Seam is the thickest and most extensive coal bed in the Appalachian Basin; hence, it is the most economically important coal bed in the eastern United States. The Upper Pennsylvanian Pittsburgh coal bed of the Monongahela Group is extensive and continuous, extending over 11,000 mi2 through 53 counties. It extends from Allegany County, Maryland to Belmont County, Ohio and from Allegheny County, Pennsylvania southwest to Putnam County, West Virginia.

John Means was a mayor of Ashland, Kentucky and a leader in the banking and iron industries. He helped organize the Cincinnati and Big Sandy Packet Company, laid out Ashland Cemetery, built furnaces, served as vice-president of the Ashland National Bank, and served then led the growing iron business of the Means family. The Kentucky Encyclopedia of 2015 described the Means-owned iron empire as having "created massive enterprises out of the disorganized and weakened industry that emerged from the Civil War."

The Hope Furnace is a historic blast furnace in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Ohio. Located along State Route 278, approximately 5 miles (8.0 km) northeast of the village of Zaleski, it is one of two extant iron furnaces in Vinton County. Between 1854 and 1874, the furnace was used to smelt iron ore, using coal or charcoal for fuel. It is a rectangular structure, built of sandstone and shaped like a truncated pyramid.
Hope is an unincorporated community in Brown Township, Vinton County, Ohio.
Puritan is an unincorporated community in Vinton County, in the U.S. state of Ohio. It is situated to the east of Hamden, Ohio, and to the west of Wilkesville, Ohio, as well as north of Wellston, Ohio.
Richland is a ghost town in Vinton County, in the U.S. state of Ohio. The GNIS classifies it as a populated place.

















