The Antarctic is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole.

The Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands (HIMI) is an Australian external territory comprising a volcanic group of mostly barren Antarctic islands, about two-thirds of the way from Madagascar to Antarctica. The group's overall area is 372 km2 (144 sq mi) and it has 101.9 km (63 mi) of coastline. Discovered in the mid-19th century, the islands lie on the Kerguelen Plateau in the Indian Ocean and have been an Australian territory since 1947.

The history of Antarctica emerges from early Western theories of a vast continent, known as Terra Australis, believed to exist in the far south of the globe. The term Antarctic, referring to the opposite of the Arctic Circle, was coined by Marinus of Tyre in the 2nd century AD.

Peter I Island is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Bellingshausen Sea, 450 kilometres (240 nmi) from continental Antarctica. It is claimed as a dependency of Norway and, along with Bouvet Island and Queen Maud Land, composes one of the three Norwegian dependent territories in the Antarctic and Subantarctic. The island measures approximately 11 by 19 kilometres, with an area of 156 km2 (60 sq mi); its highest point is the ultra-prominent, 1,640-metre-tall (5,380 ft) Lars Christensen Peak. Nearly all the island is covered by a glacier, and it is surrounded most of the year by pack ice, making it inaccessible during these times. There is little vertebrate animal life on the island, apart from some seabirds and seals.

Deception Island is in the South Shetland Islands close to the Antarctic Peninsula with a large and usually "safe" natural harbor, which is occasionally affected by the underlying active volcano. This island is the caldera of an active volcano, which seriously damaged local scientific stations in 1967 and 1969. The island previously held a whaling station. It is now a tourist destination with over 15,000 visitors per year. Two research stations are operated by Argentina and Spain during the summer season. While various countries have asserted sovereignty, it is still administered under the Antarctic Treaty System.

Macquarie Island is an island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, about halfway between New Zealand and Antarctica. Regionally part of Oceania and politically a part of Tasmania, Australia, since 1900, it became a Tasmanian State Reserve in 1978 and was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1997.

Antarctic flora are a distinct community of vascular plants which evolved millions of years ago on the supercontinent of Gondwana. Presently, species of Antarctica flora reside on several now separated areas of the Southern Hemisphere, including southern South America, southernmost Africa, New Zealand, Australia, and New Caledonia. Joseph Dalton Hooker was the first to notice similarities in the flora and speculated that Antarctica had served as either a source or a transitional point, and that land masses now separated might formerly have been adjacent.

The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctica.
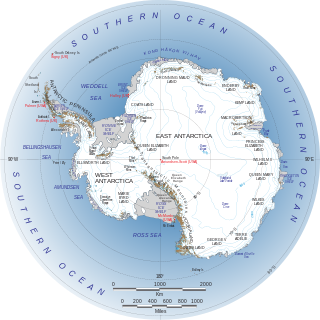
West Antarctica, or Lesser Antarctica, one of the two major regions of Antarctica, is the part of that continent that lies within the Western Hemisphere, and includes the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from East Antarctica by the Transantarctic Mountains and is covered by the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. It lies between the Ross Sea, and the Weddell Sea. It may be considered a giant peninsula, stretching from the South Pole towards the tip of South America.

Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rocks or on ice that are fixed in place.

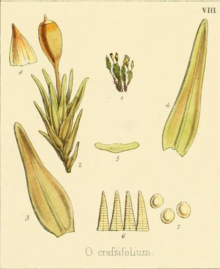
Deschampsia is a genus of plants in the grass family, commonly known as hair grass or tussock grass. The genus is widespread across many countries.
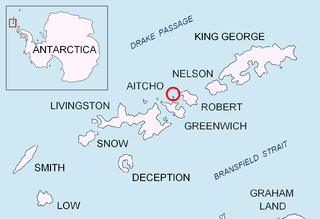
The Aitcho Islands are a group of minor islands on the west side of the north entrance to English Strait separating Greenwich Island and Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, which are situated between Dee Island to the south and Table Island to the north. The group is separated from Dee Island and Sierra Island to the southwest by Villalón Passage. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Clothier Harbour. During the austral summer the islands are often visited by Antarctic cruise ships with tourists who land to watch wildlife.

Coppermine Peninsula is the rugged, rocky promontory forming the northwest extremity of Alfatar Peninsula and Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It lies between the English Strait to the west and Carlota Cove to the east. It is 1.7 km long, 500 m wide and rising to 105 m.
Caughley Beach is the northernmost beach on the ice-free coast south-west of Cape Bird, Ross Island, Antarctica. It was mapped by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1958–59, and named for Graeme Caughley, biologist with the party that visited Cape Bird. New College Valley, Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.116, lies above the beach.

The Guébriant Islands are two islands west of the Antarctic Peninsula, in the northern part of Marguerite Bay, lying 9.3 kilometres (5 nmi) southeast of Cape Alexandra, the southeast cape of Adelaide Island. They were discovered by the fourth French Antarctic Expedition 1908–1910 under Jean-Baptiste Charcot and named by him as "Îlots de Guébriant" after the Reverend Jean Budes de Guébriant, a French Catholic missionary to China.

Harmony Point is a point which lies close west of Harmony Cove and forms both the south side of the entrance to Malak Sechko Cove and the western extremity of Guangzhou Peninsula and Nelson Island, in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It was charted in 1935 by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery II, and named from association with Harmony Cove.

Lagotellerie Island is an island 1.9 kilometres (1 nmi) long, lying 3.7 kilometres (2 nmi) west of Horseshoe Island in Marguerite Bay, off the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered and named by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot.

The Cierva Point and offshore islands Important Bird Area is a 6540 ha tract of land and sea on the Danco Coast of the Antarctic Peninsula.

The wildlife of Antarctica are extremophiles, having adapted to the dryness, low temperatures, and high exposure common in Antarctica. The extreme weather of the interior contrasts to the relatively mild conditions on the Antarctic Peninsula and the subantarctic islands, which have warmer temperatures and more liquid water. Much of the ocean around the mainland is covered by sea ice. The oceans themselves are a more stable environment for life, both in the water column and on the seabed.