In chemistry, hydronium is the cation [H3O]+, also written as H3O+, the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid is dissolved in water, as Arrhenius acid molecules in solution give up a proton to the surrounding water molecules. In fact, acids must be surrounded by more than a single water molecule in order to ionize, yielding aqueous H+ and conjugate base.

In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds.
In chemistry, an oxonium ion is any cation containing an oxygen atom that has three bonds and 1+ formal charge. The simplest oxonium ion is the hydronium ion.

In organic chemistry, crown ethers are cyclic chemical compounds that consist of a ring containing several ether groups (R−O−R’). The most common crown ethers are cyclic oligomers of ethylene oxide, the repeating unit being ethyleneoxy, i.e., −CH2CH2O−. Important members of this series are the tetramer (n = 4), the pentamer (n = 5), and the hexamer (n = 6). The term "crown" refers to the resemblance between the structure of a crown ether bound to a cation, and a crown sitting on a person's head. The first number in a crown ether's name refers to the number of atoms in the cycle, and the second number refers to the number of those atoms that are oxygen. Crown ethers are much broader than the oligomers of ethylene oxide; an important group are derived from catechol.
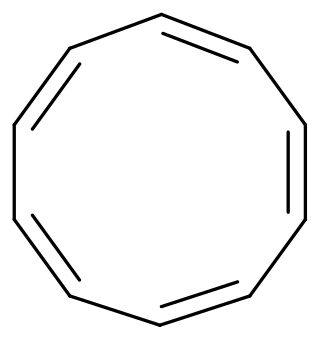
Cyclodecapentaene or [10]annulene is an annulene with molecular formula C10H10. This organic compound is a conjugated 10 pi electron cyclic system and according to Huckel's rule it should display aromaticity. It is not aromatic, however, because various types of ring strain destabilize an all-planar geometry.
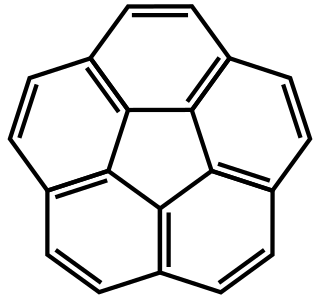
Corannulene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C20H10. The molecule consists of a cyclopentane ring fused with 5 benzene rings, so another name for it is [5]circulene. It is of scientific interest because it is a geodesic polyarene and can be considered a fragment of buckminsterfullerene. Due to this connection and also its bowl shape, corannulene is also known as a buckybowl. Buckybowls are fragments of buckyballs. Corannulene exhibits a bowl-to-bowl inversion with an inversion barrier of 10.2 kcal/mol (42.7 kJ/mol) at −64 °C.
Cycloheptatriene (CHT) is an organic compound with the formula C7H8. It is a closed ring of seven carbon atoms joined by three double bonds (as the name implies) and four single bonds. This colourless liquid has been of recurring theoretical interest in organic chemistry. It is a ligand in organometallic chemistry and a building block in organic synthesis. Cycloheptatriene is not aromatic, as reflected by the nonplanarity of the methylene bridge (-CH2-) with respect to the other atoms; however the related tropylium cation is.

A carbenium ion is a positive ion with the structure RR′R″C+, that is, a chemical species with carbon atom having three covalent bonds, and it bears a +1 formal charge. Carbenium ions are a major subset of carbocations, which is a general term for diamagnetic carbon-based cations. In parallel with carbenium ions is another subset of carbocations, the carbonium ions with the formula R5+. In carbenium ions charge is localized. They are isoelectronic with monoboranes such as B(CH3)3.

In chemistry, a carbonium ion is a cation that has a pentacoordinated carbon atom. They are a type of carbocation. In older literature, the name "carbonium ion" was used for what is today called carbenium. Carbonium ions charge is delocalized in three-center, two-electron bonds. The more stable members are often bi- or polycyclic.

In organic chemistry, the term 2-norbornyl cation describes a carbonium ionic derivative of norbornane. A salt of the 2-norbornyl cation was crystallized and characterized by X-ray crystallography confirmed the non-classical structure.

The Prins reaction is an organic reaction consisting of an electrophilic addition of an aldehyde or ketone to an alkene or alkyne followed by capture of a nucleophile or elimination of an H+ ion. The outcome of the reaction depends on reaction conditions. With water and a protic acid such as sulfuric acid as the reaction medium and formaldehyde the reaction product is a 1,3-diol (3). When water is absent, the cationic intermediate loses a proton to give an allylic alcohol (4). With an excess of formaldehyde and a low reaction temperature the reaction product is a dioxane (5). When water is replaced by acetic acid the corresponding esters are formed.
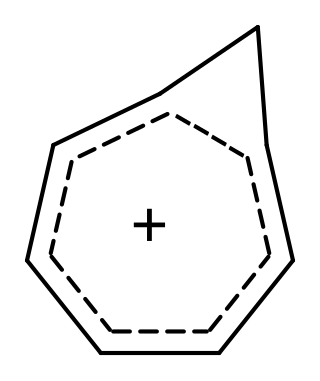
Homoaromaticity, in organic chemistry, refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.

Maitotoxin (MTX) is an extremely potent biotoxin produced by Gambierdiscus toxicus, a dinoflagellate species. Maitotoxin has been shown to be more than one hundred thousand times as potent as VX nerve agent. Maitotoxin is so potent that it has been demonstrated that an intraperitoneal injection of 130 ng/kg was lethal in mice. Maitotoxin was named from the ciguateric fish Ctenochaetus striatus—called "maito" in Tahiti—from which maitotoxin was isolated for the first time. It was later shown that maitotoxin is actually produced by the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus.

A halonium ion is any onium ion containing a halogen atom carrying a positive charge. This cation has the general structure R−+X−R′ where X is any halogen and no restrictions on R, this structure can be cyclic or an open chain molecular structure. Halonium ions formed from fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine are called fluoronium, chloronium, bromonium, and iodonium, respectively. The 3-membered cyclic variety commonly proposed as intermediates in electrophilic halogenation may be called haliranium ions, using the Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature system.

Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is the organic oxonium compound with the formula [(CH3CH2)3O]+[BF4]−. It is often called Meerwein's reagent or Meerwein's salt after its discoverer Hans Meerwein. Also well known and commercially available is the related trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate. The compounds are white solids that dissolve in polar organic solvents. They are strong alkylating agents. Aside from the BF−4 salt, many related derivatives are available.
The Blanc chloromethylation is the chemical reaction of aromatic rings with formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride to form chloromethyl arenes. The reaction is catalyzed by Lewis acids such as zinc chloride. The reaction was discovered by Gustave Louis Blanc (1872-1927) in 1923.
In organic and physical organic chemistry, Clar's rule is an empirical rule that relates the chemical stability of a molecule with its aromaticity. It was introduced in 1972 by the Austrian organic chemist Erich Clar in his book The Aromatic Sextet. The rule states that given a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, the resonance structure most important to characterize its properties is that with the largest number of aromatic π-sextets i.e. benzene-like moieties.
Saul Winstein was a Jewish Canadian chemist who discovered the Winstein reaction. He argued a non-classical cation was needed to explain the stability of the norbornyl cation. This fueled a debate with Herbert C. Brown over the existence of σ-delocalized carbocations. Winstein also first proposed the concept of an intimate ion pair. He was co-author of the Grunwald–Winstein equation, concerning solvolysis rates.
Oxatriquinane (oxoniaperhydrotriquinacene) is an alkyl oxonium ion with formula (CH2CH2CH)3O+. It has a cyclononane backbone, with a tricoordinated oxygen connected to carbon 1, 4, and 7, forming three fused pentagonal rings. In contrast to most trialkyloxonium ions, oxatriquinane hydrolyzes slowly.
Hydrogen-bridged cations are a type of charged species in which a hydrogen atom is simultaneously bonded to two atoms through partial sigma bonds. While best observable in the presence of superacids at room temperature, spectroscopic evidence has suggested that hydrogen-bridged cations exist in ordinary solvents. These ions have been the subject of debate as they constitute a type of charged species of uncertain electronic structure.












