Protease, serine, 2 (trypsin 2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRSS2 gene. [5]
Protease, serine, 2 (trypsin 2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRSS2 gene. [5]
This gene encodes a trypsinogen, which is a member of the trypsin family of serine proteases. This enzyme is secreted by the pancreas and cleaved to its active form in the small intestine. It is active on peptide linkages involving the carboxyl group of lysine or arginine. This gene and several other trypsinogen genes are localized to the T cell receptor beta locus on chromosome 7. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008].

Trypsin is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the digestive system of many vertebrates, where it hydrolyzes proteins. Trypsin is formed in the small intestine when its proenzyme form, the trypsinogen produced by the pancreas, is activated. Trypsin cuts peptide chains mainly at the carboxyl side of the amino acids lysine or arginine. It is used for numerous biotechnological processes. The process is commonly referred to as trypsin proteolysis or trypsinisation, and proteins that have been digested/treated with trypsin are said to have been trypsinized. Trypsin was discovered in 1876 by Wilhelm Kühne and was named from the Ancient Greek word for rubbing since it was first isolated by rubbing the pancreas with glycerin.
Trypsinogen is the precursor form of trypsin, a digestive enzyme. It is produced by the pancreas and found in pancreatic juice, along with amylase, lipase, and chymotrypsinogen. It is cleaved to its active form, trypsin, by enteropeptidase, which is found in the intestinal mucosa. Once activated, the trypsin can cleave more trypsinogen into trypsin, a process called autoactivation. Trypsin cleaves the peptide bond on the carboxyl side of basic amino acids such as arginine and lysine.
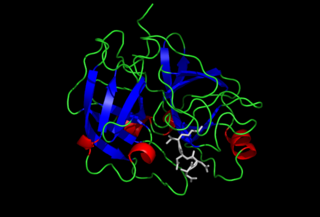
Enteropeptidase is an enzyme produced by cells of the duodenum and is involved in digestion in humans and other animals. Enteropeptidase converts trypsinogen into its active form trypsin, resulting in the subsequent activation of pancreatic digestive enzymes. Absence of enteropeptidase results in intestinal digestion impairment.
A trypsin inhibitor (TI) is a protein and a type of serine protease inhibitor (serpin) that reduces the biological activity of trypsin by controlling the activation and catalytic reactions of proteins. Trypsin is an enzyme involved in the breakdown of many different proteins, primarily as part of digestion in humans and other animals such as monogastrics and young ruminants. When trypsin inhibitor is consumed it acts as an irreversible and competitive substrate.

Hereditary pancreatitis (HP) is an inflammation of the pancreas due to genetic causes. It was first described in 1952 by Comfort and Steinberg but it was not until 1996 that Whitcomb et al isolated the first responsible mutation in the trypsinogen gene (PRSS1) on the long arm of chromosome seven (7q35).

Trypsin-1, also known as cationic trypsinogen, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRSS1 gene. Trypsin-1 is the main isoform of trypsinogen secreted by pancreas, the others are trypsin-2, and trypsin-3 (meso-trypsinogen).

Pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor (PSTI) also known as serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 1 (SPINK1) or tumor-associated trypsin inhibitor (TATI) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPINK1 gene.

Kallikrein-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLK6 gene.

Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 2 is an enzyme inhibitor that in humans is encoded by the SPINT2 gene. SPINT2 is a transmembrane protein with two extracellular Kunitz domains to inhibit serine proteases. This gene is a presumed tumor suppressor by inhibiting HGF activator which prevents the formation of active hepatocyte growth factor. Mutations in SPINT2 could result in congenital sodium diarrhea (CSD).
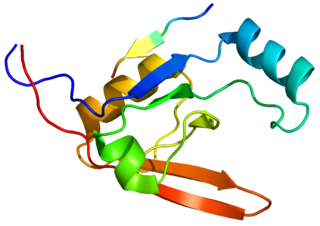
Serine protease HTRA1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HTRA1 gene. The HTRA1 protein is composed of four distinct protein domains. They are from amino-terminus to carboxyl-terminus an Insulin-like growth factor binding domain, a kazal domain, a trypsin-like peptidase domain and a PDZ domain.

Kallikrein-related peptidase 4 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the KLK4 gene.

Kallikrein-11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLK11 gene.
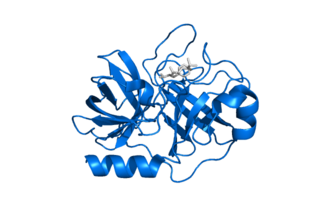
Kallikrein-related peptidase 7 (KLK7) is a serine protease that in humans is encoded by the KLK7 gene. KLK7 was initially purified from the epidermis and characterised as stratum corneum chymotryptic enzyme (SCCE). It was later identified as the seventh member of the human kallikrein family, which includes fifteen homologous serine proteases located on chromosome 19 (19q13).

Prostasin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRSS8 gene.

Chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 3B also known as elastase-3B, protease E, or fecal elastase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CELA3B gene.

Chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 3A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CELA3A gene.

Chymotrypsin-like elastase family member 1 (CELA1) also known as elastase-1 (ELA1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CELA1 gene. Elastases form a subfamily of serine proteases that hydrolyze many proteins in addition to elastin. Humans have six elastase genes which encode the structurally similar proteins elastase 1, 2, 2A, 2B, 3A, and 3B.

Brain-specific serine protease 4 (BSSP-4), also known as serine protease 22 or tryptase epsilon, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRSS22 gene.

Putative serine protease 56 (PRSS56) is a serine protease that in humans is encoded by the PRSS56 gene. This protein has been implicated in human eye development.

Protease, serine, 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRSS3 gene.
|journal= (help)This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
| This article on a gene on human chromosome 9 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |