Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell. Proteins can be targeted to the inner space of an organelle, different intracellular membranes, the plasma membrane, or to the exterior of the cell via secretion. Information contained in the protein itself directs this delivery process. Correct sorting is crucial for the cell; errors have been linked to multiple disease-states.
Protein subcellular localization prediction involves the prediction of where a protein resides in a cell, its subcellular localization.
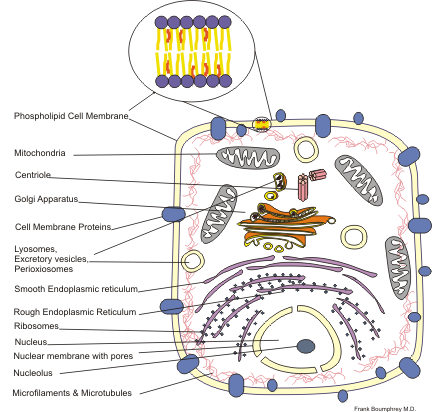
The cells of eukaryotic organisms are elaborately subdivided into functionally-distinct membrane-bound compartments. Some major constituents of eukaryotic cells are: extracellular space, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), peroxisome, vacuoles, cytoskeleton, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, nuclear matrix and ribosomes.
KIAA0090 is a human gene coding for a protein of unknown function. KIAA0090 has two aliases OTTHUMP00000002581 and RP1-43E13.1. The gene codes for multiple transcript variants which can localize to different subcellular compartments. KIAA0090 interacts with multiple effector proteins. KIAA0090 contains a conserved COG1520 WD40 like repeat domain thought to be the method of such interaction.

PSORTdb is a database of protein subcellular localization (SCL) for bacteria and archaea. It is a member of the PSORT family of bioinformatics tools. The database consists of two datasets, ePSORTdb and cPSORTdb, which contain information determined through experimental validation and computational prediction, respectively. The ePSORTdb dataset is the largest curated collection of experimentally verified SCL data.
Secretomics is a type of proteomics which involves the analysis of the secretome—all the secreted proteins of a cell, tissue or organism. Secreted proteins are involved in a variety of physiological processes, including cell signaling and matrix remodeling, but are also integral to invasion and metastasis of malignant cells. Secretomics has thus been especially important in the discovery of biomarkers for cancer and understanding molecular basis of pathogenesis. The analysis of the insoluble fraction of the secretome has been termed matrisomics.

CXorf26, also known as MGC874, is a well conserved human gene found on the plus strand of the short arm of the X chromosome. The exact function of the gene is poorly understood, but the polysaccharide biosynthesis domain that spans a major portion of the protein product, as well as the yeast homolog, YPL225, offer insights into its possible function.

TMEM106A is a gene that encodes the transmembrane protein 106A (TMEM106A) in Homo sapiens. It is located at 17q21.31 on the plus strand next to cancer-related genes NBR1 and BRCA1. The TMEM106A gene contains a domain of unknown function, DUF1356.
A target peptide is a short peptide chain that directs the transport of a protein to a specific region in the cell, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), chloroplast, apoplast, peroxisome and plasma membrane. Some target peptides are cleaved from the protein by signal peptidases after the proteins are transported.

Protein FAM214A, also known as protein family with sequence similarity 214, A (FAM214A) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the FAM214A gene. FAM214A is a gene with unknown function found at the q21.2-q21.3 locus on Chromosome 15 (human). The protein product of this gene has two conserved domains, one of unknown function (DUF4210) and another one called Chromosome_Seg. Although the function of the FAM214A protein is uncharacterized, both DUF4210 and Chromosome_Seg have been predicted to play a role in chromosome segregation during meiosis.
Proteome Analyst (PA) is a freely available web server and online toolkit for predicting protein subcellular localization, or where a protein resides in a cell. In the field of proteomics, accurately predicting a protein’s subcellular localization, or where a specific protein is located inside a cell, is an important step in the large scale study of proteins. This computational prediction problem is known as Protein subcellular localization prediction. Over the last decade, more than a dozen web servers and computer programs have been developed to attempt to solve this problem. Proteome Analyst is an example of one of the better performing subcellular prediction tools. Proteome Analyst makes predictions for both prokaryotic eukaryotic proteins using a text mining approach. Proteome Analyst was originally developed by the Proteome Analyst Research Group at the University of Alberta, and was initially released on March 2004. It was recently updated on January 2014.

C3orf70 also known as Chromosome 3 Open Reading Frame 70, is a 250aa protein in humans that is encoded by the C3orf70 gene. The protein encoded is predicted to be a nuclear protein; however, its exact function is currently unknown. C3orf70 can be identified with known aliases: Chromosome 3 Open Reading Frame 70, AK091454, UPF0524, and LOC285382.

C8orf48 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C8orf48 gene. C8orf48 is a nuclear protein specifically predicted to be located in the nuclear lamina. C8orf48 has been found to interact with proteins that are involved in the regulation of various cellular responses like gene expression, protein secretion, cell proliferation, and inflammatory responses. This protein has been linked to breast cancer and papillary thyroid carcinoma.

GRAM domain containing 1B, also known as GRAMD1B, Aster-B and KIAA1201, is a protein that is encoded by the GRAMD1B gene. It contains a transmembrane region and two domains of known function; the GRAM domain and a VASt domain. It is predicted to localize in the nucleus, supported by several nuclear transport signals and nuclearly associated motifs. This highly conserved gene is found in a variety of vertebrates and invertebrates, however is not found in bacteria or fungi.

KIAA0825 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene of the same name, located on chromosome 5, 5q15. It is a possible risk factor in Type II Diabetes, and associated with high levels of glucose in the blood. It is a relatively fast mutating gene, compared to other coding genes. There is however one region which is highly conserved across the species that have the gene, known as DUF4495. It is predicted to travel between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Chromosome 19 open reading frame 18 (c19orf18) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the c19orf18 gene. The gene is exclusive to mammals and the protein is predicted to have a transmembrane domain and a coiled coil stretch. This protein has a function that is not yet fully understood by the scientific community.

Chromosome 18 open reading frame 63 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the C18orf63 gene. This protein is not yet well understood by the scientific community. Research has been conducted suggesting that C18orf63 could be a potential biomarker for early stage pancreatic cancer and breast cancer.
LOC100287387 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene LOC100287387. The function of the protein is not yet understood in the scientific community. The gene is located on the q arm of chromosome 2.

SH3 Domain Binding Kinase Family Member 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SBK3 gene. SBK3 is a member of the serine/threonine protein kinase family. The SBK3 protein is known to exhibit transferase activity, especially phosphotransferase activity, and tyrosine kinase activity. It is well-conserved throughout mammalian organisms and has two paralogs: SBK1 and SBK2.