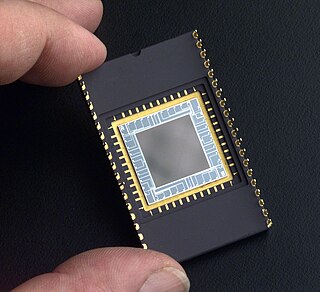
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging.

A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices like smartphones with the same or more capabilities and features of dedicated cameras. High-end, high-definition dedicated cameras are still commonly used by professionals and those who desire to take higher-quality photographs.
DV is a family of codecs and tape formats used for storing digital video, launched in 1995 by a consortium of video camera manufacturers led by Sony and Panasonic. It includes the recording or cassette formats DV, MiniDV, DVCAM, Digital8, HDV, DVCPro, DVCPro50 and DVCProHD. DV has been used primarily for video recording with camcorders in the amateur and professional sectors.

Digital8 is a consumer digital recording videocassette for camcorders developed by Sony, and introduced in 1999. It is technically identical to DV cassettes, but uses physical Hi8 tapes instead.

A camcorder is a self-contained portable electronic device with video and recording as its primary function. It is typically equipped with an articulating screen mounted on the left side, a belt to facilitate holding on the right side, hot-swappable battery facing towards the user, hot-swappable recording media, and an internally contained quiet optical zoom lens.

A digital camera back is a device that attaches to the back of a camera in place of the traditional negative film holder and contains an electronic image sensor. This allows cameras that were designed to use film take digital photographs. These camera backs are generally expensive by consumer standards and are primarily built to be attached on medium- and large-format cameras used by professional photographers.

HDV is a format for recording of high-definition video on DV videocassette tape. The format was originally developed by JVC and supported by Sony, Canon, and Sharp. The four companies formed the HDV Consortium in September 2003.

Sadie T. Benning is an American artist, who has worked primarily in video, painting, drawing, sculpture, photography and sound. Benning creates experimental films and explores a variety of themes including surveillance, gender, ambiguity, transgression, play, intimacy, and identity. They became a known artist as a teenager, with their short films made with a PixelVision camera that have been described as "video diaries".

A digital single-lens reflex camera is a digital camera that combines the optics and mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a solid-state image sensor and digitally records the images from the sensor.

Digital cinematography is the process of capturing (recording) a motion picture using digital image sensors rather than through film stock. As digital technology has improved in recent years, this practice has become dominant. Since the 2000s, most movies across the world have been captured as well as distributed digitally.

Mattes are used in photography and special effects filmmaking to combine two or more image elements into a single, final image. Usually, mattes are used to combine a foreground image with a background image. In this case, the matte is the background painting. In film and stage, mattes can be physically huge sections of painted canvas, portraying large scenic expanses of landscapes.

A three-CCD (3CCD) camera is a camera whose imaging system uses three separate charge-coupled devices (CCDs), each one receiving filtered red, green, or blue color ranges. Light coming in from the lens is split by a beam-splitter prism into three beams, which are then filtered to produce colored light in three color ranges or "bands". The system is employed by high quality still cameras, telecine systems, professional video cameras and some prosumer video cameras.

Digital photography uses cameras containing arrays of electronic photodetectors interfaced to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to produce images focused by a lens, as opposed to an exposure on photographic film. The digitized image is stored as a computer file ready for further digital processing, viewing, electronic publishing, or digital printing. It is a form of digital imaging based on gathering visible light.

Sony Corporation produces professional, consumer, and prosumer camcorders such as studio and broadcast, digital cinema cameras, camcorders, pan-tilt-zoom and remote cameras.

The Mattel Vidster is a digital tapeless camcorder that was marketed as a children's toy and sold around 2005. It features a 1.1-inch (28 mm) LCD display, a 2x digital zoom, and records into AVI 320x240 video files encoded with the M-JPEG codec at 15 frames per second, with 22 kHz monaural sound. It also takes still photos with 1.3 megapixel resolution.

The Panasonic AG-DVX100 was a video camera that released in October 2002. Its 60Hz version was the first consumer-affordable digital camcorder capable of recording video at 24 progressive frames per second.
Another Girl Another Planet is a 1992 film written and directed by Michael Almereyda. The film is notable for being shot on a Fisher-Price PXL 2000 children's camera.

Gerry Fialka is an American experimental filmmaker, curator, lecturer, interviewer, and writer. He lectures and leads workshops on experimental film, avant-garde music and art, subversive social media, books by James Joyce, and Marshall McLuhan’s media theory. He was Frank Zappa’s archivist and production assistant for ten years, and also worked for George Carlin. LA Weekly has described Fialka as a “cultural revolutionary”.