Related Research Articles

The Oghuz Turks were a western Turkic people who spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conventionally named the Oghuz Yabgu State in Central Asia. Today, much of the populations of Turkey, Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan are descendants of Oghuz Turks. Byzantine sources call them Uzes. The term Oghuz was gradually supplanted by the terms Turkmen and Turcoman by 13th century.

The Qara Qoyunlu or Kara Koyunlu, also known as the Black Sheep Turkomans, were a culturally Persianate, Muslim Turkoman monarchy that ruled over the territory comprising present-day Azerbaijan, Armenia, northwestern Iran, eastern Turkey, and northeastern Iraq from about 1374 to 1468.

Agsu District is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the east of the country, in the Mountainous Shirvan Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Ismayilli, Shamakhi, Kurdamir, and Hajigabul. Its capital and largest city is Agsu. As of 2020, the district had a population of 81,000.

Shamakhi District is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the east of the country and belongs to the Mountainous Shirvan Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Quba, Khizi, Gobustan, Hajigabul, Agsu, and Ismayilli. Its capital and largest city is Shamakhi. As of 2020, the district had a population of 106,400.

Qizilbash or Kizilbash were a diverse array of mainly Turkoman Shia militant groups that flourished in Azerbaijan, Anatolia, the Armenian highlands, the Caucasus, and Kurdistan from the late 15th century onwards, and contributed to the foundation of the Safavid dynasty in early modern Iran.

The Book of Dede Korkut or Book of Korkut Ata is the most famous among the dastans or epic stories of the Oghuz Turks. The stories carry morals and values significant to the social lifestyle of the nomadic Turkic peoples and their pre-Islamic beliefs. The book's mythic narrative is part of the cultural heritage of the peoples of Oghuz origin, mainly of Azerbaijan, Turkey and Turkmenistan. Only two manuscripts of the text, one in the Vatican and one in Dresden, Germany. were known before a third manuscript was discovered in a private collection in Gonbad-e Kavus, Iran, in 2018.

Oğuz is a city, municipality and the capital of the Oghuz District of Azerbaijan. The village was populated by Armenians and Udis before the exodus of Armenians from Azerbaijan after the outbreak of the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict.

Shamakhi is a city in Azerbaijan and the administrative centre of the Shamakhi District. The city's estimated population as of 2010 was 31,704. It is famous for its traditional dancers, the Shamakhi Dancers, and also for perhaps giving its name to the Soumak rugs.

Khinalug or Khinalyg, is a municipality and an ancient Caucasian village with origins dating back to the Caucasian Albanian period. It is located high up in the mountains of Quba District, Azerbaijan. The municipality of Khinalug is part of the Quba District and consists of the villages of Khinalug and Galaykhudat. The village was included in the Cultural Landscape of Khinalig People and "Köç Yolu" Transhumance Route UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2023.

The Karapapakhs, or Terekeme, are a Turkic people, who originally spoke the Karapapakh language, a western Oghuz language closely related to Azerbaijani and Turkish. Nowadays, the Karapapakh language has been largely supplanted by Azerbaijani and Turkish.
Azerbaijanis in Russia or Russian Azerbaijanis are people of Azeri descent in Russia. These may be either ethnic Azeris residents in the country or recent immigrants who profess Azeri ancestry.

The Aq Qoyunlu or the White Sheep Turkomans was a culturally Persianate, Sunni Turkoman tribal confederation. Founded in the Diyarbakir region by Qara Yuluk Uthman Beg, they ruled parts of present-day eastern Turkey from 1378 to 1503, and in their last decades also ruled Armenia, Azerbaijan, much of Iran, Iraq, and Oman where the ruler of Hormuz recognised Aq Qoyunlu suzerainty. The Aq Qoyunlu empire reached its zenith under Uzun Hasan.
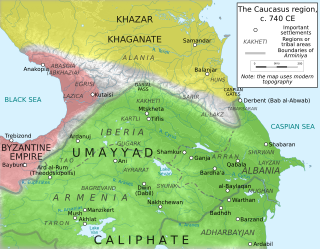
Arabs first established themselves in the Caucasus in the eighth century, during the Arab conquest of Persia. The process of shrinking of the Abbasid Caliphate in the tenth century was followed by the establishment of several Arab-ruled principalities in the region, chiefly the principality of Shirvan ruled by the Mazyadid dynasty. As the rulers of Shirvan spread their control over much of the Southeast Caucasus and at the same time found themselves more and more isolated from the Arab world, they were undergoing gradual Persianisation. Arab personal names of the Shirvanshahs gave way to Persian ones, members of the ruling dynasty were claiming Ancient Persian descent and Persian gradually became the language of the court and the urban population, while the rural population continued to speak the indigenous languages of Caucasian Albania. However by the seventeenth century a local Turkic idiom became the language of everyday life, as well as the language of interethnic communication.
Armeno-Tats are a distinct group of Christian Tat-speaking Armenians that historically populated eastern parts of the South Caucasus, in what constitutes the modern-day Republic of Azerbaijan. Most scholars researching the Tat language, such as Boris Miller and Igrar Aliyev, agree that Armeno-Tats are ethnic Armenians who underwent a language shift and adopted Tat as their first language. This is explained on one hand by the self-identification of Armeno-Tats who stated during Miller's research that they consider themselves Armenian as well as by some linguistic features of their dialect. The Armeno-Tats formerly lived in Madrasa and Kilvar in Azerbaijan, but have almost entirely moved to Armenia and Russia.

Mountainous Shirvan Economic Region is one of the 14 economic regions of Azerbaijan. It borders the economic regions of Shaki-Zagatala, Guba-Khachmaz, Absheron-Khizi, Shirvan-Salyan, and Central Aran. The region consists of the districts of Agsu, Ismayilli, Gobustan, and Shamakhi. It has an area of 6,130 square kilometres (2,370 sq mi). Its population was estimated to be at 324.8 thousand people in January 2021.
Begdili were an Oghuz Turkic people and a sub-branch of the Bozok tribal federation. Currently, the descendants of Begdili tribe and those who identify themselves as such are part of the Geklen Turkmens living in the Balkan velayat of Turkmenistan. They also can be found among Ersari Turkmens, who live predominantly in the Lebap velayat (region) of Turkmenistan and northern provinces of Afghanistan. Turkish Begdili Turkomans live in Tarsus, Aleppo, and in many parts of Anatolia. Cerit/Ceritli Turkomans are a branch of Begdili tribe.

Turkoman, also known as Turcoman, was a term for the people of Oghuz Turkic origin, widely used during the Middle Ages. Oghuz Turks were a western Turkic people that, in the 8th century A.D, formed a tribal confederation in an area between the Aral and Caspian seas in Central Asia, and spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family.

Armenians have had a longstanding historical presence in the Shamakhi District. From the 16th century up until the 18th century, Armenians formed the majority population of the capital, Shamakhi. Armenians retained a significant presence in the Shamakhi district until the First Nagorno-Karabakh war, which resulted in the forced displacement of the remaining unassimilated Shamakhi Armenians to Armenia.

Azerbaijani nomadic life- refers to the historical and contemporary practice of individuals or groups living a nomadic (tərəkəmə) or semi-nomadic (elat) lifestyle within the cultural environment of Azerbaijan, along with its historical, cultural, and customary aspects. Temporary dwellings used by nomads in Azerbaijan include various types such as "oba, shenlik, sığırxana, yataq, binə, yurd, düşərgə, qışlaq, dəkkə, dəngə, yaylaq, etc". During the summer season, nomadic homes such as "alaçıq, coma, dəyə, muxuru, qarakeçə, dünnüklü ev, kolux, mağardəyə, etc.," are used.
References
- ↑ Swietochowski, Tadeusz; Collins, Brian C. (1999). Historical Dictionary of Azerbaijan. Scarecrow Press. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-8108-3550-4.
- ↑ Mahammadhasan Valili-Baharlu― «"Azerbaijan" (Etnographic ocherk)» Bakı. 1993. Padars.
- ↑ The Voyages and Travells of the Ambassadors Sent by Frederick Duke of Holstein, to the Great Duke of Muscovy, and the King of Persia
- ↑ Olearius, page 299
- ↑ Documentary about Padar tribe (Azerbaijani language)
- ↑ Johannes Albrecht Bernhard Dorn, Mohammedanische Quellen zur Geschichte der südlichen Küstenländer des Kaspischen Meers (St. Petersburg 1850-58, 4 Tle.)
- ↑ Aziza Jafarzadeh, "Abdulla Padarlu", 1979