
Legnica is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River and the Czarna Woda. Between 1 June 1975 and 31 December 1998 Legnica was the capital of the Legnica Voivodeship. It is the seat of the county and since 1992 the city has been the seat of a Diocese. As of 2023, Legnica had a population of 97,300 inhabitants.

Henry II the Pious was Duke of Silesia and High Duke of Poland as well as Duke of South-Greater Poland from 1238 until his death. Between 1238 and 1239 he also served as regent of Sandomierz and Opole–Racibórz. He was the son of Henry the Bearded and a member of the Silesian Piast dynasty. In October 2015, the Roman Catholic Diocese of Legnica opened up his cause for beatification, obtaining him the title of Servant of God.
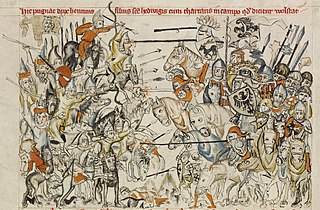
The Battle of Legnica, also known as the Battle of Liegnitz or Battle of Wahlstatt, was a battle between the Mongol Empire and combined European forces that took place at the village of Legnickie Pole (Wahlstatt), approximately 10 kilometres (6 mi) southeast of the city of Legnica in the Duchy of Silesia on 9 April 1241.

Batu Khan was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Golden Horde, a constituent of the Mongol Empire. Batu was a son of Jochi, thus a grandson of Genghis Khan. His ulus ruled over the Kievan Rus', Volga Bulgaria, Cumania, and the Caucasus for around 250 years.

Upper Silesia is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic.

Wenceslaus I, called One-Eyed, was King of Bohemia from 1230 to 1253.

Legnickie Pole is a village in Legnica County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the seat of the administrative district (gmina) called Gmina Legnickie Pole.

From the 1220s into the 1240s, the Mongols conquered the Turkic states of Volga Bulgaria, Cumania and Iranian state of Alania, and various principalities in Eastern Europe. Following this, they began their invasion into Central Europe by launching a two-pronged invasion of then-fragmented Poland, culminating in the Battle of Legnica, and the Kingdom of Hungary, culminating in the Battle of Mohi. Invasions also were launched into the Caucasus against the Kingdom of Georgia and the Chechens and Ingush, as well as into the Southeast Europe against Bulgaria, Croatia, and the Latin Empire. The operations were planned by General Subutai (1175–1248) and commanded by Batu Khan and Kadan, two grandsons of Genghis Khan. Their conquests integrated much of Eastern European territory into the empire of the Golden Horde. Warring European princes realized they had to cooperate in the face of a Mongol invasion, so local wars and conflicts were suspended in parts of central Europe, only to be resumed after the Mongols had withdrawn. After the initial invasions, subsequent raids and punitive expeditions continued into the late 13th century.

The Duchy of Silesia with its capital at Wrocław was a medieval duchy located in the historic Silesian region of Poland. Soon after it was formed under the Piast dynasty in 1138, it fragmented into various Silesian duchies. In 1327, the remaining Duchy of Wrocław as well as most other duchies ruled by the Silesian Piasts passed to the Kingdom of Bohemia as Duchies of Silesia. The acquisition was completed when King Casimir III the Great of Poland renounced his rights to Silesia in the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin.

Kadan was the son of the second Great Khan of the Mongols Ögedei and a concubine. He was the grandson of Genghis Khan and the brother of Güyük Khan. During the Mongol invasion of Europe, Kadan, along with Baidar and Orda Khan, led the Mongol diversionary force that attacked Poland, while the main Mongol force struck the Kingdom of Hungary.

Orda Ichen was a Mongol Khan and military strategist who ruled the eastern part of the Golden Horde during the 13th century.
Boroldai, also known as Burundai, was a notable Mongol general of the mid 13th century. He participated in the Mongol invasion of Russia and Europe in 1236-1242 and other Mongol raids to Europe until 1263.

The Mongol Invasion of Poland from late 1240 to 1241 culminated in the Battle of Legnica, where the Mongols defeated an alliance which included forces from fragmented Poland and their allies, led by Henry II the Pious, the Duke of Silesia. The first invasion's intention was to secure the flank of the main Mongolian army attacking the Kingdom of Hungary. The Mongols neutralized any potential help to King Béla IV being provided by the Poles or any military orders.

Mieszko II the Fat was a Duke of Opole-Racibórz from 1230 until his death, and Duke of Kalisz-Wieluń during 1234–1239.
The Battle of Chmielnik occurred on 18 March 1241 during the Mongol invasion of Poland. It ended in the defeat of the Polish armies of Sandomierz and Kraków provinces. The Mongols were able to move unimpeded, and plunder the abandoned city of Kraków.
The Battle of Tarczek took place on 13 February 1241, during the first Mongol invasion of Poland. It ended in the defeat of the Polish armies of Lesser Poland.
The Battle of Raciborz took place in the Polish town of Raciborz, on 20 March 1241, during the Mongol invasion of Poland. It ended in the victory of a Polish army from Silesia, commanded by Duke of Opole and Raciborz, Mieszko II the Fat.
The Battle of Opole took place in the Polish town of Opole, in early April 1241, during the Mongol invasion of Poland. It ended in the victory of the Mongol forces, who defeated knights from Opole Silesia and Lesser Poland, headed by Duke Wladyslaw Opolski.

The first Mongol invasion of Hungary started in March 1241, and the Mongols started to withdraw in late March 1242.
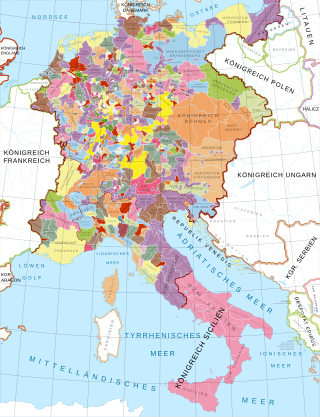
Mongol incursions in the Holy Roman Empire took place in the spring of 1241 and again in the winter of 1241–42. They were part of the first Mongol invasion of Europe.















