
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan, and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Ionic order has the narrowest columns.
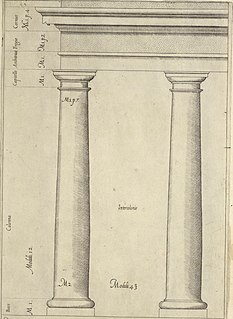
The Tuscan order is one of the two classical orders developed by the Romans, the other being the composite order. It is influenced by the Doric order, but with un-fluted columns and a simpler entablature with no triglyphs or guttae. While relatively simple columns with round capitals had been part of the vernacular architecture of Italy and much of Europe since at least Etruscan architecture, the Romans did not consider this style to be a distinct architectural order. Its classification as a separate formal order is first mentioned in Isidore of Seville's Etymologies and refined during the Italian Renaissance.

The Royal Palace of Madrid is the official residence of the Spanish royal family at the city of Madrid, although now used only for state ceremonies. The palace has 135,000 square metres (1,450,000 sq ft) of floor space and contains 3,418 rooms. It is the largest functioning royal palace and the largest by floor area in Europe.

Juan de Herrera was a Spanish architect, mathematician and geometrician.

The Toledo Museum of Art is an internationally known art museum located in the Old West End neighborhood of Toledo, Ohio. It houses a collection of more than 30,000 objects. With 45 galleries, it covers 280,000 square feet and is currently in the midst of a massive multiyear expansion plan to its 40-acre campus. The museum was founded by Toledo glassmaker Edward Drummond Libbey in 1901, and moved to its current location, a Greek revival building designed by Edward B. Green and Harry W. Wachter, in 1912. The main building was expanded twice, in the 1920s and 1930s. Other buildings were added in the 1990s and 2006. The Museum’s main building consists of 4 1/2 acres of floor space on two levels. Features include fifteen classroom studios, a 1,750-seat Peristyle concert hall, a 176-seat lecture hall, a café and gift shop. The museum averages some 380,000 visitors per year and, in 2010, was voted America’s favorite museum by the readers of the visual arts website Modern Art Notes.

Ventura Rodríguez Tizón was a Spanish architect and artist. Born at Ciempozuelos, Rodríguez was the son of a bricklayer. In 1727, he collaborated with his father in the work at the Royal Palace of Aranjuez.

Villafranca de los Caballeros is a municipality located in the province of Toledo, Castile-La Mancha, Spain. According to the 2006 census (INE), the municipality had a population of 5327 inhabitants.

Francisco Antonio de Lorenzana y Butrón was a Catholic Cardinal, who had also earlier served as Archbishop of Mexico.

The Colegio de Doncellas Nobles is a former girls' school in Toledo. It was founded in 1551 by the archbishop of Toledo and cardinal Juan Martínez Silíceo. The project, which had as its patron the king Philip II as well as the archbishop, had as its object the education of young women to be good mothers. Some came from humble families and others from noble families from all over Europe. They were expected to be of "clean blood". Funding was provided for the dowries of former pupils.

The Palace of Iturbide is a large palatial residence located in the historic center of Mexico City at Madero Street #17. It was built by the Count of San Mateo Valparaíso as a wedding gift for his daughter. It gained the name “Palace of Iturbide” because Agustín de Iturbide lived there and accepted the crown of the First Mexican Empire at the palace after independence from Spain. Today, the restored building houses the Fomento Cultural Banamex; it has been renamed the Palacio de Cultura Banamex.

The Cathedral of Sigüenza, officially Catedral de Santa María de Sigüenza, is the seat of the bishop of Sigüenza, in the town of Sigüenza, in Castile-La Mancha, Spain. It was declared Bien de Interés Cultural in 1931.

The Primate Cathedral of Saint Mary of Toledo, otherwise Toledo Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic church in Toledo, Spain. It is the seat of the Metropolitan Archdiocese of Toledo.

The Archiepiscopal Palace of Alcalá de Henares is a palace located in Alcalá de Henares, in the Community of Madrid, Spain. It is now home to the Diocese of Alcalá de Henares. It is located in the Plaza del Palacio and this form part of the monumental set declared World Heritage Site by UNESCO.
The Palace and Gardens of Panaca, sometimes characterized as the Palácio Palha is a palatial residence in the Santa Engrácia area of the civil parish of São Vicente, in the municipality in the Portuguese capital of Lisbon.

The Museum of Santa Cruz is an art, archaeology and ethnographic museum located in the historic centre of the city of Toledo, Spain. It exhibits collections pertaining to the province of Toledo, including works painted by El Greco in the city of Toledo.

The Palacio Arzobispal de Toledo or Archbishop's Palace of Toledo is a palace located in front of the Cathedral and next to the City Hall in the city of Toledo, region of Castile-La Mancha, Spain.

The Convento de Premonstratenses de San Norberto, also known as Convento de Mostenses or Convento de San Norberto, in reference to the founder of the Premonstratensian Order, for who was dedicated, is a religious building disappeared it was located on the ground of the current Plaza de los Mostenses, next to the Gran Vía of Madrid (Spain). It was founded in 1611 by the community of the Fathers Canons Premonstratensians with the permission of Cardinal Archbishop of Toledo Bernardo de Rojas and financed by a benefactor, the Count of Miranda, Juan of Zúñiga, the then president of the Council of Castile. Today the site of the convent is occupied by a market built in the 19th century, known as Mercado de los Mostenses.

The Hospital de Tavera, also known as the Hospital de San Juan Bautista, Hospital de afuera, or simply as Hospital Tavera, is an important Building of Renaissance style that is in the Spanish city of Toledo. It was built between 1541 and 1603 by order of the Cardinal Tavera. This hospital is dedicated to John the Baptist and also served as pantheon for its patron, Cardinal Tavera. Initially it began to be constructed under the supervision of Alonso de Covarrubias, being succeeded by other architects and finishing the work Bartolomé Bustamante.

The Hospital del Nuncio Nuevo is a Neoclassical hospital located in city of Toledo, in Castile-La Mancha, Spain. It was commissioned by Cardinal Lorenzana at the end of the 18th century. Built to house people with mental illness, it represents an advanced hospital architecture for its time.

The Palacio del Marqués de Malpica is a building in the city of Toledo, Castile-La Mancha, Spain. It's located at the Plaza de Santa Clara and next to the monastery of the same name. It is of Renaissance style and belonged to the Marquis of Malpica y Valdepusa.






















