
The Amu Darya, also called the Amu, the Amo, and historically the Oxus, is a major river in Central Asia, which flows through Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Kush, the Amu Darya is formed by the confluence of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers, in the Tigrovaya Balka Nature Reserve on the border between Afghanistan and Tajikistan, and flows from there north-westwards into the southern remnants of the Aral Sea. In its upper course, the river forms part of Afghanistan's northern border with Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. In ancient history, the river was regarded as the boundary of Greater Iran with Turan, which roughly corresponded to present-day Central Asia. The Amu Darya has a flow of about 70 cubic kilometres per year on average.
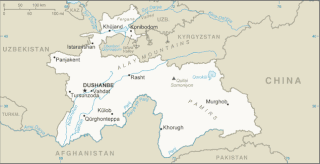
Tajikistan is nestled between Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan to the north and west, China to the east, and Afghanistan to the south. Mountains cover 93 percent of Tajikistan's surface area. The two principal ranges, the Pamir Mountains and the Alay Mountains, give rise to many glacier-fed streams and rivers, which have been used to irrigate farmlands since ancient times. Central Asia's other major mountain range, the Tian Shan, skirts northern Tajikistan. Mountainous terrain separates Tajikistan's two population centers, which are in the lowlands of the southern and northern sections of the country. Especially in areas of intensive agricultural and industrial activity, the Soviet Union's natural resource utilization policies left independent Tajikistan with a legacy of environmental problems.
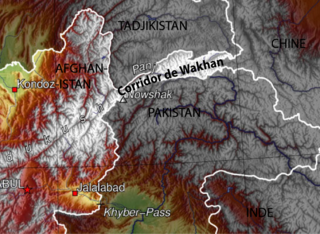
The Wakhan Corridor is a narrow strip of territory located within the Badakhshan province of Afghanistan. This corridor stretches eastward, connecting Afghanistan to Xinjiang, China. It also separates the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region of Tajikistan in the north from northern Pakistan in the south. This high mountain valley serves as the source of both the Panj and Pamir rivers, which converge to form the larger Amu River. For countless centuries, a vital trade route has traversed this valley, facilitating the movement of travelers to and from East, South, and Central Asia.

Khorog is the capital of Gorno-Badakhshan, Tajikistan. It is also the capital of the Shughnon District of Gorno-Badakhshan. It has a population of 30,500.

The Pamir Mountains are a range of mountains between Central Asia and South Asia. They are located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world's highest mountains.

Gorno-Badakhshan, officially the Badakhshan Mountainous Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region in eastern Tajikistan, in the Pamir Mountains. It makes up nearly forty-five percent of the country's land area but only two percent of its population.

Wakhan, or "the Wakhan", is a rugged, mountainous part of the Pamir, Hindu Kush and Karakoram regions of Afghanistan. Wakhan District is a district in Badakshan Province.

The Wakhi people, also locally referred to as the Wokhik, are an Iranian ethnic group native to Central and South Asia. They are found in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Pakistan and China—primarily situated in and around Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor, the northernmost part of Pakistan's Gilgit−Baltistan and Chitral, Tajikistan's Gorno−Badakhshan Autonomous Region and the southwestern areas of China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region. The Wakhi people are native speakers of the Wakhi language, an Eastern Iranian language.
The Pamir languages are an areal group of the Eastern Iranian languages, spoken by numerous people in the Pamir Mountains, primarily along the Panj River and its tributaries.

The Panj, traditionally known as the Ochus River and also known as Pyandzh (derived from its Slavic word, is a river in Afghanistan and Tajikistan and is a tributary of the Amu Darya. The river is 921 kilometres long and has a basin area of 114,000 square kilometres. It forms a considerable part of the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border.

Zorkul is a lake in the Pamir Mountains that runs along the border between the Wakhan District in Badakhshan Province of Afghanistan and the Gorno-Badakhshan autonomous region of Tajikistan. It is part of both the Wakhan National Park of Afghanistan and the Tajik National Park.

The Gunt is a river in the south of Tajikistan, north of the Shughnon Range. It is 296 kilometres (184 mi) long and has a basin area of 13,700 square kilometres (5,300 sq mi). Its source, Lake Yashilkul, is situated at the edge of the Alichur Pamir, a high plateau or pamir at an elevation of 3,720 m. The city of Khorog is located at the confluence of the Gunt with the Panj. See Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region for surrounding area.

The M41, known informally and more commonly as the Pamir Highway, is a road traversing the Pamir Mountains through Afghanistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan with a length of over 1,200 km. It is the only continuous route through the difficult terrain of the mountains and is the main supply route to Tajikistan's Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region. The route has been in use for millennia, as there are a limited number of viable routes through the high Pamir Mountains. The road formed one link of the ancient Silk Road trade route. M41 is the Soviet road number, but it only remains as an official designation in post-Soviet Uzbekistan, as confirmed by official decree. Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan have passed decrees abolishing Soviet numbering of highways and assigning their own national numbering.

The Bartang is a river of Central Asia, and is a tributary to the Panj which itself is a tributary to the Amu Darya. In its upper reaches, it is also known as the Murghab and Aksu; it flows through the Wakhan in Afghanistan, then through the Rushon District of the Gorno-Badakhshan autonomous region, Tajikistan. The river is 528 kilometres (328 mi) long and has a basin area of 24,700 square kilometres (9,500 sq mi).

Murghob District is a district in Tajikistan, occupying the eastern two-thirds of the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region (GBAO). The area of Murghob District is 37,300 km2, covering 26 percent of Tajikistan's soil, but only 0.17% of its population. Murghob District borders on Kyrgyzstan to the north, China to the east, and Afghanistan to the south. The population of Murghob District is 15,900. Its administrative capital is the village Murghob.
Langar is a village in the Wakhan District of Badakhshan Province, in north-eastern Afghanistan. It lies on the river Panj, opposite the larger village of Toqakhona in Tajikistan.

Wakhan River ; known locally as Ab-i-Wakhan or Abe Vâxân, Вахондарё and Vaxondaryo) is the name of the Sarhadd branch of the Panj River along its upper length in the Wakhan District of Badakhshan province of Afghanistan.
The Nicholas Range, known locally as Selselehi-i Koh-i-Wakhan is a range of mountains in the Pamir Mountains on the border of Afghanistan and Tajikistan that crosses the Wakhan in Afghanistan. The range separates the Little Pamir and Great Pamir in the Wakhan. The area is sparsely populated by Wakhi and Kyrgyz.

Zorkul Nature Reserve is a 1,610 km2 (620 sq mi) nature reserve in the south-eastern section of the Gorno-Badakhshan autonomous region of Tajikistan, adjoining the border with the Wakhan National Park of Afghanistan in the Wakhan District of Badakhshan Province. The area was made a zakaznik in 1972 for the conservation of bar-headed geese and upgraded to a full nature reserve in 2000. It has also been identified by BirdLife International as an Important Bird Area (IBA).

The Afghanistan–Tajikistan border is 1,357 km (843 mi) in length and runs from the tripoint with Uzbekistan in the west to the tripoint with China in the east, almost entirely along the Amu Darya, Pyanj and Pamir Rivers, except for the easternmost section along the Wakhan Corridor and divides the Tajik community in two.

















