
Bogotá, officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá during the Spanish Colonial period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the largest cities in the world. The city is administered as the Capital District, as well as the capital of, though not part of, the surrounding department of Cundinamarca. Bogotá is a territorial entity of the first order, with the same administrative status as the departments of Colombia. It is the main political, economic, administrative, industrial, cultural, airport, technological, scientific, healthcare and educational center of the country and northern South America.

Coro is the capital of Falcón State and the second oldest city in Venezuela. It was founded on July 26, 1527, by Juan de Ampíes as Santa Ana de Coro. It was historically known as Neu-Augsburg by the German Welsers, and Coro by the Spanish colonizers and Venezuelans, the city and buildings were built during the Spanish Empire. It is established at the south of the Paraguaná Peninsula in a coastal plain, flanked by the Médanos de Coro National Park to the north and the Sierra de Coro to the south, at a few kilometers from its port in the Caribbean Sea at a point equidistant between the Ensenada de La Vela and Golfete de Coro.

Cúcuta, officially San José de Cúcuta, is a Colombian municipality, capital of the department of Norte de Santander and nucleus of the Metropolitan Area of Cúcuta. The city is located in the homonymous valley, at the foot of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, on the border with Venezuela. It comprises an area of approximately 1119 km2, with an urban area of 64 km2 and a rural area of 1055 km2. The city has a population of 777,106 inhabitants, which makes it the most populous municipality in the department and the sixth most populous municipality in the country. Similarly, its metropolitan area has an approximate population of 1,046,347.

The Museum of Gold is an archaeology museum located in Bogotá, Colombia. It is one of the most visited touristic highlights in the country. The museum receives around 500,000 tourists per year.

San José de Suaita is a former industrial village located about 200 km north of Bogotá in the Department of Santander, Colombia. It became a corregimiento in 1924, by decision of the local council.

Colonia Roma, also called La Roma or simply, Roma, is a district located in the Cuauhtémoc borough of Mexico City just west of the city's historic center, and in fact is no longer a single colonia (neighbourhood) but now two officially defined ones, Roma Norte and Roma Sur, divided by Coahuila street.

The Museo Casa de Moneda is a numismatics museum located in La Candelaria neighborhood of Bogotá, Colombia. It is managed by the Bank of the Republic of Colombia and used to display its numismatic collection that is composed by around 18,600 objects that include artwork, banknotes, bonds, coins, derivatives, medals, negotiable instruments, and printing instruments from various time periods and regions of the world.

Pamplona is a municipality and city in Norte de Santander, Colombia. It is the fifth most populated city and the sixth most populated municipality in the department.

The Casa Natal del General Santander is the birthplace of the Colombian General Francisco de Paula Santander, and is where he lived until the age of 13.

Ciudad Colonial is the historic central neighborhood of the Dominican Republic's capital Santo Domingo. It is the oldest continuously inhabited European-established settlement in the Americas. The area has been declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. It is also known as Zona Colonial or more colloquially as "La Zona".
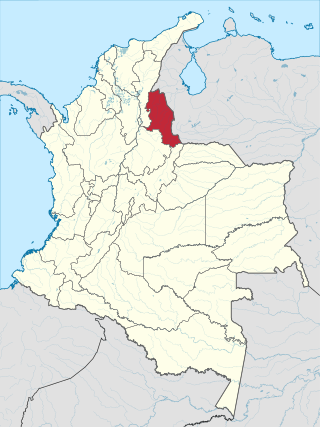
North Santander is a department of Northeastern Colombia. It is in the north of the country, bordering Venezuela. Its capital is Cúcuta, one of the country's major cities.

The Museo Soumaya is a private museum in Mexico City and a non-profit cultural institution with two museum buildings in Mexico City — Plaza Carso and Plaza Loreto. It has over 66,000 works from 30 centuries of art including sculptures from Pre-Hispanic Mesoamerica, 19th- and 20th-century Mexican art and an extensive repertoire of works by European old masters and masters of modern western art such as Auguste Rodin, Salvador Dalí, Bartolomé Esteban Murillo and Tintoretto. It is called one of the most complete collections of its kind.

Centro Cultural Mexiquense is a cultural center located on the western edge of the city of Toluca in central Mexico. The center is run by the State of Mexico government through an agency called the Instituto Mexiquense de Cultura (IMC), the largest and most important of this agency, receiving about 80,000 visitors a year. It contains the Museum of Anthropology and History, the Modern Art Museum and the Museum of Popular Cultures as well as a Central Public Library and the Historical Archives of the State of Mexico, as well as facilities for research.

The Captain Antonio Ricaurte House Museum is a historical museum located in Villa de Leyva, Colombia. The museum is dedicated to show various tools and weapons used in the colonial times of Colombia as well as the history of the country.
The Norte de Santander and City of Cucutá Museum is a museum located in northeastern Colombia. The museum is in charge of exhibiting art and photographs of the department of Norte de Santander. The museum is dedicated to preserving the regional heritage.

The Pumapungo Museum is an ethnographic and art museum in Cuenca, Ecuador.

The Anton Garcia de Bonilla Museum is a museum located in Ocaña, Colombia. The museum contains historical objects of the city and the old province of Ocaña.

The Historical Complex of the Great Convention is a colonial construction located in Ocaña, Colombia. It consists of the temple of San Francisco, the adjacent convent and the square of the Gran Convención. Its construction began in 1584 by the Franciscan religious order. The complex has a museum with historical artifacts. The Historical Complex is a property of cultural interest of national character.

















