Related Research Articles

Gir National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary, also known as Sasan Gir, is a forest, national park, and wildlife sanctuary near Talala Gir in Gujarat, India. It is located 43 km (27 mi) north-east of Somnath, 65 km (40 mi) south-east of Junagadh and 60 km (37 mi) south-west of Amreli. It was established in 1965 in the erstwhile Nawab of Junagarh's private hunting area, with a total area of 1,410.30 km2 (544.52 sq mi), of which 258.71 km2 (99.89 sq mi) is fully protected as a national park and 1,151.59 km2 (444.63 sq mi) as wildlife sanctuary. It is part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests ecoregion.

The Asiatic lion is a population of Panthera leo leo that today survives in the wild only in India. Since the turn of the 20th century, its range has been restricted to Gir National Park and the surrounding areas in the Indian state of Gujarat. The first scientific description of the Asiatic lion was published in 1826 by the Austrian zoologist Johann N. Meyer, who named it Felis leo persicus. Until the 19th century, it occurred in Saudi Arabia, eastern Turkey, Iran, Mesopotamia, and from east of the Indus River in Pakistan to the Bengal region and the Narmada River in Central India.

The Khathiar–Gir dry deciduous forests is a mostly arid ecoregion in northwestern India that stretches over 103,100 sq mi (267,000 km2) across Gujarat, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh. The dry deciduous forests in the region are dominated by teak, and thorny trees and scrub in drier areas.

Dahod district is a district of Gujarat state in western India. This largely tribal district is mostly covered by forests and hills.

Vansda National Park, also known as Bansda National Park, is a protected area which represents the thick woodlands of the Dangs and southern Gujarat, and is situated in the Vansda tehsil, Navsari District of Gujarat state, India. Riding on the banks of Ambika River and measuring roughly 24 km2 in area, the park lies about 65 km east of the town of Chikhali on the National Highway 48, and about 80 km northeast of the city of Valsad. Vansda, the town from which the name of the park is derived, is an important trading place for the surrounding area where the majority of the population is represented by adivasis. Vansda-Waghai state highway runs through the park, so does the narrow gauge rail link connecting Waghai to Billimora.

The Indian Wild Ass Sanctuary, or Wild Ass Wildlife Sanctuary, is located in the Little Rann of Kutch in the state of Gujarat, India, spread over an area of 4954 km².
Kuno National Park is a national park and Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh, India. It derives its name from Kuno River. It was established in 1981 as a wildlife sanctuary with an initial area of 344.686 km2 (133.084 sq mi) in the Sheopur and Morena districts. In 2018, it was given the status of a national park. It is part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests ecoregion.

The Asiatic Lion Reintroduction Project is an initiative of the Indian Government to provide safeguards to the Asiatic lion from extinction in the wild by means of reintroduction. The last wild population of the Asiatic lion is found in the region of Gir Forest National Park, in the state of Gujarat. The single population faces the threats of epidemics, natural disasters and other anthropogenic factors. The project aims to establish a second independent population of Asiatic lions at the Kuno National Park in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. However, the proposed translocation has been bitterly contested by the state government.
India is home to a large variety of wildlife. It is a biodiversity hotspot with various ecosystems ranging from the Himalayas in the north to the evergreen rainforests in the south, the sands of the west to the marshy mangroves of the east. India lies within the Indomalayan realm and is home to about 7.6% of mammal, 14.7% of amphibian, 6% of bird, 6.2% of reptilian, and 6.2% of flowering plant species. India's forests contain about 500 species of mammals and more than 1300 bird species.

More than 70 years after India's native subspecies of the cheetah—the Asiatic cheetah —became extinct there, small numbers of Southeast African cheetah have been flown in from Namibia and South Africa to a national park in India. The experiment has been permitted by India's supreme court on a short-term basis to test long-term adaptation. The Asiatic subspecies is now found only in Iran in critically endangered numbers.

Narayan Sarovar Sanctuary also popularly known as Narayan Sarovar Wildlife Sanctuary or Narayan Sarovar Chinkara Sanctuary notified as such in April 1981 and subsequently denotified in 1995 with reduced area, is a unique eco-system near Narayan Sarovar in the Lakhpat taluka of Kutch district in the state of Gujarat, India. The desert forest in this sanctuary is said to be the only one of its kind in India. Located in the arid zone, a part of it is a seasonal wetland. It has 15 threatened wildlife species and has desert vegetation comprising thorn and scrub forests. Its biodiversity has some rare animals and birds, and rare flowering plants. Wildlife Institute of India (WII) has identified it as one of the last remaining habitats of the cheetah in India and a possible reintroduction site for the species. The most sighted animal here is the chinkara, which is currently the flagship species of the sanctuary.

Kutch Bustard Sanctuary or Kachchh Great Indian Bustard Sanctuary, also known as Lala–Parjan Sanctuary, is located near Jakhau village in Taluka Abdasa, Gujarat, India. This sanctuary is one of the two great Indian bustard sanctuaries in Gujarat; the other one is in Jamnagar. It was declared as a sanctuary in July 1992, specifically for the conservation of the great Indian bustard, the heaviest flying bird belonging to the avian family of Otididae. However, the sanctuary presently legally covers a protected area of about 2 square kilometres (0.77 sq mi) of area (202.86 hectares of fenced land only and is the smallest sanctuary in the country. Several suggestions have been made to vastly increase the size of this sanctuary as it is a breeding ground of the endangered great Indian bustard. The reason is that its ecological zone is much larger on account of anthropogenic and cattle population pressure that are considered as a ‘biotic threat’ to this omnivorous species.

Parishan Lake is a lake in Iran. The Parishan Lake is in Jereh and Baladeh District in Fars Province and is the largest freshwater lake in the country. It receives very small amount of water from feeder rivers and the whole lake or wetland is a protected area, as it is considered a globally significant wetland ecosystem. Another lake in this area is that of Arzhan. The whole protected area is called "Arzhan National Park." This area is an important sanctuary for birds.
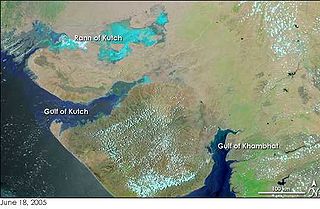
The Gulf of Khambhat, also known as the Gulf of Cambay, is a bay on the Arabian Sea coast of India, bordering the state of Gujarat just north of Mumbai and Diu Island. The Gulf of Khambhat is about 200 km (120 mi) long, about 20 km (12 mi) wide in the north and up to 70 km (43 mi) wide in the south. Major rivers draining Gujarat are the Narmada, Tapti, Mahi and the Sabarmati, that form estuaries in the gulf.
Bhavnagar Amreli Forest is a reserved area for conservation of Asiatic lions. The new location is east side of Gir National Park in Amreli district of Gujarat. After inclusion of New Jesal sanctuary the area of this forest will go to 1600 km2 which is bigger than Gir sanctuary. The Gujarat state government insisted on shifting the lions to this forest claiming that lions were pride of Gujarat. However the central government is pressuring Gujarat state government to shift some lions in Kuno Wildlife Sanctuary. There are almost 110 lions outside the protected area in Gir forest. A pride of about 20 lions will be introduced in three different area in this forest. A large number of lions have been wiped out of Tanzania's Serengeti National Park. To prevent this from happing at Gir forest, Gujarat state government has proposed this habitat.

Purna Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary in the Western Ghats mountain range, in the States of Gujarat and Maharashtra, India. In the South Gujarat, it is located between Vyara, Tapi District and Ahwa, Dang District, and in Maharashtra, it is located in Nandurbar District. Apart from the Dangs' District, it is a part of the Northern Division of the Dangs' Forest.
The fauna of Gujarat, a state in Western India, encompasses a range of ecosystems, including coastal areas along the Arabian Sea, the semi-arid forests on the Kathiawar Peninsula, and the arid salt flats of the Rann of Kutch.
Hingolgadh Nature Education Sanctuary is a protected area located in the Jasdan Taluka of Rajkot district, Gujarat, India. Managed by the Gujarat Ecological Education and Research (GEER) Foundation, the sanctuary is dedicated to the conservation of local wildlife and provides educational programs on environmental conservation.
The Rampara Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area located in the Morbi district of Gujarat, India. Established in November 1988, the sanctuary spans approximately 15 square kilometres and is managed by the Gujarat Forest Department.
The Gujarat Forest Department is the governmental agency responsible for the management and conservation of forests and wildlife in the Indian state of Gujarat. Headquartered in Gandhinagar, the department plays a crucial role in preserving the state's rich biodiversity, promoting afforestation, and implementing sustainable forest management practices.
References
- ↑ "Top wildlife safaris in Gujarat that are a must-try". The Times of India. ISSN 0971-8257 . Retrieved 2024-03-12.
- ↑ "'Nearly 200 Asiatic lions died in and around Gir in 2016 & 2017'". www.downtoearth.org.in. Retrieved 2024-03-12.
- ↑ "Pania Wildlife Sanctuary - History & Best Time to Visit" . Retrieved 2024-03-12.
- ↑ Team, WSON (2021-01-05). "Pania Wildlife Sanctuary: is home to the Chinkara (Indian Gazelle)". wildstreak of nature. Retrieved 2024-03-12.
- ↑ "Pania Wild Life Sanctuary – Forests Gujarat ORG" . Retrieved 2024-03-12.
- ↑ "Pania Wildlife Sanctuary | Wildlife sanctuaries in Gujarat". www.gujaratorbit.com. Retrieved 2024-03-12.