Related Research Articles

The brainstem is the stalk-like part of the brain that interconnects the cerebrum and diencephalon with the spinal cord. In the human brain, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch.
In neuroanatomy, a nucleus is a cluster of neurons in the central nervous system, located deep within the cerebral hemispheres and brainstem. The neurons in one nucleus usually have roughly similar connections and functions. Nuclei are connected to other nuclei by tracts, the bundles (fascicles) of axons extending from the cell bodies. A nucleus is one of the two most common forms of nerve cell organization, the other being layered structures such as the cerebral cortex or cerebellar cortex. In anatomical sections, a nucleus shows up as a region of gray matter, often bordered by white matter. The vertebrate brain contains hundreds of distinguishable nuclei, varying widely in shape and size. A nucleus may itself have a complex internal structure, with multiple types of neurons arranged in clumps (subnuclei) or layers.

Dopaminergic pathways in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including movement, cognition, executive functions, reward, motivation, and neuroendocrine control. Each pathway is a set of projection neurons, consisting of individual dopaminergic neurons.

The solitary nucleus is a series of sensory nuclei forming a vertical column of grey matter in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. It receives general visceral and/or special visceral inputs from the facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve and vagus nerve ; it receives and relays stimuli related to taste and visceral sensation. It sends outputs to various parts of the brain. Neuron cell bodies of the SN are roughly somatotopically arranged along its length according to function.

The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata. The reticular formation includes ascending pathways to the cortex in the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) and descending pathways to the spinal cord via the reticulospinal tracts.

The ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO), also known as the intermediate nucleus of the preoptic area (IPA), is a small cluster of neurons situated in the anterior hypothalamus, sitting just above and to the side of the optic chiasm in the brain of humans and other animals. The brain's sleep-promoting nuclei, together with the ascending arousal system which includes components in the brainstem, hypothalamus and basal forebrain, are the interconnected neural systems which control states of arousal, sleep, and transitions between these two states. The VLPO is active during sleep, particularly during non-rapid eye movement sleep, and releases inhibitory neurotransmitters, mainly GABA and galanin, which inhibit neurons of the ascending arousal system that are involved in wakefulness and arousal. The VLPO is in turn innervated by neurons from several components of the ascending arousal system. The VLPO is activated by the endogenous sleep-promoting substances adenosine and prostaglandin D2. The VLPO is inhibited during wakefulness by the arousal-inducing neurotransmitters norepinephrine and acetylcholine. The role of the VLPO in sleep and wakefulness, and its association with sleep disorders – particularly insomnia and narcolepsy – is a growing area of neuroscience research.

The subthalamus or prethalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its most prominent structure is the subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamus connects to the globus pallidus, a basal nucleus of the telencephalon.

Slow-wave sleep (SWS), often referred to as deep sleep, consists of stage three of non-rapid eye movement sleep. It usually lasts between 70 and 90 minutes and takes place during the first hours of the night. Initially, SWS consisted of both Stage 3, which has 20–50 percent delta wave activity, and Stage 4, which has more than 50 percent delta wave activity.
The zona incerta (ZI) is a horizontally elongated region of gray matter in the subthalamus below the thalamus. Its connections project extensively over the brain from the cerebral cortex down into the spinal cord.
The dorsal longitudinal fasciculus (DLF) is a longitudinal tract interconnecting the posterior hypothalamus, and the inferior medulla oblongata. It contains both ascending tracts and descending tracts, and serves to link the forebrain, and the visceral autonomic centres of the lower brainstem. It conveys both visceral motor signals, and sensory signals.

The tegmentum is a general area within the brainstem. The tegmentum is the ventral part of the midbrain and the tectum is the dorsal part of the midbrain. It is located between the ventricular system and distinctive basal or ventral structures at each level. It forms the floor of the midbrain (mesencephalon) whereas the tectum forms the ceiling. It is a multisynaptic network of neurons that is involved in many subconscious homeostatic and reflexive pathways. It is a motor center that relays inhibitory signals to the thalamus and basal nuclei preventing unwanted body movement.
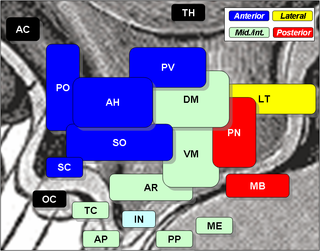
The lateral hypothalamus (LH), also called the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), contains the primary orexinergic nucleus within the hypothalamus that widely projects throughout the nervous system; this system of neurons mediates an array of cognitive and physical processes, such as promoting feeding behavior and arousal, reducing pain perception, and regulating body temperature, digestive functions, and blood pressure, among many others. Clinically significant disorders that involve dysfunctions of the orexinergic projection system include narcolepsy, motility disorders or functional gastrointestinal disorders involving visceral hypersensitivity, and eating disorders.

The median preoptic nucleus is located dorsal to the other three nuclei of the preoptic area of the anterior hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is located just beneath the thalamus, the main sensory relay station of the nervous system, and is considered part of the limbic system, which also includes structures such as the hippocampus and the amygdala. The hypothalamus is highly involved in maintaining homeostasis of the body, and the median preoptic nucleus is no exception, contributing to regulation of blood composition, body temperature, and non-REM sleep.
The rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM), also known as the pressor area of the medulla, is a brain region that is responsible for basal and reflex control of sympathetic activity associated with cardiovascular function. Abnormally elevated sympathetic activity in the RVLM is associated with various cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure and hypertension. The RVLM is notably involved in the baroreflex.

The external globus pallidus combines with the internal globus pallidus (GPi) to form the globus pallidus, an anatomical subset of the basal ganglia. Globus pallidus means "pale globe" in Latin, indicating its appearance. The external globus pallidus is the segment of the globus pallidus that is relatively further (lateral) from the midline of the brain.
Sleep onset is the transition from wakefulness into sleep. Sleep onset usually transmits into non-rapid eye movement sleep but under certain circumstances it is possible to transit from wakefulness directly into rapid eye movement sleep.
Dopaminergic cell groups, DA cell groups, or dopaminergic nuclei are collections of neurons in the central nervous system that synthesize the neurotransmitter dopamine. In the 1960s, dopaminergic neurons or dopamine neurons were first identified and named by Annica Dahlström and Kjell Fuxe, who used histochemical fluorescence. The subsequent discovery of genes encoding enzymes that synthesize dopamine, and transporters that incorporate dopamine into synaptic vesicles or reclaim it after synaptic release, enabled scientists to identify dopaminergic neurons by labeling gene or protein expression that is specific to these neurons.
The parabrachial nuclei, also known as the parabrachial complex, are a group of nuclei in the dorsolateral pons that surrounds the superior cerebellar peduncle as it enters the brainstem from the cerebellum. They are named from the Latin term for the superior cerebellar peduncle, the brachium conjunctivum. In the human brain, the expansion of the superior cerebellar peduncle expands the parabrachial nuclei, which form a thin strip of grey matter over most of the peduncle. The parabrachial nuclei are typically divided along the lines suggested by Baxter and Olszewski in humans, into a medial parabrachial nucleus and lateral parabrachial nucleus. These have in turn been subdivided into a dozen subnuclei: the superior, dorsal, ventral, internal, external and extreme lateral subnuclei; the lateral crescent and subparabrachial nucleus along the ventrolateral margin of the lateral parabrachial complex; and the medial and external medial subnuclei
The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg), also known as the tail of the ventral tegmental area (tVTA), is a GABAergic nucleus which functions as a "master brake" for the midbrain dopamine system. This region was discovered by the researchers, M. Barrot, J.Kaufling and T. Jhou. It is poorly differentiated from the rest of the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and possesses robust functional and structural links to the dopamine pathways. Notably, both acute and chronic exposure to psychostimulants have been shown to induce FosB and ΔFosB expression in the RMTg; no other drug type has been shown to induce these proteins in the RMTg.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Anaclet C, Ferrari L, Arrigoni E, Bass CE, Saper CB, Lu J, Fuller PM (September 2014). "The GABAergic parafacial zone is a medullary slow wave sleep-promoting center" (PDF). Nat. Neurosci. 17 (9): 1217–1224. doi:10.1038/nn.3789. PMC 4214681 . PMID 25129078.
In the present study we show, for the first time, that activation of a delimited node of GABAergic neurons located in the medullary PZ can potently initiate SWS and cortical SWA in behaving animals. ... For now however it remains unclear if the PZ is interconnected with other sleep– and wake–promoting nodes beyond the wake–promoting PB. ... The intensity of cortical slow–wave–activity (SWA: 0.5–4Hz) during SWS is also widely accepted as a reliable indicator of sleep need ... In conclusion, in the present study we demonstrated that all polygraphic and neurobehavioral manifestation of SWS, including SWA, can be initiated in behaving animals by the selective activation of a delimited node of GABAergic medullary neurons.
- 1 2 3 Schwartz MD, Kilduff TS (December 2015). "The Neurobiology of Sleep and Wakefulness". The Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 38 (4): 615–644. doi:10.1016/j.psc.2015.07.002. PMC 4660253 . PMID 26600100.
This ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) is comprised of cholinergic laterodorsal and pedunculopontine tegmentum (LDT/PPT), noradrenergic locus coeruleus (LC), serotonergic (5-HT) Raphe nuclei and dopaminergic ventral tegmental area (VTA), substantia nigra (SN) and periaqueductal gray projections that stimulate the cortex directly and indirectly via the thalamus, hypothalamus and BF.6, 12-18 These aminergic and catecholaminergic populations have numerous interconnections and parallel projections which likely impart functional redundancy and resilience to the system.6, 13, 19 ... More recently, the medullary parafacial zone (PZ) adjacent to the facial nerve was identified as a sleep-promoting center on the basis of anatomical, electrophysiological and chemo- and optogenetic studies.23, 24 GABAergic PZ neurons inhibit glutamatergic parabrachial (PB) neurons that project to the BF,25 thereby promoting NREM sleep at the expense of wakefulness and REM sleep. ... Sleep is regulated by GABAergic populations in both the preoptic area and the brainstem; increasing evidence suggests a role for the melanin-concentrating hormone cells of the lateral hypothalamus and the parafacial zone of the brainstem
- 1 2 Brown RE, McKenna JT (June 2015). "Turning a Negative into a Positive: Ascending GABAergic Control of Cortical Activation and Arousal". Front. Neurol. 6: 135. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2015.00135 . PMC 4463930 . PMID 26124745.
The sleep-promoting action of GABAergic neurons located in the preoptic hypothalamus (6–8) is now well-known and accepted (9). More recently, other groups of sleep-promoting GABAergic neurons in the lateral hypothalamus (melanin-concentrating hormone neurons) and brainstem [parafacial zone; (10)] have been identified.
- 1 2 Cherasse Y, Urade Y (November 2017). "Dietary Zinc Acts as a Sleep Modulator". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 18 (11): 2334. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112334 . PMC 5713303 . PMID 29113075.
More recently, Fuller's laboratory also discovered that sleep can be promoted by the activation of a gamma-aminobutyric acid-ergic (GABAergic) population of neurons located in the parafacial zone [11,12], while the role of the GABAergic A2AR-expressing neurons of the nucleus accumbens [13] and the striatum has just been revealed [14,15].
- ↑ Oishi Y, Xu Q, Wang L, Zhang BJ, Takahashi K, Takata Y, Luo YJ, Cherasse Y, Schiffmann SN, de Kerchove d'Exaerde A, Urade Y, Qu WM, Huang ZL, Lazarus M (September 2017). "Slow-wave sleep is controlled by a subset of nucleus accumbens core neurons in mice". Nature Communications. 8 (1): 734. Bibcode:2017NatCo...8..734O. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00781-4. PMC 5622037 . PMID 28963505.
Here, we show that chemogenetic or optogenetic activation of excitatory adenosine A2A receptor-expressing indirect pathway neurons in the core region of the NAc strongly induces slow-wave sleep. Chemogenetic inhibition of the NAc indirect pathway neurons prevents the sleep induction, but does not affect the homoeostatic sleep rebound.
- ↑ Yuan XS, Wang L, Dong H, Qu WM, Yang SR, Cherasse Y, Lazarus M, Schiffmann SN, d'Exaerde AK, Li RX, Huang ZL (October 2017). "Striatal adenosine A2A receptor neurons control active-period sleep via parvalbumin neurons in external globus pallidus". eLife. 6: e29055. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29055 . PMC 5655138 . PMID 29022877.
- ↑ Borbély, Alexander A.; Achermann, Peter (2005), "Sleep Homeostasis and Models of Sleep Regulation" (PDF), Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine, Elsevier, pp. 405–417, doi:10.1016/b0-72-160797-7/50040-9, ISBN 9780721607979
- 1 2 Anaclet, C.; Lin, J.-S.; Vetrivelan, R.; Krenzer, M.; Vong, L.; Fuller, P. M.; Lu, J. (2012-12-12). "Identification and Characterization of a Sleep-Active Cell Group in the Rostral Medullary Brainstem". Journal of Neuroscience. 32 (50): 17970–17976. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0620-12.2012. ISSN 0270-6474. PMC 3564016 . PMID 23238713.
- 1 2 Su, Yun-Ting; Gu, Meng-Yang; Chu, Xi; Feng, Xiang; Yu, Yan-Qin (2018-03-20). "Whole-Brain Mapping of Direct Inputs to and Axonal Projections from GABAergic Neurons in the Parafacial Zone". Neuroscience Bulletin. 34 (3): 485–496. doi:10.1007/s12264-018-0216-8. ISSN 1673-7067. PMC 5960452 . PMID 29557546.