Related Research Articles

Kaikō was a remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) built by the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC) for exploration of the deep sea. Kaikō was the second of only five vessels ever to reach the bottom of the Challenger Deep, as of 2019. Between 1995 and 2003, this 10.6 ton unmanned submersible conducted more than 250 dives, collecting 350 biological species, some of which could prove to be useful in medical and industrial applications. On 29 May 2003, Kaikō was lost at sea off the coast of Shikoku Island during Typhoon Chan-Hom, when a secondary cable connecting it to its launcher at the ocean surface broke.
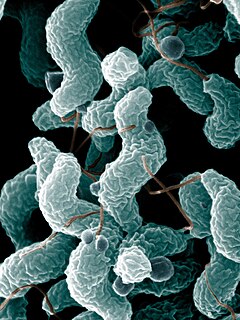
Campylobacterota are a phylum of bacteria. All species of this phylum are Gram-negative.
Nitratireductor indicus is a Gram-negative, oxidase- and catalase-positive mobile bacteria from the genus of Nitratireductor which was isolated from deep-sea water of the Indian Ocean.
Parvibaculum indicum is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped and motile bacterium with a polar flagellum species from the genus of Parvibaculum which has been isolated from deep-sea water from the Indian Ocean.
Microbacterium indicum is a bacterium from the genus of Microbacterium which has been isolated from deep-sea sediments from the Chagos Trench in the Indian Ocean.
Microbacterium marinum is a Gram-positive and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Microbacterium which has been isolated from seawater from the South-West Indian Ocean.
Desmospora profundinema is a bacterium from the genus of Desmospora which has been isolated from deep-sea sediments from the Indian Ocean near China.
Melghirimyces profundicolus is a bacterium from the genus of Melghirimyces which has been isolated from deep-sea sediments from the Indian Ocean.
Bhargavaea is a bacteria genus from the family of Planococcaceae.
Bhargavaea beijingensis is a Gram-positive, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Bhargavaea which has been isolated from deep-sea sediments from the Chagos-Laccadive Ridge from the Indian Ocean.
Novosphingobium indicum is a bacterium from the genus Novosphingobium which has been isolated from deep-sea water from the Indian Ocean. Novosphingobium indicum hasd the ability to degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon.
Abyssicoccus albus is a Gram-positive, aerobic and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Abyssicoccus which has been isolated from deep sea sediments from the Indian Ocean.
Prauserella marina is a bacterium from the genus of Prauserella which has been isolated from ocean sediments from the South China Sea in China.
Thalassotalea is an aerobic and chemo-organo-heterotrophic genus of bacteria from the family Colwelliaceae which occur in the ocean and in sea ice.
Cellulomonas marina is a bacterium from the genus of Cellulomonas which has been isolated from deep-sea water from the Indian Ocean.
Serinicoccus profundi is a Gram-positive bacterium species from the genus of Serinicoccus which has been isolated from deep-sea sediments from the Indian Ocean.
Celeribacter indicus is a bacterium from the genus of Celeribacter which has been isolated from deep sea sediments from the Indian Ocean.Celeribacter indicus can degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Roseovarius indicus is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Roseovarius which has been isolated from deep sea-water from the Indian Ocean.
Galbibacter marinus is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped moderately halophilic and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Galbibacter which has been isolated from deep-sea sediments from the Indian Ocean Ridge. Galbibacter marinus has the ability to denitrification.
Sunxiuqinia indica is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Sunxiuqinia which has been isolated from deep sea water from the Indian Ocean.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Genus: Paramesonia". lpsn.dsmz.de.
- ↑ "Paramesonia". www.uniprot.org.
- 1 2 Wang, Lei; Lai, Qiliang; Liu, Xiupian; Shao, Zongze (1 April 2020). "Paramesonia marina gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from deep-sea water of the Indian Ocean". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 70 (4): 2325–2333. doi:10.1099/ijsem.0.004041.