Hubris, or less frequently hybris, describes a personality quality of extreme or excessive pride or dangerous overconfidence and complacency, often in combination with arrogance. The term arrogance comes from the Latin adrogare, meaning "to feel that one has a right to demand certain attitudes and behaviors from other people". To arrogate means "to claim or seize without justification... To make undue claims to having", or "to claim or seize without right... to ascribe or attribute without reason". The term pretension is also associated with the term hubris, but is not synonymous with it.

An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an idea is unique enough either as a stand-alone invention or as a significant improvement over the work of others, it can be patented. A patent, if granted, gives the inventor a proprietary interest in the patent over a specific period of time, which can be licensed for financial gain.

A wife is a woman in a marital relationship. A woman who has separated from her partner continues to be a wife until their marriage is legally dissolved with a divorce judgment. On the death of her partner, a wife is referred to as a widow. The rights and obligations of a wife to her partner and her status in the community and law vary between cultures and have varied over time.
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment by the groom, or his family, to the bride, or her family, dowry is the wealth transferred from the bride, or her family, to the groom, or his family. Similarly, dower is the property settled on the bride herself, by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control.

In Islam, a mahr is the bride wealth obligation, in the form of money, possessions or teaching of verses from the Quran by the groom, to the bride in connection with an Islamic wedding. While the mahr is often money, it can also be anything agreed upon by the bride such as jewelry, home goods, furniture, a dwelling or some land. Mahr is typically specified in the marriage contract signed upon marriage.

The legal rights of women refers to the social and human rights of women. One of the first women's rights declarations was the Declaration of Sentiments. The dependent position of women in early law is proved by the evidence of most ancient systems.
Seisin is a legal concept that denotes the right to legal possession of a thing, usually a fiefdom, fee, or an estate in land. It is similar, but legally separate from the idea of ownership.
Jointure was a legal concept used largely in late mediaeval and early modern Britain, denoting the estate given to a married couple by the husband's family. One of its most important functions was providing a livelihood for the wife if she became widowed, and it is most often used in this sense, interchangeably with dower.
In the common law, emblements are annual crops produced by cultivation legally belonging to the tenant with the implied right for its harvest, and are treated as the tenant's property.

Dower is a provision accorded traditionally by a husband or his family, to a wife for her support should she become widowed. It was settled on the bride by agreement at the time of the wedding, or as provided by law.
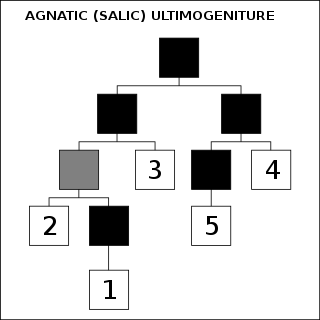
Ultimogeniture, also known as postremogeniture or junior right, is the tradition of inheritance by the last-born of a privileged position in a parent's wealth or office. The tradition has been far rarer historically than primogeniture or partible inheritance.

Myra Colby Bradwell was an American publisher and political activist. She attempted in 1869 to become the first woman to be admitted to the Illinois bar to practice law, but was denied admission by the Illinois Supreme Court in 1870 and the United States Supreme Court in 1873, in rulings upholding a separate women's sphere. Bradwell had founded and published Chicago Legal News from 1868, reporting on the law and continued that work. Meanwhile, influenced by her case, in 1872 the Illinois legislature passed a state law prohibiting gender discrimination in admission to any occupation or profession.

The Married Women's Property Act 1882 was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that significantly altered English law regarding the property rights of married women, which besides other matters allowed married women to own and control property in their own right.

A husband is a man involved in a marital relationship, commonly referred to as a spouse. The specific rights, responsibilities, and societal status attributed to a husband can vary significantly across different cultures and historical periods, reflecting a global perspective on this role.
A putative marriage is an apparently valid marriage, entered into in good faith on the part of at least one of the partners, but that is legally invalid due to a technical impediment, such as a preexistent marriage on the part of one of the partners. Unlike someone in a common-law, statutory, or ceremonial marriage, a putative spouse is not legally married. Instead, a putative spouse believes themselves to be married in good faith and is given legal rights as a result of this person's reliance upon this good-faith belief.
In law, sequestration is the act of removing, separating, or seizing anything from the possession of its owner under process of law for the benefit of creditors or the state.

Erusin is the Hebrew term for betrothal. In modern Hebrew, "erusin" means engagement, but this is not the historical meaning of the term, which is the first part of marriage.
In Louisiana law, extra-dotal property is that property which forms no part of the dowry of a woman, but is hers alone. It is also called "paraphernal property", from the Greek for "beyond the dowry", which gives us the word "paraphernalia".

The Custom of Paris was one of France's regional custumals of civil law. It was the law of the land in Paris and the surrounding region in the 16th–18th centuries and was applied to French overseas colonies, including New France. First written in 1507 and revised in 1580 and 1605, the Custom of Paris was a compilation and systematization of Renaissance-era customary law. Divided into 16 sections, it contained 362 articles concerning family and inheritance, property, and debt recovery. It was the main source of law in New France from the earliest settlement, but other provincial customs were sometimes invoked in the early period.
The dowry system in India refers to the durable goods, cash, and real or movable property that the bride's family gives to the groom, his parents and his relatives as a condition of the marriage. Dowry is called "दहेज" in Hindi and as جہیز in Urdu.












