Parietal (literally: "pertaining or relating to walls") is an adjective used predominantly for the parietal lobe and other relevant anatomy.
Contents
Parietal may also refer to:
Parietal (literally: "pertaining or relating to walls") is an adjective used predominantly for the parietal lobe and other relevant anatomy.
Parietal may also refer to:

The occipital bone is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput. It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of the skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord.
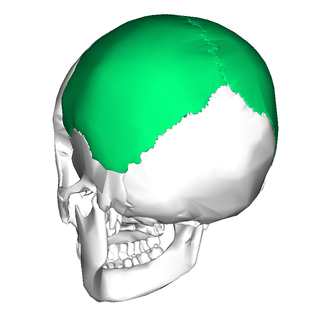
The parietal bones are two bones in the skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint known as a cranial suture, form the sides and roof of the neurocranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, and four angles. It is named from the Latin paries (-ietis), wall.

The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.

A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells. The concept was first introduced by the German anatomist Korbinian Brodmann in the early 20th century. Brodmann mapped the human brain based on the varied cellular structure across the cortex and identified 52 distinct regions, which he numbered 1 to 52. These regions, or Brodmann areas, correspond with diverse functions including sensation, motor control, and cognition.

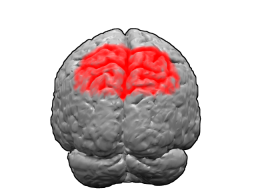
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.

In neuroanatomy, the precuneus is the portion of the superior parietal lobule on the medial surface of each brain hemisphere. It is located in front of the cuneus. The precuneus is bounded in front by the marginal branch of the cingulate sulcus, at the rear by the parieto-occipital sulcus, and underneath by the subparietal sulcus. It is involved with episodic memory, visuospatial processing, reflections upon self, and aspects of consciousness.

The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ob, 'behind', and caput, 'head'.
Brodmann area 7 is one of Brodmann's cytologically defined regions of the brain corresponding to precuneus and superior parietal lobule (SPL). It is involved in locating objects in space. It serves as a point of convergence between vision and proprioception to determine where objects are in relation to parts of the body.

Brodmann area 40 (BA40) is part of the parietal cortex in the human brain. The inferior part of BA40 is in the area of the supramarginal gyrus, which lies at the posterior end of the lateral fissure, in the inferior lateral part of the parietal lobe.
In biological morphology and anatomy, a sulcus is a furrow or fissure. It may be a groove, natural division, deep furrow, elongated cleft, or tear in the surface of a limb or an organ, most notably on the surface of the brain, but also in the lungs, certain muscles, as well as in bones, and elsewhere. Many sulci are the product of a surface fold or junction, such as in the gums, where they fold around the neck of the tooth.

The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.

The lobes of the brain are the four major identifiable regions of the human cerebral cortex, and they comprise the surface of each hemisphere of the cerebrum. The two hemispheres are roughly symmetrical in structure, and are connected by the corpus callosum. Some sources include the insula and limbic lobe but the limbic lobe incorporates parts of the other lobes. The lobes are large areas that are anatomically distinguishable, and are also functionally distinct. Each lobe of the brain has numerous ridges, or gyri, and furrows, sulci that constitute further subzones of the cortex. The expression "lobes of the brain" usually refers only to those of the cerebrum, not to the distinct areas of the cerebellum.

The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, as well as the medial and inferior aspects of the temporal lobe of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. These anastomose with the middle cerebral arteries and internal carotid arteries via the posterior communicating arteries.

The cranial cavity, also known as intracranial space, is the space within the skull that accommodates the brain. The skull is also known as the cranium. The cranial cavity is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium that in humans includes the skull cap and forms the protective case around the brain. The remainder of the skull is the facial skeleton. The meninges are three protective membranes that surround the brain to minimize damage to the brain in the case of head trauma. Meningitis is the inflammation of meninges caused by bacterial or viral infections.

In human brain anatomy, an operculum, may refer to the frontal, temporal, or parietal operculum, which together cover the insula as the opercula of insula. It can also refer to the occipital operculum, part of the occipital lobe.

The superior parietal lobule is bounded in front by the upper part of the postcentral sulcus, but is usually connected with the postcentral gyrus above the end of the sulcus. The superior parietal lobule contains Brodmann's areas 5 and 7.

The inferior parietal lobule lies below the horizontal portion of the intraparietal sulcus, and behind the lower part of the postcentral sulcus. Also known as Geschwind's territory after Norman Geschwind, an American neurologist, who in the early 1960s recognised its importance. It is a part of the parietal lobe.
The sensory cortex can refer sometimes to the primary somatosensory cortex, or it can be used as a term for the primary and secondary cortices of the different senses : the visual cortex on the occipital lobes, the auditory cortex on the temporal lobes, the primary olfactory cortex on the uncus of the piriform region of the temporal lobes, the gustatory cortex on the insular lobe, and the primary somatosensory cortex on the anterior parietal lobes. Just posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex lies the somatosensory association cortex or area, which integrates sensory information from the primary somatosensory cortex to construct an understanding of the object being felt. Inferior to the frontal lobes are found the olfactory bulbs, which receive sensory input from the olfactory nerves and route those signals throughout the brain. Not all olfactory information is routed to the olfactory cortex: some neural fibers are routed to the supraorbital region of the frontal lobe, while others are routed directly to limbic structures. The direct limbic connection makes the olfactory sense unique.

In the occipital lobe, the lateral occipital sulcus, where present, divides the lateral, or middle occipital gyrus into a superior and an inferior part, which are then continuous in front with the parietal and temporal lobes. The anterior portion is often incomplete, but in some individuals it may encounter the superior temporal sulcus whilst the posterior portion originates from the middle of the curved lunate sulcus, or from a curved portion of the transverse occipital sulcus if absent.

In neuroanatomy, the paracentral lobule is on the medial surface of the cerebral hemisphere and is the continuation of the precentral and postcentral gyri. The paracentral lobule controls motor and sensory innervations of the contralateral lower extremity. It is also responsible for control of blushing, defecation and urination.