The Lehigh Valley Railroad was a railroad in the Northeastern United States built predominantly to haul anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Northeastern Pennsylvania to major consumer markets in Philadelphia, New York City, and elsewhere.

The Main Line is a commuter rail line owned and operated by New Jersey Transit running from Suffern, New York to Hoboken, New Jersey, in the United States. It runs daily commuter service and was once the north–south main line of the Erie Railroad. It is colored yellow on NJ Transit system maps, and its symbol is a water wheel.

NJ Transit Rail Operations is the rail division of NJ Transit. It operates commuter rail service in New Jersey, with most service centered on transportation to and from New York City, Hoboken, and Newark. NJ Transit also operates rail service in Orange and Rockland counties in New York under contract to Metro-North Railroad. The commuter rail lines saw 57,179,000 riders in 2023, making it the third-busiest commuter railroad in North America and the longest commuter rail system in North America by route length.
Conrail Shared Assets Operations (CSAO) is the commonly used name for modern-day Conrail, an American railroad company. It operates three networks, the North Jersey, South Jersey/Philadelphia, and Detroit Shared Assets Areas, where it serves as a contract local carrier and switching company for its owners, CSX Transportation and the Norfolk Southern Railway. When most of the former Conrail's track was split between these two railroads, the three shared assets areas were kept separate to avoid giving one railroad an advantage in those areas. The company operates using its own employees and infrastructure but owns no equipment outside MOW equipment.

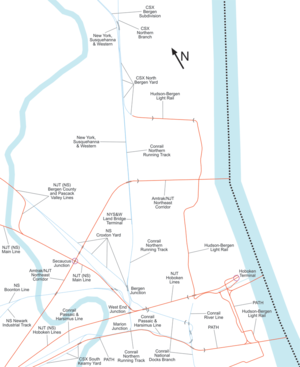
Marion Junction is a railroad junction in western Jersey City, New Jersey. Currently, it connects CSX's River Line to Conrail's Passaic and Harsimus Line. The two lines merge towards the west, allowing through trains from upstate New York to continue towards the rest of the country. The track actually making the connection is known as the Marion Running Track.

For the purposes of this article, the Jersey City area extends North to Edgewater, South to Bayonne and includes Kearny Junction and Harrison but not Newark. Many routes east of Newark are listed here.

The Northern Branch is a railroad line that runs from Jersey City to Northvale in northeastern New Jersey, and formerly extended further into New York State. The line was constructed in 1859 by the Northern Railroad of New Jersey to connect the New York and Erie Railroad's Piermont Branch terminus in Piermont, New York, directly to Erie's primary terminal in Jersey City, initially Exchange Place, later Pavonia Terminal. In 1870 the line was extended to Nyack, New York, and continued to provide passenger service until 1966. After the Erie's unsuccessful merger with the Lackawanna Railroad to form the Erie-Lackawanna, ownership of the line passed into the hands of Conrail upon its formation in 1976 from a number of bankrupt railroads.

The River Line was a Conrail rail line located between Jersey City, New Jersey and Selkirk, New York, United States. It ran along the west side of the Hudson Palisades and, after passing through a tunnel at Haverstraw, New York, along the west bank of the Hudson River. It was previously the New York Central's West Shore Railroad and Weehawken Branch. The River Line has since been split into several sections, following the 1999 division of Conrail assets between Norfolk Southern Railway and CSX Transportation.
The United New Jersey Railroad and Canal Company (UNJ&CC) was a United States–based railroad company established in 1872. It was formed by the consolidation of three existing companies: the Camden and Amboy Railroad, Delaware and Raritan Canal Company, and New Jersey Rail Road and Transportation Company. The Camden and Amboy and New Jersey Rail Road were among the earliest North American railroads. The Pennsylvania Railroad leased the United New Jersey Railroad and Canal Company in 1872.

The Lehigh and Hudson River Railway (L&HR) was the smallest of the six railroads that were merged into Conrail in 1976. It was a bridge line running northeast–southwest across northwestern New Jersey, connecting the line to the Poughkeepsie Bridge at Maybrook, New York, with Easton, Pennsylvania, where it interchanged with various other companies.
The Lehigh and New England Railroad was a Class I railroad located in Northeastern United States that acted as a bridge line. It was the second notable U.S. railroad to file for abandonment in its entirety after the New York, Ontario and Western Railway. It was headquartered in Philadelphia.

Bergen Hill refers to the lower Hudson Palisades in New Jersey, where they emerge on Bergen Neck, which in turn is the peninsula between the Hackensack and Hudson Rivers, and their bays. In Hudson County, it reaches a height of 260 feet.
The Shellpot Branch is a former Pennsylvania Railroad/Penn Central through-freight railroad owned and operated by Norfolk Southern since its acquisition, along with CSX Transportation, of Conrail in 1999. The branch allows Norfolk Southern, since the opening of a new bridge in 2001, to bypass the city of Wilmington, Delaware and allows direct access to both the Port of Wilmington and the New Castle Secondary, which connects to the Delmarva Subdivision of the Delmarva Central Railroad that runs to Central Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia's Eastern Shore. Both ends of the branch connect with Amtrak's Northeast Corridor and, like all of the PRR's through-freight lines, was electrified from 1935 until the Conrail era. The line was originally built doubly tracked, but was subsequently converted to single track.

Oak Island Yard is a freight rail yard located north of Port Newark-Elizabeth Marine Terminal and Newark International Airport in an industrial area of Ironbound, Newark, New Jersey at 91 Bay Ave., United States. The sprawling complex includes engine house, classification yard, auto unloading terminal, and maintenance facilities. It has ten reception tracks, an automated hump, 30 relatively short classification tracks, and nine departure tracks. In 1999, it classified 800 to 1000 cars per day.
National Docks Secondary is a freight rail line within Conrail's North Jersey Shared Assets Area in Hudson County, New Jersey, used by CSX Transportation. It provides access for the national rail network to maritime, industrial, and distribution facilities at Port Jersey, the Military Ocean Terminal at Bayonne (MOTBY), and Constable Hook as well as carfloat operations at Greenville Yard. The line is an important component in the planned expansion of facilities in the Port of New York and New Jersey. The single track right of way comprises rail beds, viaducts, bridges, and tunnels originally developed at the end of the 19th century by competing railroads.

The North Bergen Yard is freight rail yard and intermodal terminal in North Bergen, New Jersey parallel to Tonnelle Avenue between 49th and 69th Streets. Located within the North Jersey Shared Assets Area, the facility is part of CSX Transportation (CSXT) and the origination point of its CSX River Subdivision at the southern end of the Albany Division. On its west side, the New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway (NYSW) runs the length of the yard and operates a bulk transloading operation immediately adjacent to it.

Point-No-Point Bridge is a railroad bridge crossing the Passaic River between Newark and Kearny, New Jersey, United States, in the New Jersey Meadowlands. The swing bridge is the fourth from the river's mouth at Newark Bay and is 2.6 miles (4.2 km) upstream from it. A camelback through truss bridge, it is owned by Conrail as part of its North Jersey Shared Assets and carries the Passaic and Harsimus Line used by CSX Transportation and Norfolk Southern. River Subdivision accesses the line via Marion Junction. Conrail is replacing the bridge, which was opened in 1901. Work began in November 2022.

Little Ferry Yard is a railyard and intermodal terminal in the Port of New York and New Jersey served by the CSX River Subdivision (CSXT), New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway (NYSW), Norfolk Southern Railway and Conrail Shared Assets Operations (CRCX).

The Lehigh Line is a railroad line in Central New Jersey, Northeastern Pennsylvania, and the Lehigh Valley region of eastern Pennsylvania. It is owned and operated by the Norfolk Southern Railway. The line runs west from the vicinity of the Port of New York and New Jersey in Manville, New Jersey via Conrail's Lehigh Line to the southern end of Wyoming Valley's Coal Region in Lehigh Township, Pennsylvania.

Ridgefield Park station, also known as West Shore Station, was a railroad station in Ridgefield Park, New Jersey, at the foot of Mount Vernon Street served by the New York, Susquehanna and Western Railroad (NYSW) and the West Shore Railroad, a division of New York Central (NYCRR). The New York, Ontario and Western Railway (NYO&W) had running rights along the West Shore and sometimes stopped at Ridgefield Park. First opened in 1872 it was one of three passenger stations in the village, the others being the Little Ferry station to the south and Westview station to the north. Service on the West Shore Railroad began in 1883. The station house, built at a cost of $100,000 opened in 1927. Southbound service crossed Overpeck Creek and continued to terminals on the Hudson River waterfront where there was a connecting ferry service across the Hudson River to Manhattan. Northbound near Bogota the parallel NYSW and West Shore lines diverge and continue into northern New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and upstate New York. Passenger service ended in 1966.