
The Battle of Bouvines was fought on 27 July 1214 near the town of Bouvines in the County of Flanders. It was the concluding battle of the Anglo-French War of 1213–1214. Although estimates on the number of troops vary considerably among modern historians, at Bouvines, a French army commanded by King Philip Augustus routed a larger allied army led by Holy Roman Emperor Otto IV in one of the rare pitched battles of the High Middle Ages and one of the most decisive medieval engagements.

The Battle of Lens was a French victory under Louis II de Bourbon, Prince de Condé against the Spanish army under Archduke Leopold Wilhelm in the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). It was the last major battle of the war and a French victory. The battle cemented the reputation of Condé as one of the greatest generals of his age.

The Battle of Rocroi, fought on 19 May 1643, was a major engagement of the Thirty Years' War between a French army, led by the 21-year-old Duke of Enghien and Spanish forces under General Francisco de Melo only five days after the accession of Louis XIV to the throne of France after his father's death. Rocroi shattered the myth of invincibility of the Spanish Tercios, the terrifying infantry units that had dominated European battlefields for the previous 120 years. The battle is therefore often considered to mark the end of Spanish military greatness and the beginning of French hegemony in Europe during the 17th century. After Rocroi, the Spanish progressively transformed the tercio system incorporating more of the line infantry doctrine used by the French over time.

Louis II de Bourbon, Prince of Condé, known as le Grand Condé, was a French military commander. A tactician and strategist, he is regarded as one of France's greatest generals, particularly celebrated for his triumphs in the Thirty Years' War and his campaigns during the Franco-Dutch War.

Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, vicomte de Turenne, commonly known as Turenne, was a French general and one of only six Marshals to have been promoted Marshal General of France. The most illustrious member of the La Tour d'Auvergne family, his military exploits over his five-decade career earned him a reputation as one of the greatest military commanders in history.

The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521–1526 between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor as well as ruler of Spain, Austria, the Low Countries, and the Two Sicilies.

A tercio, Spanish for "[a] third") was a military unit of the Spanish Army during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain and Habsburg Spain in the early modern period. They were the elite military units of the Spanish monarchy and the essential pieces of the powerful land forces of the Spanish Empire, sometimes also fighting with the navy.

Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand was a Spanish and Portuguese prince, Governor of the Spanish Netherlands, Cardinal of the Holy Catholic Church, Archduke of Austria, Archbishop of Toledo (1619–41), and a general during the Thirty Years' War, the Eighty Years' War, and the Franco-Spanish War. He is commonly considered the last great commander and strategist of the Spanish Empire, whose premature death in a critical moment helped bring about the end of Spanish hegemony in Europe. He is, as well, one of few generals undefeated on the battlefield.

The Battle of Cerignola was fought on 28 April 1503 between Spanish and French armies outside the town of Cerignola, Apulia, Kingdom of Naples, approximately 80 kilometres (50 mi) west of Bari. The Spanish force under the command of Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba comprising 6,300 men, including 2,000 Landsknecht pikemen, 1,000 arquebusiers and 20 cannons, defeated the French force of 9,000 men, mainly gendarme heavy cavalry and Swiss mercenary pikemen, with about 40 cannons, led by Louis d'Armagnac, Duke of Nemours, who was killed during the battle.

The Battle of Kallo was a major field battle fought from 20 to 21 June 1638 in and around the forts of Kallo and Verrebroek, located on the left bank of the Scheldt river, near Antwerp, during the second phase of the Eighty Years' War. Following the symbolic recovery of Breda during the 1637 campaign, the Dutch Republic agreed with the French Crown, with whom it had allied in 1635, to besiege a major city in the Spanish Netherlands during the 1638 campaign. The commander of the Dutch States Army, Frederick Henry of Orange, planned an approach over Antwerp from the two sides of the Scheldt. After marching the army, Frederick Henry transferred 50 barges to Count William of Nassau-Siegen and he was left entrusted to land in the Spanish-controlled Waasland region, west of Antwerp, to seize the forts of Kallo and Verrebroek, along with several other key fortifications, to invest Antwerp from the west. In the meantime, Frederick Henry would advance on the opposite bank to complete the blockade of the city while the armies of France invaded the Spanish Netherlands from the south to oblige the Spanish Army of Flanders to divide its forces.

The Battle of La Marfée, also known as the Battle of Sedan, took place on 6 July 1641, during the 1635 to 1659 Franco-Spanish War, a related conflict of the Thirty Years War.

The Battle of Les Avins took place on 20 May 1635, outside the town of Les Avins, near Huy in modern Belgium, then part of the Bishopric of Liège. It was the first major engagement of the 1635 to 1659 Franco-Spanish War, a connected conflict of the Thirty Years' War.

The Army of Flanders was a multinational army in the service of the kings of Spain that was based in the Spanish Netherlands during the 16th to 18th centuries. It was notable for being the longest-serving army of the period, being in continuous service from 1567 until its disestablishment in 1706 and taking part in numerous pivotal battles of the Dutch Revolt (1566–1609) and the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). Because it employed or pioneered many developing military concepts more reminiscent of later military units, enjoying permanent, standing regiments (tercios), barracks, military hospitals and rest homes long before they were adopted in most of Europe, the Army of Flanders has been considered the world's de facto first modern professional standing army. Sustained at huge cost and at significant distances from Spain via the Spanish Road, the Army of Flanders also became infamous for successive mutinies and its ill-disciplined activity on and off the battlefield, including the Sack of Antwerp in 1576.

Henri de Saint-Nectaire, 1st Duke of La Ferté-Senneterre was a marshal of France and governor of Lorraine.

The Battle of Valenciennes was fought on 16 July 1656 between the Spanish troops commanded by John Joseph of Austria and the French troops under Henri de la Tour d'Auvergne, Vicomte de Turenne, in the outskirts of the city of Valenciennes in the Spanish Netherlands during the Franco-Spanish War. After a period of Spanish recovery following the Peace of Münster in 1648, France went again on the offensive in 1654, having succeeded in suppressing internal rebellions, and took several towns in the province of Hainaut over the course of two years. On early 1656, Turenne was instructed by the French court to continue the offensive. He intended at first to besiege Tournai, but realising that it had been strongly reinforced by the Army of Flanders under the newly appointed John Joseph of Austria, illegitimate son of Philip IV of Spain, he went instead to besiege Valenciennes, in the course of the Scheldt River.
The following units and commanders of the French and Spanish armies fought in the Battle of Rocroi on May 19, 1643.

Fermín Jáudenes y Álvarez was a Spanish military officer and colonial administrator who served as Governor-General of the Philippines from July 24 to August 13, 1898, during the Spanish–American War and the second phase of the Philippine Revolution.

Alfonso Pérez de Vivero, Count of Fuensaldaña, was a Spanish soldier, nobleman and officeholder.
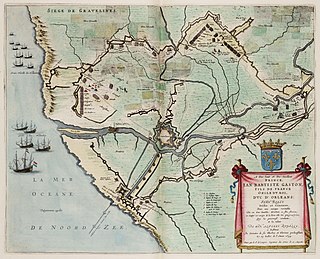
The siege of Gravelines, May to July 1644, took place during the 1635–1659 Franco-Spanish War. A French army captured the port of Gravelines, then in the Spanish Netherlands, now the Pas-de-Calais region of northern France.

Carlo Andrea Caracciolo was an Italian nobleman and military commander serving the Spanish Empire.




















