
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a morphinan opioid substance synthesized from the dried latex of the Papaver somniferum plant; it is mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Medical-grade diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt. Various white and brown powders sold illegally around the world as heroin are routinely diluted with cutting agents. Black tar heroin is a variable admixture of morphine derivatives—predominantly 6-MAM (6-monoacetylmorphine), which is the result of crude acetylation during clandestine production of street heroin. Heroin is used medically in several countries to relieve pain, such as during childbirth or a heart attack, as well as in opioid replacement therapy.

Pope Pius IX was head of the Catholic Church from 1846 to 1878. His reign of 32 years is the second longest of any pope in history, behind that of Saint Peter. He was notable for convoking the First Vatican Council in 1868 and for permanently losing control of the Papal States in 1870 to the Kingdom of Italy. Thereafter, he refused to leave Vatican City, declaring himself a "prisoner in the Vatican".

Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of intentional practices and public health policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. Harm reduction is used to decrease negative consequences of recreational drug use and sexual activity without requiring abstinence, recognizing that those unable or unwilling to stop can still make positive change to protect themselves and others.
Incapacitating agent is a chemical or biological agent which renders a person unable to harm themselves or others, regardless of consciousness.

Churchill is an Arctic port town in northern Manitoba, Canada, on the west shore of Hudson Bay, roughly 140 km (87 mi) from the Manitoba–Nunavut border. It is most famous for the many polar bears that move toward the shore from inland in the autumn, leading to the nickname "Polar Bear Capital of the World" and to the benefit of its burgeoning tourism industry.
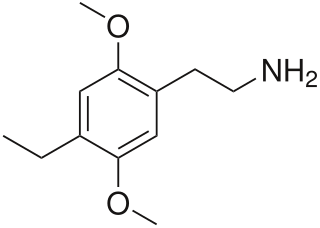
2C-E is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and documented in his book PiHKAL. Like the other substances in its family, it produces sensory and cognitive effects in its physical reactions with living organisms.
Riccardo Galeazzi-Lisi was an Italian medical doctor who served as Pope Pius XII's personal physician from 1939 until his dismissal in 1958. During his service in the Vatican he was officially titled "Archiatra Pontificio". The pope also made him an honorary member of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences. He managed to be present at the 1958 death of Pius XII and created a scandal in this context with his attempt to publish pictures and stories about the dying pontiff. He was also a member of the International Society for the History of Medicine.
Native American studies is an interdisciplinary academic field that examines the history, culture, politics, issues, spirituality, sociology and contemporary experience of Native peoples in North America, or, taking a hemispheric approach, the Americas. Increasingly, debate has focused on the differences rather than the similarities between other Ethnic studies disciplines such as African American studies, Asian American Studies, and Latino/a Studies.

Levorphanol is an opioid medication used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of the compound racemorphan. Its dextrorotatory counterpart is dextrorphan.

Bath salts are water-soluble, pulverized minerals that are added to water to be used for bathing. It is said that these salts improve cleaning, enhance the enjoyment of bathing, and serve as a vehicle for cosmetic agents. Bath salts have been developed which mimic the properties of natural mineral baths or hot springs. Some bath salts contain glycerine so the product will act as an emollient, humectant, or lubricant. Fragrances and colors are often added to bath salts; the fragrances are used to increase the users' enjoyment of the bathing experience.
Jeanne Harley Guillemin was an American medical anthropologist and author, who for 25 years taught at Boston College as a professor of Sociology and for over ten years was a senior fellow in the Security Studies Program at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She was an authority on biological weapons and published four books on the topic.
WinPepi is a freeware package of statistical programs for epidemiologists, comprising seven programs with over 120 modules. WinPepi is not a complete compendium of statistical routines for epidemiologists but it provides a very wide range of procedures, including those most commonly used and many that are not easy to find elsewhere. This has repeatedly led reviewers to use a "Swiss army knife" analogy. Each program has a comprehensive fully referenced manual.
David George Gratzer is a physician, columnist, author, Congressional expert witness; he was a senior fellow at both the Manhattan Institute and the Montreal Economic Institute. Though he has written essays on topics as diverse as obesity and political campaigns, he is best known for his first book, published by ECW Press, when he was just 24: Code Blue: Reviving Canada's Health Care System. That book won the Donner Prize established by the Donner Canadian Foundation and was a national bestseller in his native Canada. Gratzer is a critic of the Canadian health care system, and of U.S. President Barack Obama's health care reform proposals. Gratzer was health care policy advisor to Rudy Giuliani's 2008 presidential campaign.

Social teachings of Pope Pius XII refers to encyclicals, apostolic constitutions and speeches by Pope Pius XII on non-theological issues involving medicine, science, education, social justice, family and sexuality, and occupations.

Cyclofenil, sold under the brand name Sexovid among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) medication which is used as a gonadotropin stimulant or ovulation inducer and in menopausal hormone therapy in women. It is mostly no longer available. The medication is taken by mouth.
Since their discovery, anabolic steroids (AAS) have been widely used as performance-enhancing drugs to improve performance in sports, to improve one's physical appearance, as self-medication to recover from injury, and as an anti-aging aid. Use of anabolic steroids for purposes other than treating medical conditions is controversial and, in some cases, illegal. Major sports organizations have moved to ban the use of anabolic steroids. There is a wide range of health concerns for users. Legislation in many countries restricts and criminalizes AAS possession and trade.
Unethical human experimentation is human experimentation that violates the principles of medical ethics. Such practices have included denying patients the right to informed consent, using pseudoscientific frameworks such as race science, and torturing people under the guise of research. Around World War II, Imperial Japan and Nazi Germany carried out brutal experiments on prisoners and civilians through groups like Unit 731 or individuals like Josef Mengele; the Nuremberg Code was developed after the war in response to the Nazi experiments. Countries have carried out brutal experiments on marginalized populations. Examples include American abuses during Project MKUltra and the Tuskegee syphilis experiments, and the mistreatment of indigenous populations in Canada and Australia. The Declaration of Helsinki, developed by the World Medical Association (WMA), is widely regarded as the cornerstone document on human research ethics.

Doug Eyolfson is a Canadian physician and was a Member of Parliament in the House of Commons of Canada for the riding of Charleswood—St. James—Assiniboia—Headingley. He was elected in the 2015 federal election and was defeated in the 2019 Canadian federal election. He was a member of the Standing Committee on Health, the Standing Committee on Veteran Affairs and the Subcommittee on Sports-Related Concussions in Canada. He was also the chair of the Manitoba Liberal Caucus.

The Cannabis Act (C-45) of June, 2018 paved the way for the legalization of cannabis in Canada on 17 October 2018. Police and prosecution services in all Canadian jurisdictions are currently capable of pursuing criminal charges for cannabis marketing without a licence issued by Health Canada. The Supreme Court of Canada has held that the federal Parliament has the power to criminalize the possession of cannabis and that doing so does not infringe upon the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. The Ontario Court of Appeal and the Superior Court of Ontario have, however, held that the absence of a statutory provision for medical marijuana is unconstitutional, and to that extent the federal law is of no force and/or effect if a prescription is obtained. The recreational use of cannabis has been legalized by the federal government, and took effect on 17 October 2018.
Margaret Pabst Battin, also known as Peggy Battin, is an American philosopher, medical ethicist, author, and a current distinguished professor at the University of Utah. She is a supporter of assisted suicide and has worked extensively on ethical aspects of this issue. In 1993, she was named a Spinoza Chair at the University of Amsterdam for her studies on assisted suicide. Battin is a Hastings Center Fellow. In 2008, Battin's husband became quadriplegic after a bicycle accident, which caused her to refine and augment her thinking about assisted suicide; he died in 2013 after he requested to turn off his life support.











