
The pfl RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure present in some bacteria and originally discovered using bioinformatics. pfl RNAs are consistently present in genomic locations that likely correspond to the 5' untranslated regions of protein-coding genes. This arrangement in bacteria is commonly associated with cis-regulatory elements. Moreover, they are in presumed 5' UTRs of multiple non-homologous genes, suggesting that they function only in these locations. Additional evidence of cis-regulatory function came from the observation that predicted rho-independent transcription terminators overlap pfl RNAs. This overlap suggests that the alternate secondary structures of pfl RNA and the transcription terminator stem-loops compete with each other, and this is a common mechanism for cis gene control in bacteria.

The COG2908 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. COG2908 motif RNAs are found in genomic sequences extracted from fresh water environments. They have not, as of 2018, been detected in any classified organism.
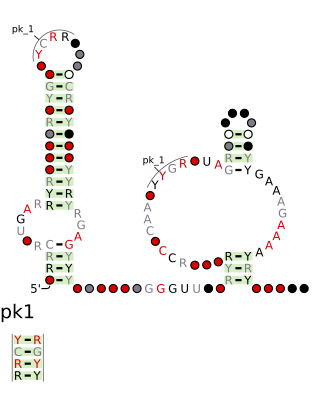
The drum RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Drum motifs are found in Bacillota, Bacteroidota, Pseudomonadota, and Spirochaetota, and exhibit multiple highly conserved nucleotide positions, despite their widespread distribution.
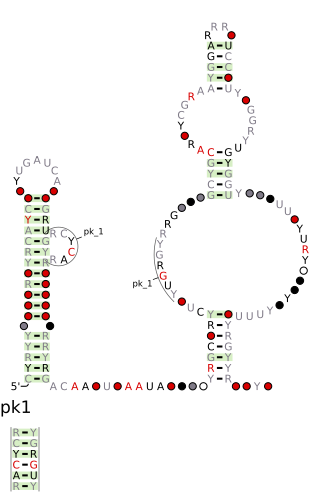
The DUF2800 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF2800 motif RNAs are found in Bacillota. DUF2800 RNAs are also predicted in the phyla Actinomycetota and Synergistota, although these RNAs are likely the result of recent horizontal gene transfer or conceivably sequence contamination.

The DUF3268 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF3268 motifs are found in Bacillota and Clostridia.

The DUF3577 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF3577 motifs are found in the organism Cardiobacterium valvarum and metagenomic sequences from unknown organisms.

The DUF805 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The motif is subdivided into the DUF805 motif and the DUF805b motif, which have similar, but distinct secondary structures. Together, these motifs are found in Bacteroidota, Chlorobiota, and Pseudomonadota.

The folP RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. folP motifs are found in the genus Dialister.

The GA-cis RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. GA-cis motif RNAs are found in one species classified within the phylum Bacillota: specifically, there are 9 predicted copies in Coprocuccus eutactus ATCC 27759.

The hya RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. hya motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota.
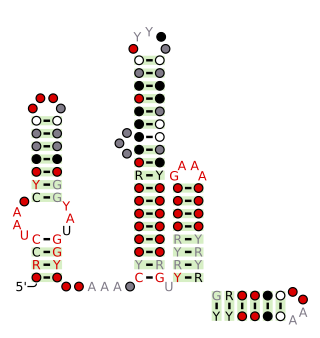
The Latescibacteria, OD1, OP11, TM7 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. LOOT motif RNAs are found in multiple bacterial phyla that have only recently been discovered, and are currently not well understood: Latescibacteria, OD1/Parcubacteria, OP11 AND TM7. In some cases, no specific organism has been isolated in the relevant phylum, but the existence of the bacterial phylum is known only through analysis of metagenomic sequences. Curiously, the LOOT motif is not known in any phylum that has been studied for a long time.

The MDR-NUDIX RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The MDR-NUDIX motif is found in the poorly studied phylum TM7.

The PGK RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. PGK motif RNAs are found in metagenomic sequences isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals. PGK RNAs have not yet been detected in a classified organism.

The Prevotella-2 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Energetically stable tetraloops often occur in this motif. Prevotella-2 motif RNAs are found in the bacterial genus Prevotella.
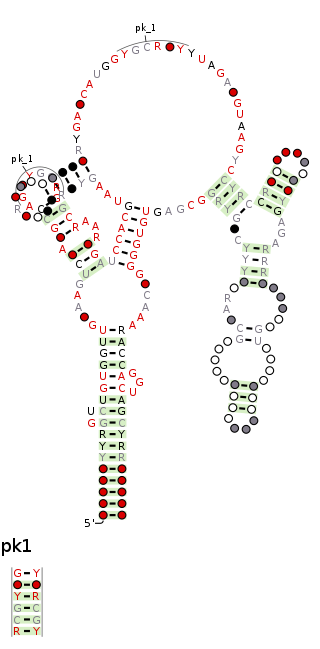
The raiA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. raiA motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota and Bacillota, and have many conserved features—including conserved nucleotide positions, conserved secondary structures and associated protein-coding genes—in both of these phyla. Some conserved features of the raiA RNA motif suggest that they function as cis-regulatory elements, but other aspects of the motif suggest otherwise.

The skipping-rope RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. skipping-rope motif RNAs are found in multiple phyla: Bacillota, Fusobacteriota, Pseudomonadota and Spirochaetota. A skipping-rope RNA was also found in a purified phage, specifically the phage Bacillus phage SPbeta, which infects Bacillus organisms that fit into the phylum Bacillota. Therefore, skipping-rope RNAs likely function, at least sometimes, to perform a function useful to phages.

The ssnA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. ssnA motif RNAs are found in Clostridiales.

The sul1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Energetically stable tetraloops often occur in this motif. sul1 motif RNAs are found in Alphaproteobacteria.

The terC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. terC motif RNAs are found in Pseudomonadota, within the sub-lineages Alphaproteobacteria and Pseudomonadales.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and Gammaproteobacteria.




















