
Clover, also called trefoil, are plants of the genus Trifolium, consisting of about 300 species of flowering plants in the legume family Fabaceae originating in Europe. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution with highest diversity in the temperate Northern Hemisphere, but many species also occur in South America and Africa, including at high altitudes on mountains in the tropics. They are small annual, biennial, or short-lived perennial herbaceous plants, typically growing up to 30 centimetres (12 in) tall. The leaves are trifoliate, with stipules adnate to the leaf-stalk, and heads or dense spikes of small red, purple, white, or yellow flowers; the small, few-seeded pods are enclosed in the calyx. Other closely related genera often called clovers include Melilotus and Medicago.

Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.

Trifolium repens, the white clover, is a herbaceous perennial plant in the bean family Fabaceae. It is native to Europe, including the British Isles, and central Asia and is one of the most widely cultivated types of clover. It has been widely introduced worldwide as a forage crop, and is now also common in most grassy areas of North America, Australia and New Zealand. The species includes varieties often classed as small, intermediate and large, according to height, which reflects petiole length. The term 'white clover' is applied to the species in general, 'Dutch clover' is often applied to intermediate varieties, and 'ladino clover' is applied to large varieties.

Joseph Boyd Poindexter was the eighth Territorial Governor of Hawaii and served from 1934 to 1942.
Isoflavones are substituted derivatives of isoflavone, a type of naturally occurring isoflavonoids, many of which act as phytoestrogens in mammals. Isoflavones are produced almost exclusively by the members of the bean family, Fabaceae (Leguminosae).

Melilotus, known as melilot, sweet clover, and kumoniga, is a genus in the family Fabaceae. Members are known as common grassland plants and as weeds of cultivated ground. Originally from Europe and Asia, it is now found worldwide.

Penicillium roqueforti is a common saprotrophic fungus in the genus Penicillium. Widespread in nature, it can be isolated from soil, decaying organic matter, and plants.
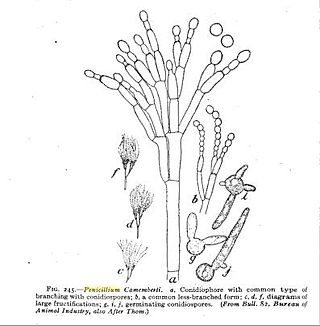
Penicillium camemberti is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is used in the production of Camembert, Brie, Langres, Coulommiers, and Cambozola cheeses, on which colonies of P. camemberti form a hard, white crust. It is responsible for giving these cheeses their distinctive flavors. An allergy to the antibiotic penicillin does not necessarily imply an allergy to cheeses made using P. camemberti.

Melilotus albus, known as honey clover, white melilot (UK), Bokhara clover (Australia), white sweetclover (US), and sweet clover, is a nitrogen-fixing legume in the family Fabaceae. Melilotus albus is considered a valuable honey plant and source of nectar and is often grown for forage. Its characteristic sweet odor, intensified by drying, is derived from coumarin.

Medicago lupulina, commonly known as black medick, nonesuch, or hop clover, is a plant of dry grassland belonging to the legume or clover family. Plants of the genus Medicago, or bur clovers, are closely related to the true clovers (Trifolium) and sweet clover (Melilotus). Like the true clovers, black medick has three leaflets and a small, yellow flower closely resembling those of lesser trefoil. Black medick belongs to the same genus as alfalfa.
Mycotoxicology is the branch of mycology that focuses on analyzing and studying the toxins produced by fungi, known as mycotoxins. In the food industry it is important to adopt measures that keep mycotoxin levels as low as practicable, especially those that are heat-stable. These chemical compounds are the result of secondary metabolism initiated in response to specific developmental or environmental signals. This includes biological stress from the environment, such as lower nutrients or competition for those available. Under this secondary path the fungus produces a wide array of compounds in order to gain some level of advantage, such as incrementing the efficiency of metabolic processes to gain more energy from less food, or attacking other microorganisms and being able to use their remains as a food source.

4-Chloroindole-3-acetic acid (4-Cl-IAA) is an organic compound that functions as a plant hormone.

Penicillium rubens is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium and was the first species known to produce the antibiotic penicillin. It was first described by Philibert Melchior Joseph Ehi Biourge in 1923. For the discovery of penicillin from this species Alexander Fleming shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945. The original penicillin-producing type has been variously identified as Penicillium rubrum, P. notatum, and P. chrysogenum among others, but genomic comparison and phylogenetic analysis in 2011 resolved that it is P. rubens. It is the best source of penicillins and produces benzylpenicillin (G), phenoxymethylpenicillin (V) and octanoylpenicillin (K). It also produces other important bioactive compounds such as andrastin, chrysogine, fungisporin, roquefortine, and sorbicillins.
Penicillium carneum is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium.Penicillium roqueforti var. carneum was reclassified to Penicillium carneum.P. carneum was isolated from spoiled meat products, silage, rye bread, water, beer, cheese, mouldy barkers yeast and cork. P. carneum produces patulin, penicillic acid, penitrem A, mycophenolic acid roquefortines.
Penicillium decaturense is a species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from a fungus in North America. Penicillium decaturense produces citrinin, 15-Deoxyoxalicine B, decaturins A and decaturins A

Cladosporium cladosporioides is a darkly pigmented mold that occurs world-wide on a wide range of materials both outdoors and indoors. It is one of the most common fungi in outdoor air where its spores are important in seasonal allergic disease. While this species rarely causes invasive disease in animals, it is an important agent of plant disease, attacking both the leaves and fruits of many plants. This species produces asexual spores in delicate, branched chains that break apart readily and drift in the air. It is able to grow under low water conditions and at very low temperatures.
Ensifer medicae is a species of gram-negative, nitrogen-fixing, rod-shaped bacteria. They can be free-living or symbionts of leguminous plants in root nodules. E.medicae was first isolated from root nodules on plants in the genus Medicago. Some strains of E.medicae, like WSM419, are aerobic. They are chemoorganotrophic mesophiles that prefer temperatures around 28 °C. In addition to their primary genome, these organisms also have three known plasmids, sized 1,570,951 bp, 1,245,408 bp and 219,313 bp.

Human interactions with fungi include both beneficial uses, whether practical or symbolic, and harmful interactions such as when fungi damage crops, timber, food, or are pathogenic to animals.

Acropteroxys gracilis, the slender lizard beetle, is a species of lizard beetle in the family Erotylidae. It is found in Central America and North America, including into Canada.













