
Chlorine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with formula ClF5. This colourless gas is a strong oxidant that was once a candidate oxidizer for rockets. The molecule adopts a square pyramidal structure with C4v symmetry, as confirmed by its high-resolution 19F NMR spectrum.

Bromine pentafluoride, BrF5, is an interhalogen compound and a fluoride of bromine. It is a strong fluorination reagent.
Iodine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with chemical formula IF5. It is one of the fluorides of iodine. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples appear yellow. It is used as a fluorination reagent and even a solvent in specialized syntheses.
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a valuable Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed when mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in a 2:1 ratio. It is notable for its Lewis acidity and its ability to react with almost all known compounds.

Fluoroantimonic acid is a mixture of hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride, containing various cations and anions. This substance is a superacid that can be over a billion times stronger than 100% pure sulfuric acid, depending on proportion of its ingredients. It has been shown to protonate even hydrocarbons to afford pentacoordinate carbocations. Extreme caution needs to be in place when handling fluoroantimonic acid. It is exceptionally corrosive, but can be stored in containers lined with PTFE (Teflon).
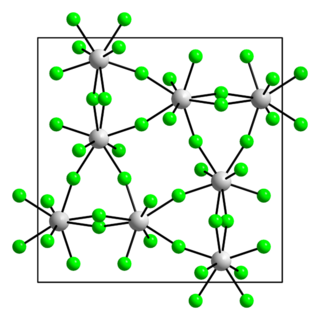
Uranium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula UF5. It is a pale yellow paramagnetic solid. The compound has attracted interest because it is related to uranium hexafluoride, which is widely used to produce uranium fuel. It crystallizes in two polymorphs, called α- and β-UF5.

Gold(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Au2F10. This fluoride compound features gold in its highest known oxidation state. This red solid dissolves in hydrogen fluoride but these solutions decompose, liberating fluorine.

Phosphorus pentafluoride, PF5, is a phosphorus halide. It is a colourless, toxic gas that fumes in air.
Arsenic pentafluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine. It is a toxic, colorless gas. The oxidation state of arsenic is +5.
Bismuth fluoride may refer to:
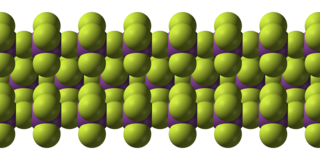
Bismuth pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula BiF5. It is a white solid that is highly reactive. The compound is of interest to researchers but not of particular value.

Niobium(V) fluoride, also known as niobium pentafluoride, is the inorganic compound with the formula NbF5. The solid consists of tetramers [NbF5]4. It is a colorless solid that is rarely used.
Chromium hexafluoride or chromium(VI) fluoride (CrF6) is a hypothetical chemical compound between chromium and fluorine with the chemical formula CrF6. It was previously thought to be an unstable yellow solid decomposing at −100 °C, but this has been shown to be a misidentification of chromium pentafluoride, CrF5.

Vanadium(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula VF5. It is a colorless volatile liquid. It is a highly reactive compound, as indicated by its ability to fluorinate organic substances.

Bromine monofluoride is a quite unstable interhalogen compound with the chemical formula BrF. It can be produced through the reaction of bromine trifluoride (or bromine pentafluoride) and bromine. Due to its lability, the compound can be detected but not isolated:
Chromium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF5. It is a red volatile solid that melts at 34 °C. It is the highest known chromium fluoride, since the hypothetical chromium hexafluoride has not yet been synthesized.

Molybdenum(V) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula MoF5. It is a hygroscopic yellow solid. Like most pentafluorides, it exists as a tetramer.
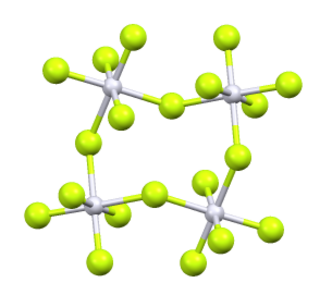
Ruthenium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula RuF5. This green volatile solid has rarely been studied but is of interest as a binary fluoride of ruthenium, i.e. a compound containing only Ru and F. It is sensitive toward hydrolysis. Its structure consists of Ru4F20 tetramers, as seen in the isostructural platinum pentafluoride. Within the tetramers, each Ru adopts octahedral molecular geometry, with two bridging fluoride ligands.

Rhodium pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula Rh4F20. It is a red solid. It is prepared by fluorination of rhodium trifluoride at 400 °C.

Osmium pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula OsF5. It is a blue-green solid. Like the pentafluorides of Ru, Rh, and Ir, OsF5 exists as a tetramer in the solid state.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.











