
Arsine (IUPAC name: arsane) is an inorganic compound with the formula AsH3. This flammable, pyrophoric, and highly toxic pnictogen hydride gas is one of the simplest compounds of arsenic. Despite its lethality, it finds some applications in the semiconductor industry and for the synthesis of organoarsenic compounds. The term arsine is commonly used to describe a class of organoarsenic compounds of the formula AsH3−xRx, where R = aryl or alkyl. For example, As(C6H5)3, called triphenylarsine, is referred to as "an arsine".
Chlorine trifluoride is an interhalogen compound with the formula ClF3. It is a colorless, poisonous, corrosive, and extremely reactive gas that condenses to a pale-greenish yellow liquid, the form in which it is most often sold. It is famous for its extreme oxidation properties. The compound is primarily of interest in plasmaless cleaning and etching operations in the semiconductor industry, in nuclear reactor fuel processing, historically as a component in rocket fuels, and various other industrial operations owing to its corrosive nature.
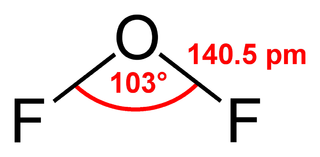
Oxygen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula OF2. As predicted by VSEPR theory, the molecule adopts a bent molecular geometry. It is a strong oxidizer and has attracted attention in rocketry for this reason. With a boiling point of −144.75 °C, OF2 is the most volatile (isolable) triatomic compound. The compound is one of many known oxygen fluorides.

Bromine pentafluoride, BrF5, is an interhalogen compound and a fluoride of bromine. It is a strong fluorinating agent.

Nitrogen trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula. It is a colorless, non-flammable, toxic gas with a slightly musty odor. In contrast with ammonia, it is nonbasic. It finds increasing use within the manufacturing of flat-panel displays, photovoltaics, LEDs and other microelectronics. NF
3 is a greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential (GWP) 17,200 times greater than that of CO
2 when compared over a 100-year period.
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a strong Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed upon mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in 1:1 ratio. It is notable for its strong Lewis acidity and the ability to react with almost all known compounds.

Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula HF. It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils at near room temperature, which is much higher of a temperature than other hydrogen halides.
Tellurium hexafluoride is the inorganic compound of tellurium and fluorine with the chemical formula TeF6. It is a colorless, highly toxic gas with an unpleasant odor.

Disulfur decafluoride is a chemical compound with the formula S2F10. It was discovered in 1934 by Denbigh and Whytlaw-Gray. Each sulfur atom of the S2F10 molecule is octahedral, and surrounded by five fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom. The two sulfur atoms are connected by a single bond. In the S2F10 molecule, the oxidation state of each sulfur atoms is +5, but their valency is 6. S2F10 is highly toxic, with toxicity four times that of phosgene.
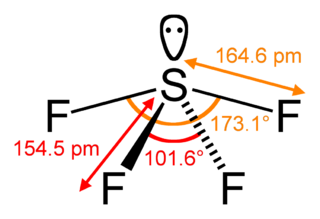
Sulfur tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with the formula SF4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous hydrogen fluoride gas upon exposure to water or moisture. Sulfur tetrafluoride is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds, some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries.

Aluminium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula AlF3. It forms hydrates AlF3·xH2O. Anhydrous AlF3 and its hydrates are all colorless solids. Anhydrous AlF3 is used in the production of aluminium. Several occur as minerals.

Selenium tetrafluoride (SeF4) is an inorganic compound. It is a colourless liquid that reacts readily with water. It can be used as a fluorinating reagent in organic syntheses (fluorination of alcohols, carboxylic acids or carbonyl compounds) and has advantages over sulfur tetrafluoride in that milder conditions can be employed and it is a liquid rather than a gas.
Carbonyl fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula COF2. It is a carbon oxohalide. This gas, like its analog phosgene, is colourless and highly toxic. The molecule is planar with C2v symmetry, bond lengths of 1.174 Å (C=O) and 1.312 Å (C–F), and an F–C–F bond angle of 108.0°.
Perchloryl fluoride is a reactive gas with the chemical formula ClO
3F. It has a characteristic sweet odor that resembles gasoline and kerosene. It is toxic and is a powerful oxidizing and fluorinating agent. It is the acid fluoride of perchloric acid.

Antimony trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF3. Sometimes called Swarts' reagent, it is one of two principal fluorides of antimony, the other being SbF5. It appears as a white solid. As well as some industrial applications, it is used as a reagent in inorganic and organofluorine chemistry.

Phosphorus pentafluoride, PF5, is a phosphorus halide. It is a colourless, toxic gas that fumes in air.

Manganese tetrafluoride, MnF4, is the highest fluoride of manganese. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used as a means of purifying elemental fluorine.
Arsenic trifluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine with the chemical formula AsF3. It is a colorless liquid which reacts readily with water. Like other inorganic arsenic compounds, it is highly toxic.

Vanadium(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula VF5. It is a colorless volatile liquid that freezes near room temperature. It is a highly reactive compound, as indicated by its ability to fluorinate organic substances.
Protactinium(V) fluoride is a fluoride of protactinium with the chemical formula PaF5.


















