
1,4-Dichlorobenzene (1,4-DCB, p-DCB, or para-dichlorobenzene, sometimes abbreviated as PDCB or para) is an aryl chloride and isomer of dichlorobenzene with the formula C6H4Cl2. This colorless solid has a strong odor. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with two chlorine atoms (replacing hydrogen atoms) on opposing sites of the ring.

Dichloromethane is an organochlorine compound with the formula CH2Cl2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odor is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is slightly polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.

Iodoform is the organoiodine compound with the chemical formula CHI3. It is a pale yellow, crystalline, volatile substance, with a penetrating and distinctive odor and, analogous to chloroform, sweetish taste. It is occasionally used as a disinfectant.

Nonane is a linear alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C9H20. It is a colorless, flammable liquid, occurring primarily in the component of the petroleum distillate fraction commonly called kerosene, which is used as a heating, tractor, and jet fuel. Nonane is also used as a solvent, distillation chaser, fuel additive, and a component in biodegradable detergents.
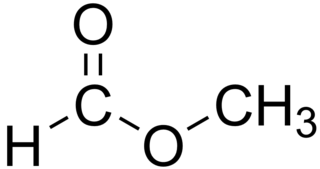
Methyl formate, also called methyl methanoate, is the methyl ester of formic acid. The simplest example of a carboxylate ester, it is a colorless liquid with an ethereal odour, high vapor pressure, and low surface tension. It is a precursor to many other compounds of commercial interest.

Pentaborane(9) is an inorganic compound with the formula B5H9. It is one of the most common boron hydride clusters, although it is a highly reactive compound. Because of its high reactivity with oxygen, it was once evaluated as rocket or jet fuel. Like many of the smaller boron hydrides, pentaborane is colourless, diamagnetic, and volatile. It is related to pentaborane(11).

Bromoform is an organic compound with the chemical formula CHBr3. It is a colorless liquid at room temperature, with a high refractive index and a very high density. Its sweet odor is similar to that of chloroform. It is one of the four haloforms, the others being fluoroform, chloroform, and iodoform. It is a brominated organic solvent. Currently its main use is as a laboratory reagent. It is very slightly soluble in water and is miscible with alcohol, benzene, chloroform, ether, petroleum ether, acetone and oils.
Dimethylacetamide (DMAc or DMA) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)N(CH3)2. This colorless, water-miscible, high-boiling liquid is commonly used as a polar solvent in organic synthesis. DMA is miscible with most other solvents, although it is poorly soluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons.

Bromine pentafluoride, BrF5, is an interhalogen compound and a fluoride of bromine. It is a strong fluorinating agent.

Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005.

Propyl acetate, also known as propyl ethanoate, is an organic compound. Nearly 20,000 tons are produced annually for use as a solvent. This colorless liquid is known by its characteristic odor of pears. Due to this fact, it is commonly used in fragrances and as a flavor additive. It is formed by the esterification of acetic acid and propan-1-ol, often via Fischer–Speier esterification, with sulfuric acid as a catalyst and water produced as a byproduct.
1,2-Dichlorotetrafluoroethane, or R-114, also known as cryofluorane (INN), is a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) with the molecular formula ClF2CCF2Cl. Its primary use has been as a refrigerant. It is a non-flammable gas with a sweetish, chloroform-like odor with the critical point occurring at 145.6 °C and 3.26 MPa. When pressurized or cooled, it is a colorless liquid. It is listed on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's list of ozone depleting chemicals, and is classified as a Montreal Protocol Class I, group 1 ozone depleting substance.
1,1-Dichloroethylene, commonly called vinylidene chloride or 1,1-DCE, is an organochloride with the molecular formula CHCl2CH3. It is a colorless liquid with a sharp odor. Like most chlorocarbons, it is poorly soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. 1,1-DCE was the precursor to the original clingwrap, Saran, for food, but this application has been phased out.

Propylene glycol dinitrate (PGDN, 1,2-propylene glycol dinitrate, or 1,2-propanediol dinitrate) is an organic chemical, an ester of nitric acid and propylene glycol. It is structurally similar to nitroglycerin, except that it has one fewer nitrate group. It is a characteristically and unpleasantly smelling colorless liquid, which decomposes at 121 °C, below its boiling point. It is flammable and explosive. It is shock-sensitive and burns with a clean flame producing water vapor, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen gas.
Propargyl alcohol, or 2-propyn-1-ol, is an organic compound with the formula C3H4O. It is the simplest stable alcohol containing an alkyne functional group. Propargyl alcohol is a colorless viscous liquid that is miscible with water and most polar organic solvents.

Bromochloromethane or methylene bromochloride and Halon 1011 is a mixed halomethane. It is a heavy low-viscosity liquid with refractive index 1.4808.
A recommended exposure limit (REL) is an occupational exposure limit that has been recommended by the United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. The REL is a level that NIOSH believes would be protective of worker safety and health over a working lifetime if used in combination with engineering and work practice controls, exposure and medical monitoring, posting and labeling of hazards, worker training and personal protective equipment. To formulate these recommendations, NIOSH evaluates all known and available medical, biological, engineering, chemical, trade, and other information. Although not legally enforceable limits, RELS are transmitted to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) or the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) of the U.S. Department of Labor for use in promulgating legal standards.

Terphenyls are a group of closely related aromatic hydrocarbons. Also known as diphenylbenzenes or triphenyls, they consist of a central benzene ring substituted with two phenyl groups. There are three substitution patterns: ortho-terphenyl, meta-terphenyl, and para-terphenyl. Commercial grade terphenyl is generally a mixture of the three isomers. This mixture is used in the production of polychlorinated terphenyls, which were formerly used as heat storage and transfer agents.

Diethylethanolamine (DEAE) is the organic compound with the molecular formula (C2H5)2NCH2CH2OH. A colorless liquid, is used as a precursor in the production of a variety of chemical commodities such as the local anesthetic procaine.
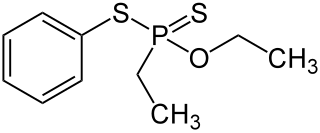
Fonofos is an organothiophosphate insecticide primarily used on corn. It is highly toxic and listed as an extremely hazardous substance.



















