Related Research Articles
Iodine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with chemical formula IF5. It is one of the fluorides of iodine. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples appear yellow. It is used as a fluorination reagent and even a solvent in specialized syntheses.

Xenon tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with chemical formula XeF
4. It was the first discovered binary compound of a noble gas. It is produced by the chemical reaction of xenon with fluorine:

Silver(II) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula AgF2. It is a rare example of a silver(II) compound - silver usually exists in its +1 oxidation state. It is used as a fluorinating agent.
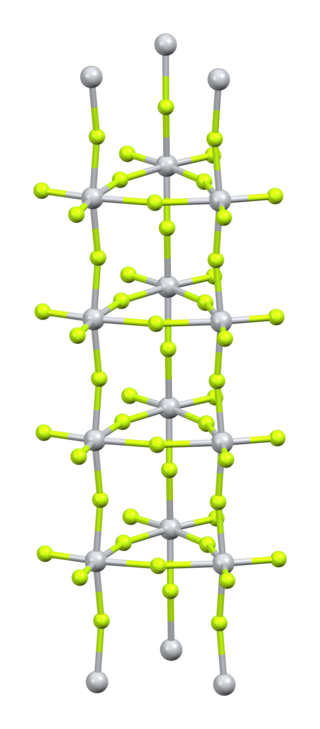
Titanium(IV) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiF4. It is a white hygroscopic solid. In contrast to the other tetrahalides of titanium, it adopts a polymeric structure. In common with the other tetrahalides, TiF4 is a strong Lewis acid.

Manganese tetrafluoride, MnF4, is the highest fluoride of manganese. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used as a means of purifying elemental fluorine.
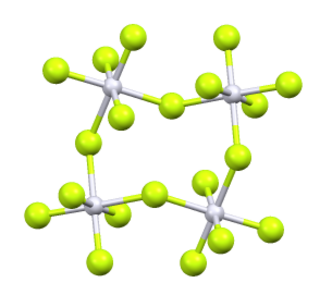
Iridium(V) fluoride, IrF5, is a chemical compound of iridium and fluorine. A highly reactive yellow low melting solid, it has a tetrameric structure, Ir4F20, which contains octahedrally coordinated iridium atoms. This structure is shared with RuF5 and OsF5. It can be prepared by the controlled decomposition of IrF6 or the reduction of IrF6 with silicon powder or H2 in anhydrous HF.

Iridium(IV) fluoride is a chemical compound of iridium and fluorine, with the chemical formula IrF4 and is a dark brown solid. Early reports of IrF4 prior to 1965 are questionable and appear to describe the compound IrF5. The solid can be prepared by reduction of IrF5 with iridium black or reduction with H2 in aqueous HF. The crystal structure of the solid is notable as it was the first example of a three-dimensional lattice structure found for a metal tetrafluoride and subsequently RhF4, PdF4 and PtF4 have been found to have the same structure. The structure has 6 coordinate, octahedral, iridium where two edges of the octahedra are shared and the two unshared fluorine atoms are cis to one another.

Tin(IV) fluoride is a chemical compound of tin and fluorine with the chemical formula SnF4 and is a white solid with a melting point above 700 °C.

Palladium (IV) fluoride, also known as palladium tetrafluoride, is the chemical compound of palladium and fluorine with the chemical formula PdF4. The palladium atoms in PdF4 are in the +4 oxidation state.

Germanium tetrafluoride (GeF4) is a chemical compound of germanium and fluorine. It is a colorless gas.

Osmium hexafluoride, also osmium(VI) fluoride, (OsF6) is a compound of osmium and fluorine, and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.

Chromium(IV) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF4. It has a dark greenish-black color when solid. It rapidly hydrolysizes in presence of moisture in air or directly in water.
Molybdenum(IV) fluoride is a binary compound of molybdenum and fluorine with the chemical formula MoF4.
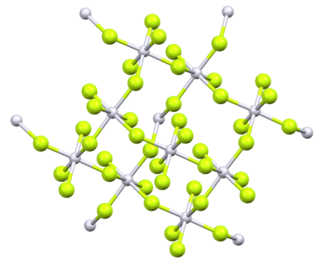
Platinum tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula PtF
4. In the solid state, the compound features platinum(IV) in octahedral coordination geometry.
The fluoronickelates are a class of chemical compounds containing an anion with nickel at its core, surrounded by fluoride ions which act as ligands. This makes it a fluoroanion. The nickel atom can be in a range of oxidation states from +2, +3 to +4. The hexafluoronickelate(IV)2− ion NiF62− contains nickel in the maximal +4 state, and is in octahedral coordination by the fluoride atoms. It forms a commercially available salt Potassium hexafluoronickelate(IV) K2NiF6. Solid double salts can also contain tetrafluoronickelate NiF4 eg K2NiF4.

Krypton(IV) fluoride is a hypothetical inorganic chemical compound of krypton and fluorine with the chemical formula KrF4. At one time researchers thought they had synthesized it, but the claim was discredited. The compound is predicted to be difficult to make and unstable if made. Theoretical analysis indicates KrF4 would have an approximately square planar molecular geometry.
Osmium heptafluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of osmium metal and fluorine with the chemical formula OsF
7. It was first reported in 1966 by the reaction of fluorine and osmium at 600 °C and 400 atm, but later experiments can’t reproduce this compound.

Curium(IV) fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound of curium and fluorine with the chemical formula CmF4.
Osmium fluoride may refer to:
References
- ↑ "osmium(IV) fluorideosmium(IV) fluoride". www.chemsrc.com. Retrieved 28 March 2023.
- ↑ Simons, J. H. (2 December 2012). Fluorine Chemistry V5. Elsevier. p. 95. ISBN 978-0-323-14724-8 . Retrieved 28 March 2023.
- ↑ Lide, David R. (19 June 2003). 1998 Freshman Achievement Award. CRC Press. p. 479. ISBN 978-0-8493-0594-8 . Retrieved 28 March 2023.