Iodine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with chemical formula IF5. It is one of the fluorides of iodine. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples appear yellow. It is used as a fluorination reagent and even a solvent in specialized syntheses.
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a strong Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed upon mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in 1:1 ratio. It is notable for its strong Lewis acidity and the ability to react with almost all known compounds.

Selenium tetrafluoride (SeF4) is an inorganic compound. It is a colourless liquid that reacts readily with water. It can be used as a fluorinating reagent in organic syntheses (fluorination of alcohols, carboxylic acids or carbonyl compounds) and has advantages over sulfur tetrafluoride in that milder conditions can be employed and it is a liquid rather than a gas.

Tantalum(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula TaF5. It is one of the principal molecular compounds of tantalum. Characteristic of some other pentafluorides, the compound is volatile but exists as an oligomer in the solid state.

Gold(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Au2F10. This fluoride compound features gold in its highest known oxidation state. This red solid dissolves in hydrogen fluoride but these solutions decompose, liberating fluorine.

Rhenium heptafluoride is the compound with the formula ReF7. It is a yellow low melting solid and is the only thermally stable metal heptafluoride. It has a distorted pentagonal bipyramidal structure similar to IF7, which was confirmed by neutron diffraction at 1.5 K. The structure is non-rigid, as evidenced by electron diffraction studies.

Iridium hexafluoride, also iridium(VI) fluoride, (IrF6) is a compound of iridium and fluorine and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is one of only a few compounds with iridium in the oxidation state +6.

Iridium(IV) fluoride is a chemical compound of iridium and fluorine, with the chemical formula IrF4 and is a dark brown solid. Early reports of IrF4 prior to 1965 are questionable and appear to describe the compound IrF5. The solid can be prepared by reduction of IrF5 with iridium black or reduction with H2 in aqueous HF. The crystal structure of the solid is notable as it was the first example of a three-dimensional lattice structure found for a metal tetrafluoride and subsequently RhF4, PdF4 and PtF4 have been found to have the same structure. The structure has 6 coordinate, octahedral, iridium where two edges of the octahedra are shared and the two unshared fluorine atoms are cis to one another.
Dinitrogen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula N2F2. It is a gas at room temperature, and was first identified in 1952 as the thermal decomposition product of the fluorine azide. It has the structure F−N=N−F and exists in both cis and trans isomers, as typical for diimides.
Bismuth pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula BiF5. It is a white solid that is highly reactive. The compound is of interest to researchers but not of particular value.

Niobium(V) fluoride, also known as niobium pentafluoride, is the inorganic compound with the formula NbF5. It is a colorless solid.
Chromium hexafluoride or chromium(VI) fluoride (CrF6) is a hypothetical chemical compound between chromium and fluorine with the chemical formula CrF6. It was previously thought to be an unstable yellow solid decomposing at −100 °C, but this has been shown to be a misidentification of chromium pentafluoride, CrF5.
Chromium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF5. It is a red volatile solid that melts at 34 °C. It is the highest known chromium fluoride, since the hypothetical chromium hexafluoride has not yet been synthesized.

Molybdenum(V) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula MoF5. It is a hygroscopic yellow solid. Like most pentafluorides, it exists as a tetramer.
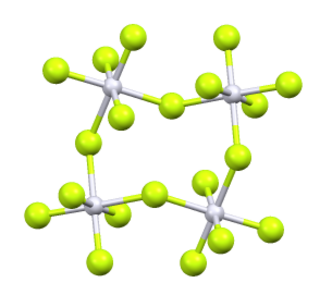
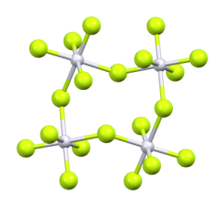
Rhodium pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula Rh4F20. It is a red solid. It is prepared by fluorination of rhodium trifluoride at 400 °C.

Osmium pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula OsF5. It is a blue-green solid. Like the pentafluorides of Ru, Rh, and Ir, OsF5 exists as a tetramer in the solid state.
Iridium compounds are compounds containing the element iridium (Ir). Iridium forms compounds in oxidation states between −3 and +9, but the most common oxidation states are +1, +2, +3, and +4. Well-characterized compounds containing iridium in the +6 oxidation state include IrF6 and the oxides Sr2MgIrO6 and Sr2CaIrO6. iridium(VIII) oxide was generated under matrix isolation conditions at 6 K in argon. The highest oxidation state (+9), which is also the highest recorded for any element, is found in gaseous [IrO4]+.
Rhenium pentafluoride is a binary inorganic compound of rhenium and fluorine with the chemical formula ReF5. This is a salt of rhenium and hydrofluoric acid.
Iridium trifluoride is a binary chemical compound of iridium and fluorine with the chemical formula IrF
3.
The fluoroantimonates are a family of polyatomic weakly coordinating anions composed of antimony and fluorine, consisting of the fluorine adducts of antimony pentafluoride, [(SbF5)nF]−. They occur in the internal chemistry of fluoroantimonic acid.