In chemistry, noble gas compounds are chemical compounds that include an element from the noble gases, group 18 of the periodic table. Although the noble gases are generally unreactive elements, many such compounds have been observed, particularly involving the element xenon.
In chemistry, an interhalogen compound is a molecule which contains two or more different halogen atoms and no atoms of elements from any other group.
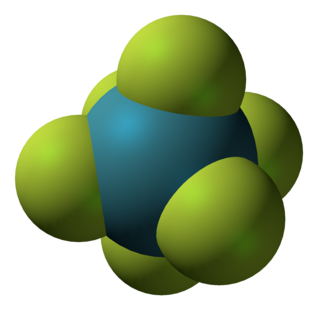
Xenon hexafluoride is a noble gas compound with the formula XeF6. It is one of the three binary fluorides of xenon that have been studied experimentally, the other two being XeF2 and XeF4. All known are exergonic and stable at normal temperatures. XeF6 is the strongest fluorinating agent of the series. It is a colorless solid that readily sublimes into intensely yellow vapors.
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a strong Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed upon mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in 1:1 ratio. It is notable for its strong Lewis acidity and the ability to react with almost all known compounds.

Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF
2, and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwise stable in storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, colourless crystalline solid.

Selenium tetrafluoride (SeF4) is an inorganic compound. It is a colourless liquid that reacts readily with water. It can be used as a fluorinating reagent in organic syntheses (fluorination of alcohols, carboxylic acids or carbonyl compounds) and has advantages over sulfur tetrafluoride in that milder conditions can be employed and it is a liquid rather than a gas.

Krypton difluoride, KrF2 is a chemical compound of krypton and fluorine. It was the first compound of krypton discovered. It is a volatile, colourless solid at room temperature. The structure of the KrF2 molecule is linear, with Kr−F distances of 188.9 pm. It reacts with strong Lewis acids to form salts of the KrF+ and Kr
2F+
3 cations.

The dioxygenyl ion, O+
2, is a rarely-encountered oxycation in which both oxygen atoms have a formal oxidation state of +1/2. It is formally derived from oxygen by the removal of an electron:

Manganese tetrafluoride, MnF4, is the highest fluoride of manganese. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used as a means of purifying elemental fluorine.
A hexafluoride is a chemical compound with the general formula QXnF6, QXnF6m−, or QXnF6m+. Many molecules fit this formula. An important hexafluoride is hexafluorosilicic acid (H2SiF6), which is a byproduct of the mining of phosphate rock. In the nuclear industry, uranium hexafluoride (UF6) is an important intermediate in the purification of this element.
Dinitrogen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula N2F2. It is a gas at room temperature, and was first identified in 1952 as the thermal decomposition product of the fluorine azide. It has the structure F−N=N−F and exists in both cis and trans isomers, as typical for diimides.

The tetrafluoroammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with chemical formula NF+
4. It is equivalent to the ammonium ion where the hydrogen atoms surrounding the central nitrogen atom have been replaced by fluorine. Tetrafluoroammonium ion is isoelectronic with tetrafluoromethane CF
4, trifluoramine oxide ONF
3 and the tetrafluoroborate BF−
4 anion.
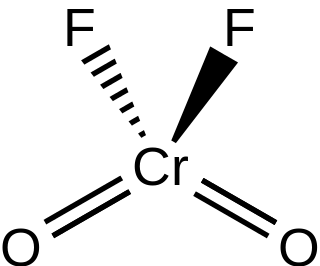
Chromyl fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO2F2. It is a violet-red colored crystalline solid that melts to an orange-red liquid.
Chromium hexafluoride or chromium(VI) fluoride (CrF6) is a hypothetical chemical compound between chromium and fluorine with the chemical formula CrF6. It was previously thought to be an unstable yellow solid decomposing at −100 °C, but this has been shown to be a misidentification of chromium pentafluoride, CrF5.
Nitrogen pentafluoride (NF5) is a theoretical compound of nitrogen and fluorine that is hypothesized to exist based on the existence of the pentafluorides of the atoms below nitrogen in the periodic table, such as phosphorus pentafluoride. Theoretical models of the nitrogen pentafluoride molecule are either a trigonal bipyramidal covalently bound molecule with symmetry group D3h, or NF+
4F−, which would be an ionic solid.
Chromium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF5. It is a red volatile solid that melts at 34 °C. It is the highest known chromium fluoride, since the hypothetical chromium hexafluoride has not yet been synthesized.
Polyhalogen ions are a group of polyatomic cations and anions containing halogens only. The ions can be classified into two classes, isopolyhalogen ions which contain one type of halogen only, and heteropolyhalogen ions with more than one type of halogen.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
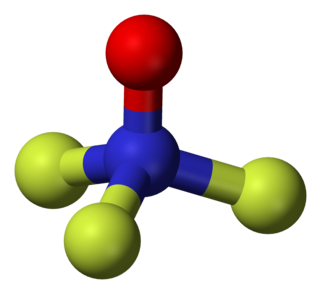
Trifluoramine oxide or Nitrogen trifluoride oxide (F3NO) is an inorganic molecule with strong fluorinating powers.

Chlorine oxide trifluoride or chlorine trifluoride oxide is a corrosive liquid molecular compound with formula ClOF3. It was developed secretly as a rocket fuel oxidiser.










