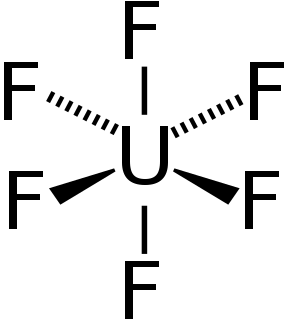
Uranium hexafluoride, colloquially known as "hex" in the nuclear industry, is a compound used in the process of enriching uranium, which produces fuel for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons.

Oxygen fluorides are compounds of elements oxygen and fluorine with the general formula OnF2, where n = 1 to 6. Many different oxygen fluorides are known:

Chlorine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with formula ClF5. This colourless gas is a strong oxidant that was once a candidate oxidizer for rockets. The molecule adopts a square pyramidal structure with C4v symmetry, as confirmed by its high-resolution 19F NMR spectrum. It was first synthesized in 1963.
Dioxygen difluoride (fluorine peroxide) is a compound of fluorine and oxygen with the molecular formula O2F2. It can exist as an orange-colored solid which melts into a red liquid at −163 °C (110 K). It is an extremely strong oxidant and decomposes into oxygen and fluorine even at −160 °C (113 K) at a rate of 4% per day — its lifetime at room temperature is thus extremely short. Dioxygen difluoride reacts vigorously with nearly every chemical it encounters (including ordinary ice) leading to its onomatopoeic nickname "FOOF" (a play on its chemical structure and its explosive tendencies).
Iodine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with chemical formula IF5. It is one of the fluorides of iodine. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples appear yellow. It is used as a fluorination reagent and even a solvent in specialized syntheses.
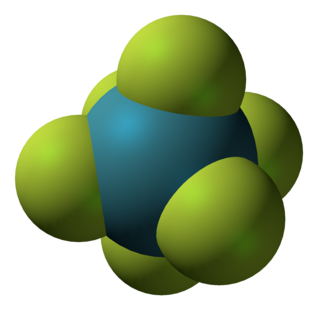
Xenon hexafluoride is a noble gas compound with the formula XeF6. It is one of the three binary fluorides of xenon, the other two being XeF2 and XeF4. All known are exergonic and stable at normal temperatures. XeF6 is the strongest fluorinating agent of the series. It is a colorless solid that readily sublimes into intensely yellow vapors.
Nitryl fluoride, NO2F, is a colourless gas and strong oxidizing agent, which is used as a fluorinating agent and has been proposed as an oxidiser in rocket propellants (though never flown).

Iron(III) fluoride, also known as ferric fluoride, are inorganic compounds with the formula FeF3(H2O)x where x = 0 or 3. They are mainly of interest by researchers, unlike the related iron(III) chlorides. Anhydrous iron(III) fluoride is white, whereas the hydrated forms are light pink.

Copper(II) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuF2. It is a white crystalline, hygroscopic solid with a rutile-type crystal structure, similar to other fluorides of chemical formulae MF2 (where M is a metal).

Cadmium fluoride (CdF2) is a mostly water-insoluble source of cadmium used in oxygen-sensitive applications, such as the production of metallic alloys. In extremely low concentrations (ppm), this and other fluoride compounds are used in limited medical treatment protocols. Fluoride compounds also have significant uses in synthetic organic chemistry. The standard enthalpy has been found to be -167.39 kcal. mole−1 and the Gibbs energy of formation has been found to be -155.4 kcal. mole−1, and the heat of sublimation was determined to be 76 kcal. mole−1.
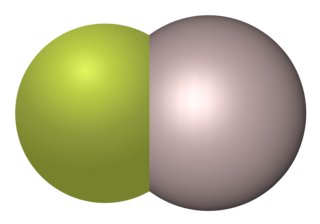
Aluminium monofluoride also known as Fluoridoaluminium is the chemical compound with the formula AlF. This elusive species is formed by the reaction between aluminium trifluoride and metallic aluminium at elevated temperatures but quickly reverts to the reactants when cooled. Clusters derived from related aluminium(I) halides can be stabilized using specialized ligands.

Gold(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Au2F10. This fluoride compound features gold in its highest known oxidation state. This red solid dissolves in hydrogen fluoride but these solutions decompose, liberating fluorine.

Tin(II) fluoride, commonly referred to commercially as stannous fluoride (from Latin stannum, 'tin'), is a chemical compound with the formula SnF2. It is a colourless solid used as an ingredient in toothpastes.

Mercury(IV) fluoride, HgF4, is the first mercury compound to be reported with mercury in the +4 oxidation state. Mercury, like the other group 12 elements (cadmium and zinc), has an s2d10 electron configuration and generally only forms bonds involving its 6s orbital. This means that the highest oxidation state mercury normally attains is +2, and for this reason it is usually considered a post-transition metal instead of a transition metal. HgF4 was first reported from experiments in 2007, but its existence remains disputed; experiments conducted in 2008 could not replicate the compound.
Diboron tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula (BF2)2. A colorless gas, the compound has a halflife of days at room temperature. It is the most stable of the diboron tetrahalides.
A hexafluoride is a chemical compound with the general formula QXnF6, QXnF6m−, or QXnF6m+. Many molecules fit this formula. An important hexafluoride is hexafluorosilicic acid (H2SiF6), which is a byproduct of the mining of phosphate rock. In the nuclear industry, uranium hexafluoride (UF6) is an important intermediate in the purification of this element.
Gold heptafluoride is a gold(V) compound with the empirical formula AuF7. The synthesis of this compound was first reported in 1986. Current calculations suggest that its structure is actually a difluorine ligand on a gold pentafluoride core, AuF5·F2. That would make it the first difluorine complex and the first compound containing a fluorine atom with an oxidation state of zero. The gold(V)–difluorine complex is calculated to be 205 kJ/mol more stable than gold(VII) fluoride. The vibrational frequency at 734 cm−1 is the hallmark of the end-on coordinated difluorine molecule.

Cyanogen fluoride is an inorganic linear compound which consists of a fluorine in a single bond with carbon, and a nitrogen in a triple bond with carbon. It is a toxic and explosive gas at room temperature. It is used in organic synthesis and can be produced by pyrolysis of cyanuric fluoride or by fluorination of cyanogen.

Neptunium(VI) fluoride (NpF6) is the highest fluoride of neptunium, it is also one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is an orange volatile crystalline solid. It is relatively hard to handle, being very corrosive, volatile and radioactive. Neptunium hexafluoride is stable in dry air but reacts vigorously with water.
Silver(III) fluoride, AgF3, is an unstable, bright-red, diamagnetic compound containing silver in the unusual +3 oxidation state. Its crystal structure is very similar to that of gold(III) fluoride: it is a polymer consisting of rectangular AgF4 units linked into chains by fluoro bridges.












