| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Diboron tetrafluoride | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name Tetrafluorodiborane(4) | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
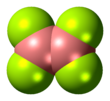
| B2F4 | |||
| Molar mass | 97.61 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Density | 4.3 kg/m3 (gas) | ||
| Melting point | −56 °C (−69 °F; 217 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −34 °C (−29 °F; 239 K) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C) | 79.1 J/mol K | ||
Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 317.3 J/mol K | ||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | −1440.1 kJ/mol | ||
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵) | −1410.4 kJ/mol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Diboron tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula (BF2)2, classed as a tetrahalodiborane. A colorless gas, the compound has a halflife of days at room temperature. It is the most stable of the diboron tetrahalides, [1] and does not appreciably decompose under standard conditions. [2]