
Bromine pentafluoride, BrF5, is an interhalogen compound and a fluoride of bromine. It is a strong fluorinating agent.
Iodine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with chemical formula IF5. It is one of the fluorides of iodine. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples appear yellow. It is used as a fluorination reagent and even a solvent in specialized syntheses.
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a strong Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed upon mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in 1:1 ratio. It is notable for its strong Lewis acidity and the ability to react with almost all known compounds.

Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula HF. It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield an aqueous solution termed hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers, e.g. polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils at near room temperature, much higher than other hydrogen halides.

Manganese tetrafluoride, MnF4, is the highest fluoride of manganese. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used as a means of purifying elemental fluorine.
Arsenic trifluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine with the chemical formula AsF3. It is a colorless liquid which reacts readily with water.
Arsenic pentafluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine. It is a toxic, colorless gas. The oxidation state of arsenic is +5.
Dinitrogen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula N2F2. It is a gas at room temperature, and was first identified in 1952 as the thermal decomposition product of the fluorine azide. It has the structure F−N=N−F and exists in both cis and trans isomers, as typical for diimides.
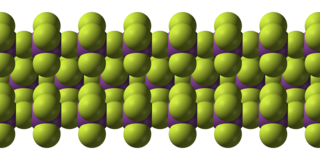
Bismuth pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula BiF5. It is a white solid that is highly reactive. The compound is of interest to researchers but not of particular value.
Chromium hexafluoride or chromium(VI) fluoride (CrF6) is a hypothetical chemical compound between chromium and fluorine with the chemical formula CrF6. It was previously thought to be an unstable yellow solid decomposing at −100 °C, but this has been shown to be a misidentification of chromium pentafluoride, CrF5.

Vanadium(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula VF5. It is a colorless volatile liquid that freezes near room temperature. It is a highly reactive compound, as indicated by its ability to fluorinate organic substances.
Chromium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF5. It is a red volatile solid that melts at 34 °C. It is the highest known chromium fluoride, since the hypothetical chromium hexafluoride has not yet been synthesized.

The hexafluoroarsenate anion is a chemical species with formula AsF−6. Hexafluoroarsenate is relatively inert, being the conjugate base of the notional superacid hexafluoroarsenic acid.
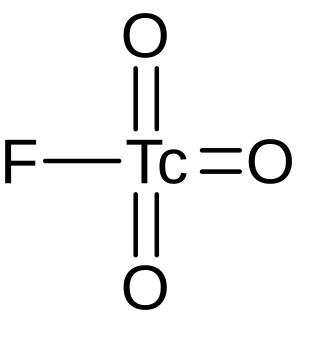
Pertechnetyl fluoride is an inorganic compound, a salt of technetium and hydrofluoric acid with the chemical formula TcO
3F. The compound was originally synthesized by H. Selig and G. Malm in 1963.
Rhenium pentafluoride is a binary inorganic compound of rhenium and fluorine with the chemical formula ReF5. This is a salt of rhenium and hydrofluoric acid.
Perbromyl fluoride is an inorganic compound of bromine, fluorine, and oxygen with the chemical formula BrO3F.
Nickel tetrafluoride is a binary inorganic compound of nickel and fluorine with a chemical formula of NiF4.
Potassium hexafluorotitanate is an inorganic compound of potassium, fluorine, and titanium with the chemical formula K2TiF6.
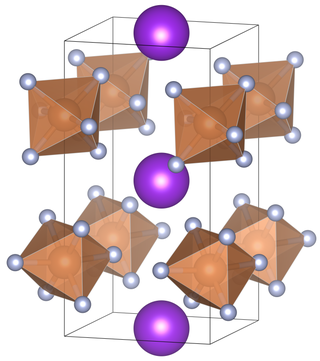
Potassium hexafluoroantimonate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula KSbF6.










