
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula C
6H
8O
6, originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves well in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.

An alum is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double sulfate salt of aluminium with the general formula XAl(SO
4)
2·12 H
2O, where X is a monovalent cation such as potassium or ammonium. By itself, "alum" often refers to potassium alum, with the formula KAl(SO
4)
2·12 H
2O. Other alums are named after the monovalent ion, such as sodium alum and ammonium alum.

Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with a sharp, salty, bitter taste and the chemical formula KNO
3. This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Indian saltpetre (large deposits of which were historically mined in India). It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrate ions NO3−, and is therefore an alkali metal nitrate. It occurs in nature as a mineral, niter (or nitre in the UK). It is a source of nitrogen, and nitrogen was named after niter. Potassium nitrate is one of several nitrogen-containing compounds collectively referred to as saltpeter (or saltpetre in the UK).
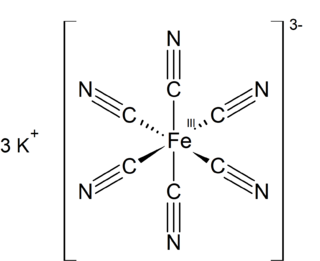
Potassium ferricyanide is the chemical compound with the formula K3[Fe(CN)6]. This bright red salt contains the octahedrally coordinated [Fe(CN)6]3− ion. It is soluble in water and its solution shows some green-yellow fluorescence. It was discovered in 1822 by Leopold Gmelin.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Potassium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2CO3. It is a white salt, which is soluble in water and forms a strongly alkaline solution. It is deliquescent, often appearing as a damp or wet solid. Potassium carbonate is mainly used in the production of soap and glass.

Potassium alum, potash alum, or potassium aluminium sulfate is a chemical compound: the double sulfate of potassium and aluminium, with chemical formula KAl(SO4)2. It is commonly encountered as the dodecahydrate, KAl(SO4)2·12H2O. It crystallizes in an octahedral structure in neutral solution and cubic structure in an alkali solution with space group P a −3 and lattice parameter of 12.18 Å. The compound is the most important member of the generic class of compounds called alums, and is often called simply alum.
Lauric acid, systematically dodecanoic acid, is a saturated fatty acid with a 12-carbon atom chain, thus having many properties of medium-chain fatty acids. It is a bright white, powdery solid with a faint odor of bay oil or soap. The salts and esters of lauric acid are known as laurates.

Arsenic triiodide is the inorganic compound with the formula AsI3. It is an orange to dark red solid that readily sublimes. It is a pyramidal molecule that is useful for preparing organoarsenic compounds.
Barium perchlorate is a powerful oxidizing agent, with the formula Ba(ClO4)2. It is used in the pyrotechnic industry.
Cobalt laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
48CoO
4. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Nickel(II) laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
46NiO
4. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Zinc laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
46ZnO
4. It is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Manganese laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
48MnO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Lanthanum laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
36H
72LaO
6. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Aluminum laurate is an metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
36H
69AlO
6. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Magnesium laurate is a metal-organic compound with the chemical formula C
24H
46MgO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.
Nickel(II) stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of nickel and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70NiO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. The compound is harmful if swallowed and may cause skin sensitization.
Potassium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of potassium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
18H
35KO
2. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.








