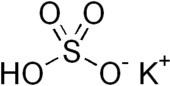 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Potassium hydrogen sulfate | |
| Other names Potassium acid sulfate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.722 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E515(ii) (acidity regulators, ...) |
PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2509 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| KHSO4 | |
| Molar mass | 136.169 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.245 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 197 °C (387 °F; 470 K) |
| Boiling point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) (decomposes to form potassium pyrosulfate and water) |
| 36.6 g/100 mL (0 °C) 49 g/100 mL (20 °C) 121.6 g/100 mL (100 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in acetone, insoluble in ethanol. |
| −49.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | −1163.3 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H314, H335 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P271, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) | 2340 mg*kg−1 |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | Potassium sulfate Sodium bisulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Potassium bisulfate (potassium bisulphate) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KHSO4 and is the potassium acid salt of sulfuric acid. It is a white, water-soluble solid.