
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.

Tin(IV) oxide, also known as stannic oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names, this oxide of tin is an important material in tin chemistry. It is a colourless, diamagnetic, amphoteric solid.
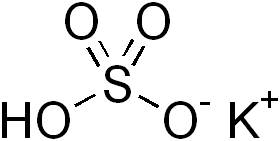
Potassium bisulfate (potassium bisulphate) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KHSO4 and is the potassium acid salt of sulfuric acid. It is a white, water-soluble solid.

Chromyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO2Cl2. It is a reddish brown compound that is a volatile liquid at room temperature, which is unusual for transition metal compounds.

Antimony pentoxide (molecular formula: Sb2O5) is a chemical compound of antimony and oxygen. It contains antimony in the +5 oxidation state.

Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula (ZrF4(H2O)x. All are colorless, diamagnetic solids. Anhydrous Zirconium(IV) fluoride' is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass.

Potassium nonahydridorhenate(VII) is an inorganic compound having the formula K2[ReH9]. This colourless salt is soluble in water but only poorly soluble in most alcohols. This salt contains the nonahydridorhenate(VII) anion, [ReH9]2−, which is a rare example of a coordination complex bearing only hydride ligands.
Organoplatinum chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to platinum chemical bond, and the study of platinum as a catalyst in organic reactions. Organoplatinum compounds exist in oxidation state 0 to IV, with oxidation state II most abundant. The general order in bond strength is Pt-C (sp) > Pt-O > Pt-N > Pt-C (sp3). Organoplatinum and organopalladium chemistry are similar, but organoplatinum compounds are more stable and therefore less useful as catalysts.

Rhenium hexafluoride, also rhenium(VI) fluoride, (ReF6) is a compound of rhenium and fluorine and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.

Polonium dioxide (also known as polonium(IV) oxide) is a chemical compound with the formula PoO2. It is one of three oxides of polonium, the other two being polonium monoxide (PoO) and polonium trioxide (PoO3). It is a pale yellow crystalline solid at room temperature. Under lowered pressure (such as a vacuum), it decomposes into elemental polonium and oxygen at 500 °C. It is the most stable oxide of polonium and is an interchalcogen.
Polonium tetraiodide is a binary inorganic compound of polonium and iodine with the chemical formula PoI
4. The compound forms volatile black crystals.
Osmium iodide refers to compounds of osmium with the formula OsIn. Several have been mentioned in the literature, but only the triiodide has been verified by X-ray crystallography.
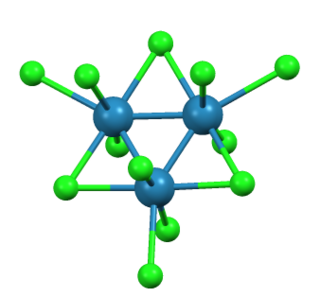
Rhenium(III) bromide is a chemical compound with the formula Re3Br9. It is a black lustrous crystalline solid. This compound reacts with water to form rhenium(IV) oxide and is isostructural with rhenium(III) chloride.
Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from -3 to +7 except -2, although the oxidation states +7, +4, and +3 are the most common. Rhenium is most available commercially as salts of perrhenate, including sodium and ammonium perrhenates. These are white, water-soluble compounds. The tetrathioperrhenate anion [ReS4]− is possible.

Disulfur diiodide is an unstable inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula S2I2. It is a red-brown solid that decomposes above −30 °C to elemental sulfur and iodine.

Potassium hexachlororhenate, also known as potassium chlororhenite, is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula K2ReCl6. It is a light-green crystalline solid soluble in hydrochloric acid.
Potassium hexafluorotitanate is an inorganic compound of potassium, fluorine, and titanium with the chemical formula K2TiF6.
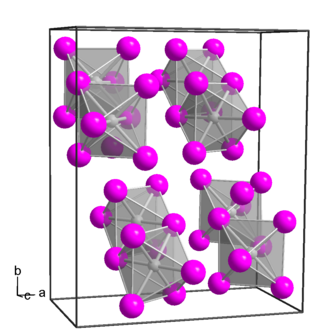
Platinum(IV) iodide is a inorganic compound with the formula PtI4. it is a dark brown diamagnetic solid and is one of several binary iodides of platinum.
Potassium hexabromorhenate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula K2ReBr6.
Potassium hexafluororhenate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula K2ReF6.













