Related Research Articles
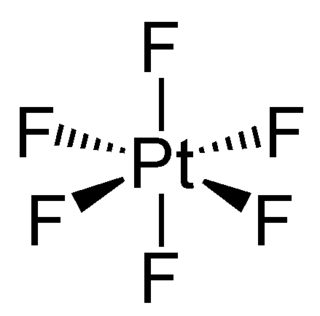
Platinum hexafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula PtF6, and is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is a dark-red volatile solid that forms a red gas. The compound is a unique example of platinum in the +6 oxidation state. With only four d-electrons, it is paramagnetic with a triplet ground state. PtF6 is a strong fluorinating agent and one of the strongest oxidants, capable of oxidising xenon and O2. PtF6 is octahedral in both the solid state and in the gaseous state. The Pt-F bond lengths are 185 picometers.
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a strong Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed upon mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in 1:1 ratio. It is notable for its strong Lewis acidity and the ability to react with almost all known compounds.

Tantalum(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula TaF5. It is one of the principal molecular compounds of tantalum. Characteristic of some other pentafluorides, the compound is volatile but exists as an oligomer in the solid state.
Osmium compounds are compounds containing the element osmium (Os). Osmium forms compounds with oxidation states ranging from −2 to +8. The most common oxidation states are +2, +3, +4, and +8. The +8 oxidation state is notable for being the highest attained by any chemical element aside from iridium's +9 and is encountered only in xenon, ruthenium, hassium, iridium, and plutonium. The oxidation states −1 and −2 represented by the two reactive compounds Na
2[Os
4(CO)
13] and Na
2[Os(CO)
4] are used in the synthesis of osmium cluster compounds.

The dioxygenyl(or dioxyl) ion, O+
2, is a rarely-encountered oxycation in which both oxygen atoms have a formal oxidation state of +1/2. It is formally derived from oxygen by the removal of an electron:
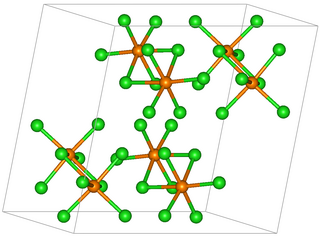
Rhenium pentachloride is an inorganic compound of chlorine and rhenium. The compound has the formula Re2Cl10 but it is usually referred to as rhenium pentachloride. It is a red-brown solid.

Rhenium heptafluoride is the compound with the formula ReF7. It is a yellow low melting solid and is the only thermally stable metal heptafluoride. It has a distorted pentagonal bipyramidal structure similar to IF7, which was confirmed by neutron diffraction at 1.5 K. The structure is non-rigid, as evidenced by electron diffraction studies.
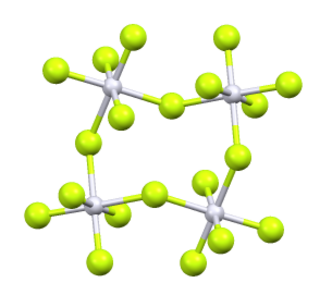
Iridium(V) fluoride, IrF5, is a chemical compound of iridium and fluorine. A highly reactive yellow low melting solid, it has a tetrameric structure, Ir4F20, which contains octahedrally coordinated iridium atoms. This structure is shared with RuF5 and OsF5. It can be prepared by the controlled decomposition of IrF6 or the reduction of IrF6 with silicon powder or H2 in anhydrous HF.

Iridium(IV) fluoride is a chemical compound of iridium and fluorine, with the chemical formula IrF4 and is a dark brown solid. Early reports of IrF4 prior to 1965 are questionable and appear to describe the compound IrF5. The solid can be prepared by reduction of IrF5 with iridium black or reduction with H2 in aqueous HF. The crystal structure of the solid is notable as it was the first example of a three-dimensional lattice structure found for a metal tetrafluoride and subsequently RhF4, PdF4 and PtF4 have been found to have the same structure. The structure has 6 coordinate, octahedral, iridium where two edges of the octahedra are shared and the two unshared fluorine atoms are cis to one another.
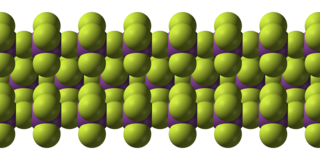
Bismuth pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula BiF5. It is a white solid that is highly reactive. The compound is of interest to researchers but not of particular value.

Rhenium hexafluoride, also rhenium(VI) fluoride, (ReF6) is a compound of rhenium and fluorine and one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Rhenium(VII) sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Re2S7. It has a complex structure, but can be synthesized from direct combination of the elements:
Chromium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF5. It is a red volatile solid that melts at 34 °C. It is the highest known chromium fluoride, since the hypothetical chromium hexafluoride has not yet been synthesized.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
Rhenium fluoride can refer to
Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from -3 to +7 except -2, although the oxidation states +7, +4, and +3 are the most common. Rhenium is most available commercially as salts of perrhenate, including sodium and ammonium perrhenates. These are white, water-soluble compounds. The tetrathioperrhenate anion [ReS4]− is possible.
Rhenium tetrafluoride is a binary inorganic compound of rhenium and fluorine with the chemical formula ReF4.

Ruthenium(IV) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of ruthenium and fluorine with the formula RuF4.
Technetium pentaluoride is a binary inorganic chemical compound of technetium metal and fluorine with the chemical formula TcF
5.

Rhenium(III) iodide is a binary chemical compound of rhenium and iodide with the chemical formula ReI
3.
References
- ↑ Gutmann, Viktor (2 December 2012). Halogen Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 192. ISBN 978-0-323-14847-4 . Retrieved 6 April 2023.
- ↑ Hawkins, Donald T. (6 December 2012). Binary Fluorides: Free Molecular Structures and Force Fields A Bibliography (1957–1975). Springer Science & Business Media. p. 50. ISBN 978-1-4684-6147-3 . Retrieved 6 April 2023.
- ↑ Colton, Ray (1965). The Chemistry of Rhenium and Technetium. Interscience Publishers. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-470-16650-5 . Retrieved 6 April 2023.