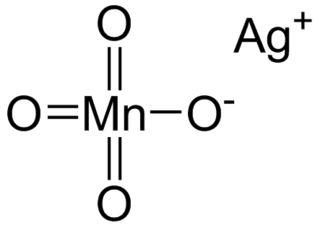Group 7, numbered by IUPAC nomenclature, is a group of elements in the periodic table. It contains manganese (Mn), technetium (Tc), rhenium (Re) and bohrium (Bh). This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table, and are hence transition metals. This group is sometimes called the manganese group or manganese family after its lightest member; however, the group itself has not acquired a trivial name because it belongs to the broader grouping of the transition metals.

A permanganate is a chemical compound with the manganate(VII) ion, MnO−
4, the conjugate base of permanganic acid. Because the manganese atom has a +7 oxidation state, the permanganate(VII) ion is a strong oxidising agent. The ion is a transition metal ion with a tetrahedral structure. Permanganate solutions are purple in colour and are stable in neutral or slightly alkaline media. The exact chemical reaction depends on the carbon-containing reactants present and the oxidant used. For example, trichloroethane (C2H3Cl3) is oxidised by permanganate ions to form carbon dioxide (CO2), manganese dioxide (MnO2), hydrogen ions (H+), and chloride ions (Cl−).

Perrhenic acid is the chemical compound with the formula Re2O7(H2O)2. It is obtained by evaporating aqueous solutions of Re2O7. Conventionally, perrhenic acid is considered to have the formula HReO4, and a species of this formula forms when rhenium(VII) oxide sublimes in the presence of water or steam. When a solution of Re2O7 is kept for a period of months, it breaks down and crystals of HReO4·H2O are formed, which contain tetrahedral ReO−4. For most purposes, perrhenic acid and rhenium(VII) oxide are used interchangeably. Rhenium can be dissolved in nitric or concentrated sulfuric acid to produce perrhenic acid.
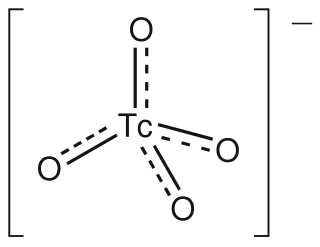
The pertechnetate ion is an oxyanion with the chemical formula TcO−
4. It is often used as a convenient water-soluble source of isotopes of the radioactive element technetium (Tc). In particular it is used to carry the 99mTc isotope which is commonly used in nuclear medicine in several nuclear scanning procedures.
A salt metathesis reaction, sometimes called a double displacement reaction, is a chemical process involving the exchange of bonds between two reacting chemical species which results in the creation of products with similar or identical bonding affiliations. This reaction is represented by the general scheme:
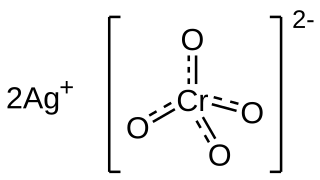
Silver chromate is an inorganic compound with formula Ag2CrO4 which appears as distinctively coloured brown-red crystals. The compound is insoluble and its precipitation is indicative of the reaction between soluble chromate and silver precursor salts (commonly potassium/sodium chromate with silver nitrate). This reaction is important for two uses in the laboratory: in analytical chemistry it constitutes the basis for the Mohr method of argentometry, whereas in neuroscience it is used in the Golgi method of staining neurons for microscopy.

Rhenium(VII) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Re2O7. This yellowish solid is the anhydride of HOReO3. Perrhenic acid, Re2O7·2H2O, is closely related to Re2O7. Re2O7 is the raw material for all rhenium compounds, being the volatile fraction obtained upon roasting the host ore.

Sodium perrhenate (also known as sodium rhenate(VII)) is the inorganic compound with the formula NaReO4. It is a white salt that is soluble in water. It is a common precursor to other rhenium compounds. Its structure resembles that of sodium perchlorate and sodium permanganate.

Potassium nonahydridorhenate(VII) is an inorganic compound having the formula K2[ReH9]. This colourless salt is soluble in water but only poorly soluble in most alcohols. This salt contains the nonahydridorhenate(VII) anion, [ReH9]2−, which is a rare example of a coordination complex bearing only hydride ligands.
The perrhenate ion is the anion with the formula ReO−
4, or a compound containing this ion. The perrhenate anion is tetrahedral, being similar in size and shape to perchlorate and the valence isoelectronic permanganate. The perrhenate anion is stable over a broad pH range and can be precipitated from solutions with the use of organic cations. At normal pH, perrhenate exists as metaperrhenate, but at high pH mesoperrhenate forms. Perrhenate, like its conjugate acid perrhenic acid, features rhenium in the oxidation state of +7 with a d0 configuration. Solid perrhenate salts takes on the color of the cation.

Ammonium permanganate is the chemical compound NH4MnO4, or NH3·HMnO4. It is a water soluble, violet-brown or dark purple salt.
Organorhenium chemistry describes the compounds with Re−C bonds. Because rhenium is a rare element, relatively few applications exist, but the area has been a rich source of concepts and a few useful catalysts.
Stock nomenclature for inorganic compounds is a widely used system of chemical nomenclature developed by the German chemist Alfred Stock and first published in 1919. In the "Stock system", the oxidation states of some or all of the elements in a compound are indicated in parentheses by Roman numerals.
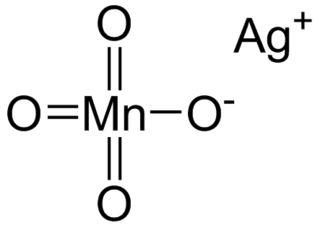
Silver permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula AgMnO4. This salt is a purple crystal adopting a monoclinic crystal system. It decomposes when heated or mixed with water, and heating to high temperature may lead to explosion. The compound is used in gas masks.

Neodymium perrhenate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Nd(ReO4)3, which exists in anhydrous and tetrahydrate. It can be obtained by reacting excess neodymium oxide with 240 g/L perrhenic acid solution. In its solution, NdReO42+ and Nd(ReO4)2+ can be observed with stability constants of 16.5 and 23.6, respectively.
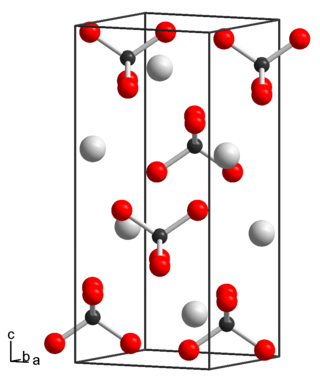
Potassium perrhenate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KReO4.
Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from -3 to +7 except -2, although the oxidation states +7, +4, and +3 are the most common. Rhenium is most available commercially as salts of perrhenate, including sodium and ammonium perrhenates. These are white, water-soluble compounds. The tetrathioperrhenate anion [ReS4]− is possible.
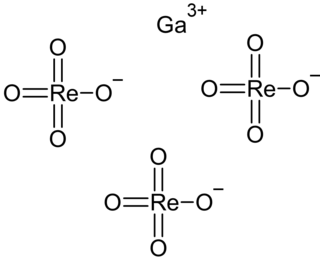
Gallium perrhenate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of Ga(ReO4)3. It exists in the anhydrous and hydrate forms.
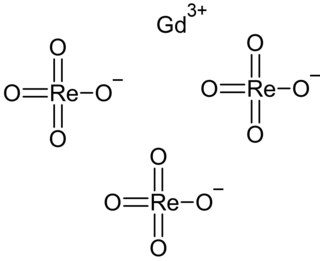
Gadolinium perrhenate is an inorganic compound, with the chemical formula of Gd(ReO4)3. It can be obtained by dissolving an excess of gadolinium oxide in a perrhenic acid solution (240 g/L) in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, from which the hydrates are precipitated. Its tetrahydrate loses water by heating to obtain the anhydrous form, which then decomposes at high temperatures to generate gadolinium oxide and rhenium heptoxide.