
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula AgNO
3. It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called lunar caustic because silver was called luna by ancient alchemists who associated silver with the moon. In solid silver nitrate, the silver ions are three-coordinated in a trigonal planar arrangement.

Silver iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula AgI. The compound is a bright yellow solid, but samples almost always contain impurities of metallic silver that give a gray coloration. The silver contamination arises because some samples of AgI can be highly photosensitive. This property is exploited in silver-based photography. Silver iodide is also used as an antiseptic and in cloud seeding.

Silver sulfide is an inorganic compound with the formula Ag
2S. A dense black solid, it is the only sulfide of silver. It is useful as a photosensitizer in photography. It constitutes the tarnish that forms over time on silverware and other silver objects. Silver sulfide is insoluble in most solvents, but is degraded by strong acids. Silver sulfide is a network solid made up of silver and sulfur where the bonds have low ionic character.

Silver chloride is a chemical compound with the chemical formula AgCl. This white crystalline solid is well known for its low solubility in water and its sensitivity to light. Upon illumination or heating, silver chloride converts to silver, which is signaled by grey to black or purplish coloration in some samples. AgCl occurs naturally as a mineral chlorargyrite.
Lead hydrogen arsenate, also called lead arsenate, acid lead arsenate or LA, chemical formula PbHAsO4, is an inorganic insecticide used primarily against the potato beetle. Lead arsenate was the most extensively used arsenical insecticide. Two principal formulations of lead arsenate were marketed: basic lead arsenate (Pb5OH(AsO4)3, CASN: 1327-31-7) and acid lead arsenate (PbHAsO4).
Naturally occurring silver (47Ag) is composed of the two stable isotopes 107Ag and 109Ag in almost equal proportions, with 107Ag being slightly more abundant. 40 radioisotopes have been characterized with the most stable being 105Ag with a half-life of 41.29 days, 111Ag with a half-life of 7.43 days, and 112Ag with a half-life of 3.13 hours.
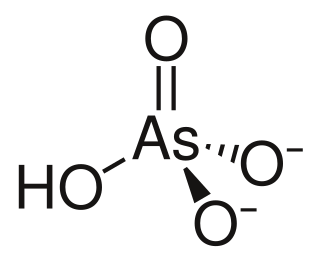
In chemistry, an arsenite is a chemical compound containing an arsenic oxyanion where arsenic has oxidation state +3. Note that in fields that commonly deal with groundwater chemistry, arsenite is used generically to identify soluble AsIII anions. IUPAC have recommended that arsenite compounds are to be named as arsenate(III), for example ortho-arsenite is called trioxidoarsenate(III). Ortho-arsenite contrasts to the corresponding anions of the lighter members of group 15, phosphite which has the structure HPO2−3 and nitrite, NO−2 which is bent.

Silver oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2O. It is a fine black or dark brown powder that is used to prepare other silver compounds.

Copper arsenate (Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, or Cu5H2(AsO4)4·2H2O), also called copper orthoarsenate, tricopper arsenate, cupric arsenate, or tricopper orthoarsenate, is a blue or bluish-green powder insoluble in water and alcohol and soluble in aqueous ammonium and dilute acids. Its CAS number is 7778-41-8 or 10103-61-4.

Silver cyanide is the chemical compound with the formula AgCN. It is a white salt that is precipitated upon treatment of solutions containing Ag+ with cyanide, which is used in some schemes to recover silver from solution. Silver cyanide is used in silver-plating.
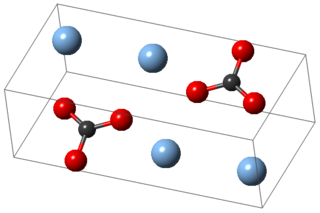
Silver carbonate is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2CO3. This salt is yellow but typical samples are grayish due to the presence of elemental silver. It is poorly soluble in water, like most transition metal carbonates.

Silver sulfate is the inorganic compound with the formula Ag2SO4. It is a white solid with low solubility in water.

Silver azide is the chemical compound with the formula AgN3. It is a silver(I) salt of hydrazoic acid. It forms a colorless crystals. Like most azides, it is a primary explosive.

Silver iodate (AgIO3) is a light-sensitive, white crystal composed of silver, iodine and oxygen. Unlike most metal iodates, it is practically insoluble in water.

Silver oxalate is commonly employed in experimental petrology to add carbon dioxide to experiments as it will break down to silver (Ag) and carbon dioxide under geologic conditions. It is also a precursor to the production of silver nanoparticles. It is explosive upon heating around 140 degrees Celsius, shock or friction.
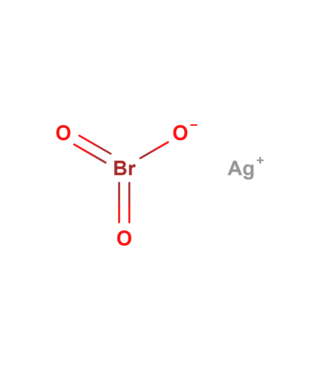
Silver bromate (AgBrO3), is a toxic, light and heat-sensitive, white powder.
Silver selenite is an inorganic compound of formula Ag2SeO3.

Silver phosphate or silver orthophosphate is a light sensitive, yellow, water-insoluble chemical compound composed of silver and phosphate ions of formula Ag3PO4.

Silver sulfite is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2SO3. This unstable silver compound when heated and/or in light it decomposes to silver dithionate and silver sulfate.

Compounds of arsenic resemble in some respects those of phosphorus which occupies the same group (column) of the periodic table. The most common oxidation states for arsenic are: −3 in the arsenides, which are alloy-like intermetallic compounds, +3 in the arsenites, and +5 in the arsenates and most organoarsenic compounds. Arsenic also bonds readily to itself as seen in the square As3−
4 ions in the mineral skutterudite. In the +3 oxidation state, arsenic is typically pyramidal owing to the influence of the lone pair of electrons.



















