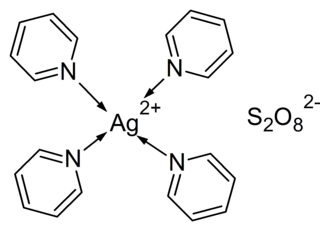In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO2H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to an organyl group, or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

In organic chemistry, an aldehyde is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure R−CH=O. The functional group itself can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology.
Chromic acid is jargon for a solution formed by the addition of sulfuric acid to aqueous solutions of dichromate. It consists at least in part of chromium trioxide.

In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula −CH2−HC=CH2. It consists of a methylene bridge attached to a vinyl group. The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, Allium sativum. In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "Schwefelallyl". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to H2C=CH−CH2, some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride.
The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. The reaction was reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912.
The Kornblum oxidation, named after Nathan Kornblum, is an organic oxidation reaction that converts alkyl halides and tosylates into carbonyl compounds.

Dess–Martin periodinane (DMP) is a chemical reagent used in the Dess–Martin oxidation, oxidizing primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary alcohols to ketones. This periodinane has several advantages over chromium- and DMSO-based oxidants that include milder conditions, shorter reaction times, higher yields, simplified workups, high chemoselectivity, tolerance of sensitive functional groups, and a long shelf life. However, use on an industrial scale is made difficult by its cost and its potentially explosive nature. It is named after the American chemists Daniel Benjamin Dess and James Cullen Martin who developed the reagent in 1983. It is based on IBX, but due to the acetate groups attached to the central iodine atom, DMP is much more reactive than IBX and is much more soluble in organic solvents.

Hydrogen iodide (HI) is a diatomic molecule and hydrogen halide. Aqueous solutions of HI are known as hydroiodic acid or hydriodic acid, a strong acid. Hydrogen iodide and hydroiodic acid are, however, different in that the former is a gas under standard conditions, whereas the other is an aqueous solution of the gas. They are interconvertible. HI is used in organic and inorganic synthesis as one of the primary sources of iodine and as a reducing agent.

Hydroperoxides or peroxols are compounds of the form ROOH, where R stands for any group, typically organic, which contain the hydroperoxy functional group. Hydroperoxide also refers to the hydroperoxide anion and its salts, and the neutral hydroperoxyl radical (•OOH) consist of an unbond hydroperoxy group. When R is organic, the compounds are called organic hydroperoxides. Such compounds are a subset of organic peroxides, which have the formula ROOR. Organic hydroperoxides can either intentionally or unintentionally initiate explosive polymerisation in materials with unsaturated chemical bonds.

Sodium dichromate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2Cr2O7. However, the salt is usually handled as its dihydrate Na2Cr2O7·2H2O. Virtually all chromium ore is processed via conversion to sodium dichromate and virtually all compounds and materials based on chromium are prepared from this salt. In terms of reactivity and appearance, sodium dichromate and potassium dichromate are very similar. The sodium salt is, however, around twenty times more soluble in water than the potassium salt (49 g/L at 0 °C) and its equivalent weight is also lower, which is often desirable.
The Corey–Kim oxidation is an oxidation reaction used to synthesize aldehydes and ketones from primary and secondary alcohols. It is named for American chemist and Nobel Laureate Elias James Corey and Korean-American chemist Choung Un Kim.
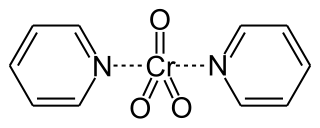
Collins reagent is the complex of chromium(VI) oxide with pyridine in dichloromethane. This metal-pyridine complex, a red solid, is used to oxidize primary alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes and secondary alcohols to the corresponding ketones. This complex is a hygroscopic orange solid.

The Cornforth reagent (pyridinium dichromate or PDC) is a pyridinium salt of dichromate with the chemical formula [C5H5NH]2[Cr2O7]. This compound is named after the Australian-British chemist Sir John Warcup Cornforth (b. 1917) who introduced it in 1962. The Cornforth reagent is a strong oxidizing agent which can convert primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones respectively. In its chemical structure and functions it is closely related to other compounds made from hexavalent chromium oxide, such as pyridinium chlorochromate and Collins reagent. Because of their toxicity, these reagents are rarely used nowadays.

N,N′-Dimethylpropyleneurea (DMPU) is a cyclic urea sometimes used as a polar, aprotic organic solvent. In 1985, Dieter Seebach showed that it is possible to replace the suspected carcinogen hexamethylphosphoramide (HMPA) with DMPU.
Alcohol oxidation is a collection of oxidation reactions in organic chemistry that convert alcohols to aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters where the carbon carries a higher oxidation state. The reaction mainly applies to primary and secondary alcohols. Secondary alcohols form ketones, while primary alcohols form aldehydes or carboxylic acids.
Oxidation with chromium(VI) complexes involves the conversion of alcohols to carbonyl compounds or more highly oxidized products through the action of molecular chromium(VI) oxides and salts. The principal reagents are Collins reagent, PDC, and PCC. These reagents represent improvements over inorganic chromium(VI) reagents such as Jones reagent.

Oxoammonium-catalyzed oxidation reactions involve the conversion of organic substrates to more highly oxidized materials through the action of an N-oxoammonium species. Nitroxides may also be used in catalytic amounts in the presence of a stoichiometric amount of a terminal oxidant. Nitroxide radical species used are either 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO) or derivatives thereof.
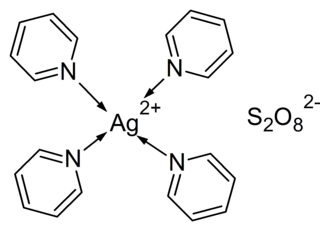
Tetrakis(pyridine)silver(II) peroxydisulfate is a chemical compound which contains silver in the rare oxidation state of +2.

MoOPH, also known as oxodiperoxymolybdenum(pyridine)-(hexamethylphosphoric triamide), is a reagent used in organic synthesis. It contains a molybdenum(VI) center with multiple oxygen ligands, coordinated with pyridine and HMPA ligands, although the HMPA can be replaced by DMPU. It is an electrophilic source of oxygen that reacts with enolates and related structures, and thus can be used for alpha-hydroxylation of carbonyl-containing compounds. Other reagents used for alpha-hydroxylation via enol or enolate structures include Davis oxaziridine, oxygen, and various peroxyacids. This reagent was first utilized by Edwin Vedejs as an efficient alpha-hydroxylating agent in 1974 and an effective preparative procedure was later published in 1978.

Transition metal pyridine complexes encompass many coordination complexes that contain pyridine as a ligand. Most examples are mixed-ligand complexes. Many variants of pyridine are also known to coordinate to metal ions, such as the methylpyridines, quinolines, and more complex rings.