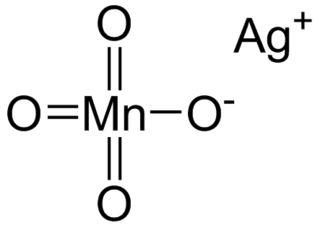Urea, also called carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two amino groups joined by a carbonyl functional group. It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula NH4NO3. It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer.

Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula AgNO
3. It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called lunar caustic because silver was called luna by ancient alchemists who associated silver with the moon. In solid silver nitrate, the silver ions are three-coordinated in a trigonal planar arrangement.

Lead(II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb(NO3)2. It commonly occurs as a colourless crystal or white powder and, unlike most other lead(II) salts, is soluble in water.
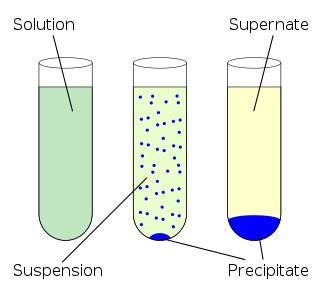
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the "sedimentation of a solid material from a liquid solution". The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemical reagent causing the solid to form is called the precipitant.

Dinitrogen pentoxide is the chemical compound with the formula N2O5. It is one of the binary nitrogen oxides, a family of compounds that contain only nitrogen and oxygen. It exists as colourless crystals that sublime slightly above room temperature, yielding a colorless gas.

Silver chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula AgCl. This white crystalline solid is well known for its low solubility in water and its sensitivity to light. Upon illumination or heating, silver chloride converts to silver, which is signaled by grey to black or purplish coloration in some samples. AgCl occurs naturally as the mineral chlorargyrite.

The cyanate ion is an anion with the chemical formula OCN−. It is a resonance of three forms: [O−−C≡N] (61%) ↔ [O=C=N−] (30%) ↔ [O+≡C−N2−] (4%).

Silver azide is the chemical compound with the formula AgN3. It is a silver(I) salt of hydrazoic acid. It forms a colorless crystals. Like most azides, it is a primary explosive.
In chemistry, an ate complex is a salt formed by the reaction of a Lewis acid with a Lewis base whereby the central atom increases its valence and gains a negative formal charge..

Organosilver chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to silver chemical bond. The theme is less developed than organocopper chemistry.

Manganese(II) nitrate refers to the inorganic compounds with formula Mn(NO3)2·(H2O)n. These compounds are nitrate salts containing varying amounts of water. A common derivative is the tetrahydrate, Mn(NO3)2·4H2O, but mono- and hexahydrates are also known as well as the anhydrous compound. Some of these compounds are useful precursors to the oxides of manganese. Typical of a manganese(II) compound, it is a paramagnetic pale pink solid.
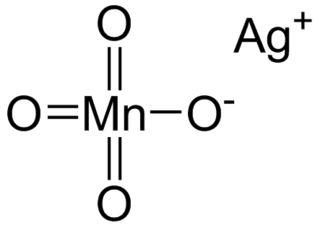
Silver permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula AgMnO4. This salt is a purple crystal adopting a monoclinic crystal system. It decomposes when heated or mixed with water, and heating to high temperature may lead to explosion. The compound is used in gas masks.

Silver thiocyanate is the silver salt of thiocyanic acid with the formula AgSCN. Silver thiocyanate appears as a white crystalline powder. It is very commonly used in the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Additionally, studies have found silver nanoparticles to be present in saliva present during the entire digestive process of silver nitrate. Silver thiocyanate is slightly soluble in water, with a solubility of 1.68 x 10−4 g/L. It is insoluble in ethanol, acetone, and acid.

Cobalt(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Co(NO3)3. It is a green, diamagnetic solid that sublimes at ambient temperature.

Cerium nitrate refers to a family of nitrates of cerium in the +3 or +4 oxidation state. Often these compounds contain water, hydroxide, or hydronium ions in addition to cerium and nitrate. Double nitrates of cerium also exist.

Thorium(IV) nitrate is a chemical compound, a salt of thorium and nitric acid with the formula Th(NO3)4. A white solid in its anhydrous form, it can form tetra- and pentahydrates. As a salt of thorium it is weakly radioactive.
Indium(III) nitrate is a nitrate salt of indium which forms various hydrates. Only the pentahydrate has been crystallographically verified. Other hydrates are also reported in literature, such as the trihydrate.

A transition metal nitrate complex is a coordination compound containing one or more nitrate ligands. Such complexes are common starting reagents for the preparation of other compounds.
Cobalt(II) cyanate is the hypothetical inorganic compound with the formula Co(OCN)2.